Java Program For Finding The Middle Element Of A Given Linked List
Last Updated :
11 Jan, 2024
Given a Singly linked list, find the middle of the linked list. If there are even nodes, then there would be two middle nodes, we need to print the second middle element.
Example of Finding Middle Element of Linked List
Input: 1->2->3->4->5
Output: 3
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->6
Output: 4
Program Finding The Middle Element of Linked List in Java
Traverse the whole linked list and count the no. of nodes. Now traverse the list again till count/2 and return the node at count/2.
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
Node head;
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
public Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
public void pushNode(int data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(data);
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
public void printNode()
{
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + "->");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.print("Null" + "\n");
}
public int getLen()
{
int length = 0;
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
length++;
temp = temp.next;
}
return length;
}
public void printMiddle()
{
if (head != null) {
int length = getLen();
Node temp = head;
int middleLength = length / 2;
while (middleLength != 0) {
temp = temp.next;
middleLength--;
}
System.out.print("The middle element is [" + temp.data + "]");
System.out.print("\n\n");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
GFG list = new GFG();
for (int i = 5; i >= 1; i--) {
list.pushNode(i);
list.printNode();
list.printMiddle();
}
}
}
|
Output
5->Null
The middle element is [5]
4->5->Null
The middle element is [5]
3->4->5->Null
The middle element is [4]
2->3->4->5->Null
The middle element is [4]
1->2->3->4->5->Null
The middle element is ...
Complexity of the above Method:
Time Complexity: O(n) where n is no of nodes in linked list
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Hare-Tortoise Algorithm in Java
Traverse linked list using two pointers. Move one pointer by one and the other pointers by two. When the fast pointer reaches the end slow pointer will reach the middle of the linked list. Also known as Floyd’s Cycle Finding Algorithm.
Below image shows how printMiddle function works in the code :
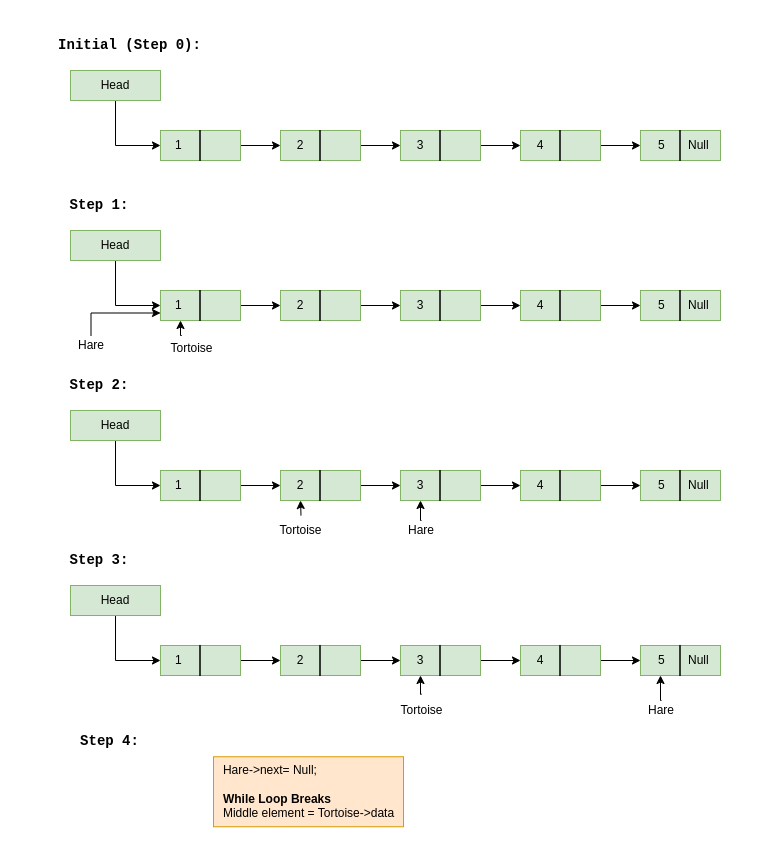
Below is the implementation of Hare and Tortoise Algorithm:
Java
class LinkedList
{
Node head;
class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
void printMiddle()
{
Node slow_ptr = head;
Node fast_ptr = head;
if (head != null)
{
while (fast_ptr != null &&
fast_ptr.next != null)
{
fast_ptr = fast_ptr.next.next;
slow_ptr = slow_ptr.next;
}
System.out.println("The middle element is [" +
slow_ptr.data + "]");
}
}
public void push(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
public void printList()
{
Node tnode = head;
while (tnode != null)
{
System.out.print(tnode.data + "->");
tnode = tnode.next;
}
System.out.println("NULL");
}
public static void main(String [] args)
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
for (int i = 5; i > 0; --i)
{
llist.push(i);
llist.printList();
llist.printMiddle();
}
}
}
|
Output:
5->NULL
The middle element is [5]
4->5->NULL
The middle element is [5]
3->4->5->NULL
The middle element is [4]
2->3->4->5->NULL
The middle element is [4]
1->2->3->4->5->NULL
The middle element is [3]
Complexity of the above method:
Time Complexity: O(n) where n is the number of nodes in the given linked list
Auxiliary Space: O(1), no extra space is required, so it is a constant
Alternative Method (Same Concept Hare-Tortoise Algorithm)
Initialize mid element as head and initialize a counter as 0. Traverse the list from head, while traversing increment the counter and change mid to mid->next whenever the counter is odd. So the mid will move only half of the total length of the list.
Below is the method to finding the middle element of a given Linked List:
Java
class GFG
{
static Node head;
class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
public Node(Node next,
int data)
{
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
}
void printMiddle(Node head)
{
int count = 0;
Node mid = head;
while (head != null)
{
if ((count % 2) == 1)
mid = mid.next;
++count;
head = head.next;
}
if (mid != null)
System.out.println("The middle element is [" +
mid.data + "]\n");
}
void push(Node head_ref, int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(head_ref,
new_data);
head = new_node;
}
void printList(Node head)
{
while (head != null)
{
System.out.print(head.data + "-> ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println("null");
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
GFG ll = new GFG();
for(int i = 5; i > 0; i--)
{
ll.push(head, i);
ll.printList(head);
ll.printMiddle(head);
}
}
}
|
Output:
5->NULL
The middle element is [5]
4->5->NULL
The middle element is [5]
3->4->5->NULL
The middle element is [4]
2->3->4->5->NULL
The middle element is [4]
1->2->3->4->5->NULL
The middle element is [3]
Complexity of the above method:
Time Complexity: O(n) where n is the number of nodes in the given linked list.
Auxiliary Space: O(1), no extra space is required, so it is a constant.
Please refer complete article on Find the middle of a given linked list for more details!
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...