Introduction to Linked List – Data Structure and Algorithm Tutorials
Last Updated :
19 Apr, 2024
Linked List is basically chains of nodes where each node contains information such as data and a pointer to the next node in the chain. It is a popular data structure with a wide range of real-world applications. In this article, we will provide a complete introduction of Linked List, which will help you tackle any problem based on Linked List.
What is a Linked List?
Linked List is a linear data structure which looks like a series of nodes, where each node has two parts: data and next pointer. Unlike Arrays, Linked List elements are not stored at a contiguous location. In the linked list there is a head pointer, which points to the first element of the linked list, and if the list is empty then it simply points to null or nothing.
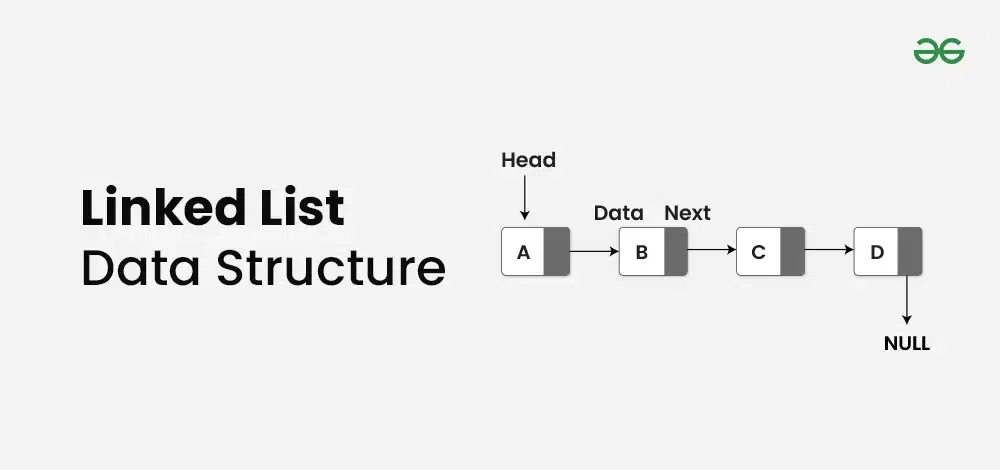
Basic Terminologies of Linked List:
- Head: The Head of a linked list is a pointer to the first node or reference of the first node of linked list. This pointer marks the beginning of the linked list.
- Node: Linked List consists of a series of nodes where each node has two parts: data and next pointer.
- Data: Data is the part of node which stores the information in the linked list.
- Next pointer: Next pointer is the part of the node which points to the next node of the linked list.
Importance of Linked List:
Here are a few advantages of a linked list that is listed below, it will help you understand why it is necessary to know.
- Dynamic Data structure: The size of memory can be allocated or de-allocated at run time based on the operation insertion or deletion.
- Ease of Insertion/Deletion: The insertion and deletion of elements are simpler than arrays since no elements need to be shifted after insertion and deletion, Just the address needed to be updated.
- Efficient Memory Utilization: As we know Linked List is a dynamic data structure the size increases or decreases as per the requirement so this avoids the wastage of memory.
- Implementation: Various advanced data structures can be implemented using a linked list like a stack, queue, graph, hash maps, etc.
There are mainly three types of linked lists:
- Singly linked list
- Doubly linked list
- Circular linked list
Singly Linked List is a type of linked list where each node has two parts: data and next pointer. The data part stores the information and the next pointer points to the next node of the linked list. The next pointer of the last node stores null as it is the last node of the linked list and there is no next node. Traversal of items can be done in the forward direction only due to the linking of every node to its next node.
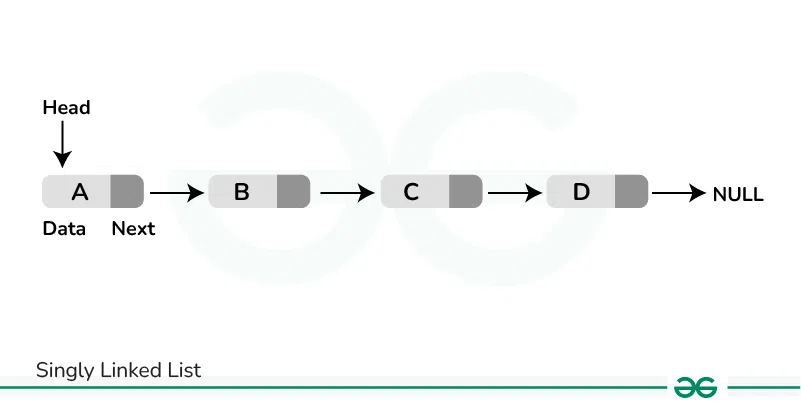
Node Definition of Singly linked list:
C++
// Singly linked list node
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
// Singly linked list node
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
// Singly Linked List Class
class LinkedList {
Node head; // head of list
/* Node Class */
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
// Constructor to create a new node
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
}
# Node class
class Node:
# Function to initialize the node object
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data # Assign data
self.next = None # Initialize next as null
# Singly Linked List class
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize the Linked List object
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
/* A Singly Linked list Node*/
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
<script>
// Singly Linked List Class
var head; // head of list
/* Node Class */
class Node {
// Constructor to create a new node
constructor(d) {
this.data = d;
this.next = null;
}
}
</script>
Operations on Singly Linked List:
The following operations are performed on a Single Linked List
- Insertion: The insertion operation can be performed in three ways. They are as follows…
- Deletion: The deletion operation can be performed in three ways. They are as follows…
- Search: It is a process of determining and retrieving a specific node either from the front, the end or anywhere in the list.
- Display: This process displays the elements of a Single-linked list.
Doubly Linked List is a type of linked list where each node has three parts: data, next pointer and previous pointer. The data part stores the information, the next pointer points to the next node of the linked list and the previous pointer points to the previous node of the linked list. The next pointer of the last node and the previous pointer of the first node stores null. Traversal of items can be done in the forward direction as well as backward direction due to the linking of every node to its next node as well as the previous node.
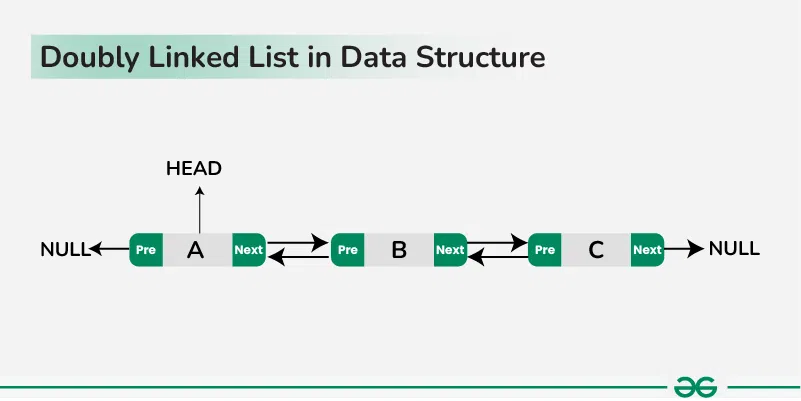
Node Definition of Doubly Linked List:
C++
/* Node of a doubly linked list */
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next; // Pointer to next node in DLL
Node* prev; // Pointer to previous node in DLL
};
/* Node of a doubly linked list */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next; // Pointer to next node in DLL
struct Node* prev; // Pointer to previous node in DLL
};
// Class for Doubly Linked List
public class DLL {
Node head; // head of list
/* Doubly Linked list Node*/
class Node {
int data;
Node prev;
Node next;
// Constructor to create a new node
// next and prev is by default initialized as null
Node(int d) { data = d; }
}
}
# Node of a doubly linked list
class Node:
def __init__(self, next=None, prev=None, data=None):
self.next = next # reference to next node in DLL
self.prev = prev # reference to previous node in DLL
self.data = data
// Class for Doubly Linked List
public class DLL {
Node head; // head of list
/* Doubly Linked list Node*/
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node prev;
public Node next;
// Constructor to create a new node
// next and prev is by default initialized as null
Node(int d) { data = d; }
}
}
<script>
// Class for Doubly Linked List
var head; // head of list
/* Doubly Linked list Node */
class Node {
// Constructor to create a new node
// next and prev is by default initialized as null
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.prev = null;
this.next = null;
}
}
</script>
Operations on Doubly Linked List:
In a doubly linked list, we perform the following operations…
- Insertion: The insertion operation can be performed in three ways as follows:
- Deletion: The deletion operation can be performed in three ways as follows…
- Display: This process displays the elements of a double-linked list.
A circular linked list is a type of linked list in which the first and the last nodes are also connected to each other to form a circle, there is no NULL at the end.
Commonly used operations on Circular Linked List:
The following operations are performed on a Circular Linked List
- Insertion: The insertion operation can be performed in three ways:
- Deletion: The deletion operation can be performed in three ways:
- Display: This process displays the elements of a Circular linked list.
Implementation of Linked List:
Below is the implementation of Linked List in different languages:
C++
// C++ program to show inserting a node
// at front of given Linked List
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// A linked list node
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
// Given a reference (pointer to pointer)
// to the head of a list and an int, inserts
// a new node on the front of the list.
void insertAtFront(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
// 1. allocate node
Node* new_node = new Node();
// 2. put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// 3. Make next of new node as head
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
// 4. move the head to point
// to the new node
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
/* Function to remove the first node
of the linked list */
Node* removeFirstNode(Node* head)
{
if (head == NULL)
return NULL;
// Move the head pointer to the next node
Node* temp = head;
head = head->next;
delete temp;
return head;
}
// This function prints contents of
// linked list starting from head
void printList(Node* node)
{
while (node != NULL) {
cout << " " << node->data;
node = node->next;
}
cout << "\n";
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Start with the empty list
Node* head = NULL;
// Insert 1 at the beginning.
insertAtFront(&head, 6);
insertAtFront(&head, 5);
insertAtFront(&head, 4);
insertAtFront(&head, 3);
insertAtFront(&head, 2);
insertAtFront(&head, 1);
cout << "After inserting nodes at the front:";
printList(head);
head = removeFirstNode(head);
cout << "After removing first node:";
printList(head);
return 0;
}
// Java program to show inserting a node
// at front of given Linked List
import java.io.*;
// A linked list node
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
}
// Class to insert element in LL
class LinkedList {
Node head; // head of list
// Given a reference (pointer to pointer)
// to the head of a list and an int, inserts
// a new node on the front of the list.
void insertAtFront(int new_data)
{
// 1. allocate node
Node new_node = new Node();
// 2. put in the data
new_node.data = new_data;
// 3. Make next of new node as head
new_node.next = head;
// 4. move the head to point
// to the new node
head = new_node;
}
// Function to remove the first node
// of the linked list /
void removeFirstNode()
{
if (head == null)
return;
// Move the head pointer to the next node
Node temp = head;
head = head.next;
}
// This function prints contents of
// linked list starting from head
void printList()
{
Node node = head;
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Start with the empty list
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.insertAtFront(6);
list.insertAtFront(5);
list.insertAtFront(4);
list.insertAtFront(3);
list.insertAtFront(2);
list.insertAtFront(1);
System.out.print("After inserting nodes at the front: ");
list.printList();
list.removeFirstNode();
System.out.print("After removing first node: ");
list.printList();
}
}
# Python3 program to show inserting a node
# at front of given Linked List
# A linked list node
class Node:
def __init__(self):
self.data = None
self.next = None
# Given a reference (pointer to pointer)
# to the head of a list and an int, inserts
# a new node on the front of the list.
def insertAtFront(head_ref, new_data):
# 1. allocate node
new_node = Node()
# 2. put in the data
new_node.data = new_data
# 3. Make next of new node as head
new_node.next = head_ref
# 4. move the head to point
# to the new node
head_ref = new_node
return head_ref
# Function to remove the first node
# of the linked list
def removeFirstNode(head):
if not head:
return None
temp = head
# Move the head pointer to the next node
head = head.next
temp = None
return head
# This function prints contents of
# linked list starting from head
def printList(node):
while (node != None):
print(node.data, end=" ")
node = node.next
print()
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Start with the empty list
head = None
head = insertAtFront(head, 6)
head = insertAtFront(head, 5)
head = insertAtFront(head, 4)
head = insertAtFront(head, 3)
head = insertAtFront(head, 2)
head = insertAtFront(head, 1)
print("After inserting nodes at the front: ", end = "")
printList(head)
head = removeFirstNode(head)
print("After removing first node: ", end = "")
printList(head)
// C# program to show inserting a node
// at front of given Linked List
using System;
class GFG {
public Node head; // head of list
/* Linked list Node*/
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
public void insertAtFront(int new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
// Function to remove the first node
// of the linked list /
public void removeFirstNode()
{
if (head == null)
return ;
// Move the head pointer to the next node
head = head.next;
}
/* This function prints contents of linked list
starting from the given node */
public void printList()
{
Node tnode = head;
while (tnode != null) {
Console.Write(tnode.data + " ");
tnode = tnode.next;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
/* Start with the empty list */
GFG llist = new GFG();
llist.insertAtFront(6);
llist.insertAtFront(5);
llist.insertAtFront(4);
llist.insertAtFront(3);
llist.insertAtFront(2);
llist.insertAtFront(1);
Console.Write("After inserting nodes at the front: ");
llist.printList();
llist.removeFirstNode();
Console.Write("After removing first node: ");
llist.printList();
}
}
// A linked list node
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
// Given a reference (pointer to pointer)
// to the head of a list and an int, inserts
// a new node on the front of the list.
function insertAtFront(head_ref, new_data) {
// 1. Create a new node
const new_node = new Node(new_data);
// 2. Make the new node point to the current head
new_node.next = head_ref[0];
// 3. Update the head to the new node
head_ref[0] = new_node;
}
// Function to remove the first node
// of the linked list /
function removeFirstNode( head) {
if (head == null)
return null;
// Move the head pointer to the next node
temp = head;
head = head.next;
return head;
}
// This function prints contents of
// linked list starting from head
function printList(node) {
let current = node;
while (current !== null) {
console.log(" " + current.data);
current = current.next;
}
console.log("\n");
}
// Driver code
function main() {
// Start with an empty list
let head = [null]; // Use an array to simulate a pointer to pointer
// Insert elements at the beginning
insertAtFront(head, 1);
insertAtFront(head, 2);
insertAtFront(head, 3);
insertAtFront(head, 4);
insertAtFront(head, 5);
insertAtFront(head, 6);
console.log("After inserting Nodes at the front:");
// The nodes will be: 6 5 4 3 2 1
printList(head[0]);
head[0] = removeFirstNode(head[0]);
console.log("After removing first node:");
// The nodes will be: 5 4 3 2 1
printList(head[0]);
}
main();
OutputAfter inserting nodes at the front: 1 2 3 4 5 6
After removing first node: 2 3 4 5 6
Array
| Linked List
|
|---|
Arrays are stored in contiguous location.
| Linked Lists are not stored in contiguous location.
|
Fixed size.
| Dynamic Size
|
Memory is allocated at compile time.
| Memory is allocated at run time.
|
Uses less memory than Linked Lists.
| Uses more memory than Arrays as it stores both data and address of next node.
|
Elements can be accessed easily in O(1) time.
| Elements can be access by traversing through all the nodes till we reach the required node.
|
Insertion and deletion operation is slower than Linked List.
| Insertion and deletion operation is faster than Linked List.
|
Time Complexity Analysis of Linked List and Array:
| Operation | Linked list | Array |
|---|
| Random Access | O(N) | O(1) |
| Insertion and deletion at beginning | O(1) | O(N) |
| Insertion and deletion at end | O(N) | O(1) |
| Insertion and deletion at a random position | O(N) | O(N) |
- Dynamic nature: Linked lists are used for dynamic memory allocation.
- Memory efficient: Memory consumption of a linked list is efficient as its size can grow or shrink dynamically according to our requirements, which means effective memory utilization hence, no memory wastage.
- Ease of Insertion and Deletion: Insertion and deletion of nodes are easily implemented in a linked list at any position.
- Implementation: For the implementation of stacks and queues and for the representation of trees and graphs.
- The linked list can be expanded in constant time.
- Memory usage: The use of pointers is more in linked lists hence, complex and requires more memory.
- Accessing a node: Random access is not possible due to dynamic memory allocation.
- Search operation costly: Searching for an element is costly and requires O(n) time complexity.
- Traversing in reverse order: Traversing is more time-consuming and reverse traversing is not possible in singly linked lists.
Here are some of the applications of a linked list:
- Linear data structures such as stack, queue, and non-linear data structures such as hash maps, and graphs can be implemented using linked lists.
- Dynamic memory allocation: We use a linked list of free blocks.
- Implementation of graphs: Adjacency list representation of graphs is the most popular in that it uses linked lists to store adjacent vertices.
- In web browsers and editors, doubly linked lists can be used to build a forwards and backward navigation button.
- A circular doubly linked list can also be used for implementing data structures like Fibonacci heaps.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Linked List:
1. What is linked list data structure?
Linked list are most commonly used to handle dynamic data elements. Linked list consists of nodes and a node consists of two fields one for storing data and other for keeping the reference of next node.
2. What is linked list example?
A linked list can be assumed as a garland that is made up of flowers. Similarly, a linked list is made up of nodes. Every flower in this particular garland is referred to as a node. In addition, each node points to the next node in this list, and it contains data (in this case, the type of flower).
3. Why do we need linked list data structure??
There are some important advantages to using linked lists over other linear data structures. This is unlike arrays, as they are resizable at runtime. Additionally, they can be easily inserted and deleted.
4. What are linked lists used for?
The linked list is a linear data structure that stores data in nodes. these nodes hold both the data and a reference to the next node in the list. Linked are very efficient at adding and removing nodes because of their simple structure.
5. What is the difference between array and linked list?
There are some following differences between them:
- Arrays are data structures containing similar data elements, whereas linked lists are non-primitive data structures containing unordered linked elements.
- In an array, elements are indexed, but in a linked list nodes are not indexed.
- Accessing an element array is fast if we know the position of an element in the array, while in the Linked list it takes linear time so, the Linked list is quite bit slower.
- Operations like insertion and deletion in arrays take a lot of time. Whereas, the performance of these operations is faster in Linked lists.
- Arrays are of fixed size and their size is static but Linked lists are dynamic and flexible and can expand and shrink their size.
6. Why is a linked list preferred over an array?
Following are the reason that linked lists are preferred over array
- Nodes in a linked array, insertions, and deletions can be done at any point in the list at a constant time.
- Arrays are of fixed size and their size is static but Linked lists are dynamic and flexible and can expand and shrink their size.
- Linked lists provide an efficient way of storing related data and performing basic operations such as insertion, deletion, and updating of information at the cost of extra space required for storing the address.
- Insertion and deletion operations in the linked list are faster as compared to the array.
7. Which is the best array or linked list?
There are some advantages and disadvantages to both arrays and linked lists when it comes to storing linear data of similar types.
Advantages of linked list over arrays:
- Dynamic size: Linked lists are dynamic and flexible and can expand and shrink their size
- Ease of Insertion/Deletion: Insertion and deletion operations in linked list are faster as compared to the array
Disadvantages of linked list over arrays:
- If the array is sorted we can apply binary search to search any element which takes O(log(n)) time. But even if the linked list is sorted we cannot apply binary search and the complexity of searching elements in the linked list is O(n).
- A linked list takes more memory as compared to the array because extra memory space is required for the pointer with each element in the linked list.
8. What are the limitations of linked list?
Following are some limitations of the linked list:
- The use of pointers is more in linked lists hence, complex and requires more memory.
- Random access is not possible due to dynamic memory allocation.
- Traversing is more time-consuming and reverse traversing is not possible in singly linked lists.
- Searching for an element is costly and requires O(n) time complexity.
9. Why insertion/deletion are faster in a linked list?
If any element is inserted/ deleted from the array, all the other elements after it will be shifted in memory this takes a lot of time whereas manipulation in Linked List is faster because we just need to manipulate the addresses of nodes, so no bit shifting is required in memory, and it will not take that much of time.
10. What is the difference between a singly and doubly linked list?
Following are some difference between single and double linked list.
| Singly-linked list (SLL) | Doubly linked list (DLL) |
|---|
| SLL nodes contains 2 field data field and next link field. | DLL nodes contains 3 fields data field, a previous link field and a next link field. |
| In SLL, the traversal can be done using the next node link only. Thus traversal is possible in one direction only. | In DLL, the traversal can be done using the previous node link or the next node link. Thus traversal is possible in both directions (forward and backward). |
| The SLL occupies less memory than DLL as it has only 2 fields. | The DLL occupies more memory than SLL as it has 3 fields. |
| The Complexity of insertion and deletion at a given position is O(n). | The Complexity of insertion and deletion at a given position is O(n / 2) = O(n) because traversal can be made from start or from the end. |
| Complexity of deletion with a given node is O(n), because the previous node needs to be known, and traversal takes O(n) | Complexity of deletion with a given node is O(1) because the previous node can be accessed easily |
| A singly linked list consumes less memory as compared to the doubly linked list. | The doubly linked list consumes more memory as compared to the singly linked list. |
Conclusion:
There are many advantages of the linked list compared to array, despite the fact that they solve the similar problem to arrays, we have also discussed the advantage, disadvantages, and its application, and we concluded the fact that we can use a linked list if we need the dynamic size of storage and list are good for adding and removing items quickly or for tasks that require sequence but are not suitable for querying or search elements in a large collection of data.
So, it becomes important that we should always keep in mind the positive and negative aspects of a data structure and how they relate to the problem you are trying to solve.
Related articles:
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...