Types of Linked List
Last Updated :
29 Jan, 2024
A linked list is a linear data structure, in which the elements are not stored at contiguous memory locations. The elements in a linked list are linked using pointers. In simple words, a linked list consists of nodes where each node contains a data field and a reference(link) to the next node in the list.
Types Of Linked List:
It is the simplest type of linked list in which every node contains some data and a pointer to the next node of the same data type.
The node contains a pointer to the next node means that the node stores the address of the next node in the sequence. A single linked list allows the traversal of data only in one way. Below is the image for the same:
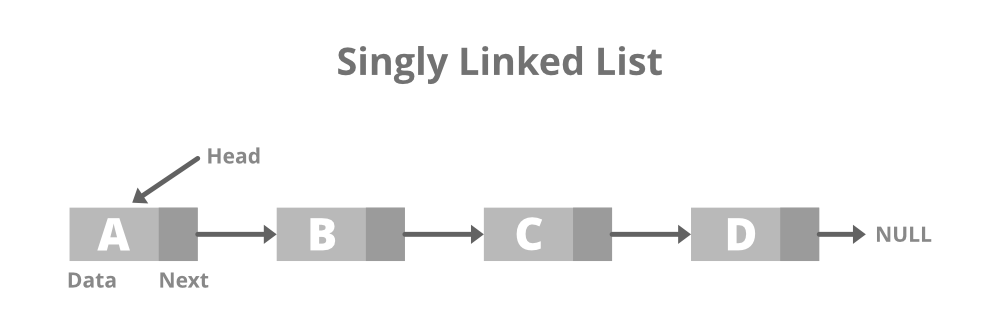
Below is the structure of the singly linked list
C++
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
|
Java
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
};
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
|
C#
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
};
|
Javascript
class Node
{
constructor()
{
this.data=0;
this.next=null;
}
}
|
Creation and Traversal of Singly Linked List:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
void printList(Node* n)
{
while (n != NULL) {
cout << n->data << " ";
n = n->next;
}
}
int main()
{
Node* head = NULL;
Node* second = NULL;
Node* third = NULL;
head = new Node();
second = new Node();
third = new Node();
head->data = 1;
head->next = second;
second->data = 2;
second->next = third;
third->data = 3;
third->next = NULL;
printList(head);
return 0;
}
|
Java
class GFG {
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
};
static void printList(Node n)
{
while (n != null) {
System.out.print(n.data + " ");
n = n.next;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node head = null;
Node second = null;
Node third = null;
head = new Node();
second = new Node();
third = new Node();
head.data = 1;
head.next = second;
second.data = 2;
second.next = third;
third.data = 3;
third.next = null;
printList(head);
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.last_node = None
def append(self, data):
if self.last_node is None:
self.head = Node(data)
self.last_node = self.head
else:
self.last_node.next = Node(data)
self.last_node = self.last_node.next
def display(self):
current = self.head
while current is not None:
print(current.data, end=' ')
current = current.next
print()
if __name__ == '__main__':
L = LinkedList()
L.append(1)
L.append(2)
L.append(3)
L.display()
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
};
static void printList(Node n)
{
while (n != null) {
Console.Write(n.data + " ");
n = n.next;
}
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Node head = null;
Node second = null;
Node third = null;
head = new Node();
second = new Node();
third = new Node();
head.data = 1;
head.next = second;
second.data = 2;
second.next = third;
third.data = 3;
third.next = null;
printList(head);
}
}
|
Javascript
class Node
{
constructor()
{
this.data=0;
this.next=null;
}
}
function printList(n)
{
while (n != null)
{
document.write(n.data + " ");
n = n.next;
}
}
let head = null;
let second = null;
let third = null;
head = new Node();
second = new Node();
third = new Node();
head.data = 1;
head.next = second;
second.data = 2;
second.next = third;
third.data = 3;
third.next = null;
printList(head);
|
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
A doubly linked list or a two-way linked list is a more complex type of linked list that contains a pointer to the next as well as the previous node in sequence.
Therefore, it contains three parts of data, a pointer to the next node, and a pointer to the previous node. This would enable us to traverse the list in the backward direction as well. Below is the image for the same:
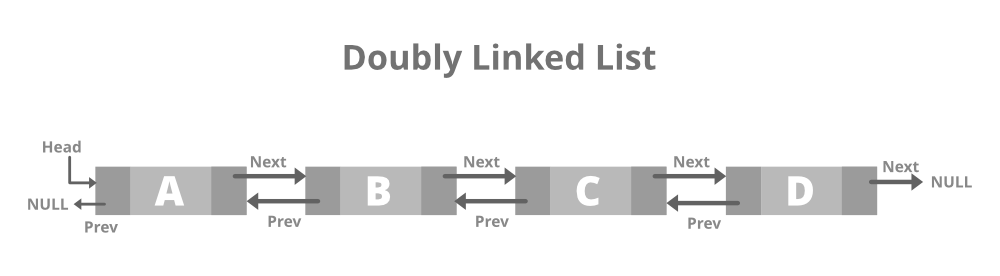
Structure of Doubly Linked List:
C++
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
struct Node* prev;
};
|
Java
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node prev;
};
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.previous = None
self.data = data
self.next = None
|
C#
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node prev;
};
|
Javascript
<script>
var head;
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.prev = null;
this.next = null;
}
}
</script>
|
Creation and Traversal of Doubly Linked List:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
Node* prev;
};
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
Node* new_node = new Node();
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
new_node->prev = NULL;
if ((*head_ref) != NULL)
(*head_ref)->prev = new_node;
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
void printList(Node* node)
{
Node* last;
cout << "\nTraversal in forward"
<< " direction \n";
while (node != NULL) {
cout << " " << node->data << " ";
last = node;
node = node->next;
}
cout << "\nTraversal in reverse"
<< " direction \n";
while (last != NULL) {
cout << " " << last->data << " ";
last = last->prev;
}
}
int main()
{
Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 6);
push(&head, 7);
push(&head, 1);
cout << "Created DLL is: ";
printList(head);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node prev;
};
static Node head_ref;
static void push(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node();
new_node.data = new_data;
new_node.next = head_ref;
new_node.prev = null;
if (head_ref != null)
head_ref.prev = new_node;
head_ref = new_node;
}
static void printList(Node node)
{
Node last = null;
System.out.print("\nTraversal in forward"
+ " direction \n");
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(" " + node.data + " ");
last = node;
node = node.next;
}
System.out.print("\nTraversal in reverse"
+ " direction \n");
while (last != null) {
System.out.print(" " + last.data + " ");
last = last.prev;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
head_ref = null;
push(6);
push(7);
push(1);
System.out.print("Created DLL is: ");
printList(head_ref);
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.previous = None
self.data = data
self.next = None
class DoublyLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.start_node = None
self.last_node = None
def append(self, data):
if self.last_node is None:
self.head = Node(data)
self.last_node = self.head
else:
new_node = Node(data)
self.last_node.next = new_node
new_node.previous = self.last_node
new_node.next = None
self.last_node = new_node
def display(self, Type):
if Type == 'Left_To_Right':
current = self.head
while current is not None:
print(current.data, end=' ')
current = current.next
print()
else:
current = self.last_node
while current is not None:
print(current.data, end=' ')
current = current.previous
print()
if __name__ == '__main__':
L = DoublyLinkedList()
L.append(1)
L.append(2)
L.append(3)
L.append(4)
L.display('Left_To_Right')
L.display('Right_To_Left')
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node prev;
};
static Node head_ref;
static void push(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node();
new_node.data = new_data;
new_node.next = head_ref;
new_node.prev = null;
if (head_ref != null)
head_ref.prev = new_node;
head_ref = new_node;
}
static void printList(Node node)
{
Node last = null;
Console.Write("\nTraversal in forward"
+ " direction \n");
while (node != null) {
Console.Write(" " + node.data + " ");
last = node;
node = node.next;
}
Console.Write("\nTraversal in reverse"
+ " direction \n");
while (last != null) {
Console.Write(" " + last.data + " ");
last = last.prev;
}
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
head_ref = null;
push(6);
push(7);
push(1);
Console.Write("Created DLL is: ");
printList(head_ref);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
var head;
class Node {
constructor(d) {
this.data = d;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
}
function push(new_data) {
var new_Node = new Node(new_data);
new_Node.next = head;
new_Node.prev = null;
if (head != null)
head.prev = new_Node;
head = new_Node;
}
function printlist(node) {
var last = null;
document.write("<br/>Traversal in forward Direction<br/>");
while (node != null) {
document.write(node.data + " ");
last = node;
node = node.next;
}
document.write();
document.write("<br/>Traversal in reverse direction<br/>");
while (last != null) {
document.write(last.data + " ");
last = last.prev;
}
}
push(6);
push(7);
push(1);
document.write("Created DLL is: ");
printlist(head);
</script>
|
Output
Created DLL is:
Traversal in forward direction
1 7 6
Traversal in reverse direction
6 7 1
Time Complexity:
The time complexity of the push() function is O(1) as it performs constant-time operations to insert a new node at the beginning of the doubly linked list. The time complexity of the printList() function is O(n) where n is the number of nodes in the doubly linked list. This is because it traverses the entire list twice, once in the forward direction and once in the backward direction. Therefore, the overall time complexity of the program is O(n).
Space Complexity:
The space complexity of the program is O(n) as it uses a doubly linked list to store the data, which requires n nodes. Additionally, it uses a constant amount of auxiliary space to create a new node in the push() function. Therefore, the overall space complexity of the program is O(n).
A circular linked list is that in which the last node contains the pointer to the first node of the list.
While traversing a circular linked list, we can begin at any node and traverse the list in any direction forward and backward until we reach the same node we started. Thus, a circular linked list has no beginning and no end. Below is the image for the same:
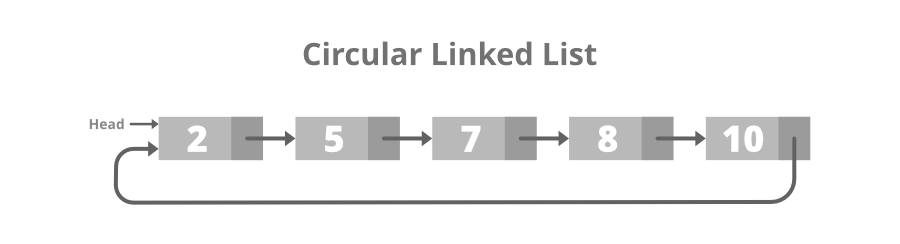
Below is the structure of the Circular Linked List:
C++
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
|
Java
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
};
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
|
C#
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
};
|
Javascript
<script>
class Node {
constructor() {
this.data = 0;
this.next = null;
}
}
</script>
|
Creation and Traversal of Circular Linked List:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
void push(Node** head_ref, int data)
{
Node* ptr1 = new Node();
Node* temp = *head_ref;
ptr1->data = data;
ptr1->next = *head_ref;
if (*head_ref != NULL) {
while (temp->next != *head_ref) {
temp = temp->next;
}
temp->next = ptr1;
}
else
ptr1->next = ptr1;
*head_ref = ptr1;
}
void printList(Node* head)
{
Node* temp = head;
if (head != NULL) {
do {
cout << temp->data << " ";
temp = temp->next;
} while (temp != head);
}
}
int main()
{
Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 12);
push(&head, 56);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 11);
cout << "Contents of Circular"
<< " Linked List\n ";
printList(head);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
};
static Node push(Node head_ref, int data)
{
Node ptr1 = new Node();
Node temp = head_ref;
ptr1.data = data;
ptr1.next = head_ref;
if (head_ref != null) {
while (temp.next != head_ref) {
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = ptr1;
}
else
ptr1.next = ptr1;
head_ref = ptr1;
return head_ref;
}
static void printList(Node head)
{
Node temp = head;
if (head != null) {
do {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
} while (temp != head);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node head = null;
head = push(head, 12);
head = push(head, 56);
head = push(head, 2);
head = push(head, 11);
System.out.print("Contents of Circular"
+ " Linked List\n ");
printList(head);
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class CircularLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.last_node = None
def append(self, data):
if self.last_node is None:
self.head = Node(data)
self.last_node = self.head
else:
self.last_node.next = Node(data)
self.last_node = self.last_node.next
self.last_node.next = self.head
def display(self):
current = self.head
while current is not None:
print(current.data, end=' ')
current = current.next
if current == self.head:
break
print()
if __name__ == '__main__':
L = CircularLinkedList()
L.append(12)
L.append(56)
L.append(2)
L.append(11)
L.display()
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
};
static Node push(Node head_ref, int data)
{
Node ptr1 = new Node();
Node temp = head_ref;
ptr1.data = data;
ptr1.next = head_ref;
if (head_ref != null) {
while (temp.next != head_ref) {
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = ptr1;
}
else
ptr1.next = ptr1;
head_ref = ptr1;
return head_ref;
}
static void printList(Node head)
{
Node temp = head;
if (head != null) {
do {
Console.Write(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
} while (temp != head);
}
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Node head = null;
head = push(head, 12);
head = push(head, 56);
head = push(head, 2);
head = push(head, 11);
Console.Write("Contents of Circular "
+ "Linked List\n ");
printList(head);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
class Node {
constructor() {
this.data = 0;
this.next = null;
}
}
function push(head, data) {
if (head == null) {
var temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
head = temp;
head.next = head;
}
else{
var temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = head.next;
head.next = temp;
}
return head;
}
function printList(head) {
var p;
if (head == null) {
document.write("List is empty.<br>");
return;
}
p = head.next;
do {
document.write(p.data + " ");
p = p.next;
} while (p != head.next);
}
var head = null;
head = push(head, 12);
head = push(head, 56);
head = push(head, 2);
head = push(head, 11);
document.write("Contents of Circular Linked List<br>");
printList(head);
</script>
|
Output
Contents of Circular Linked List
11 2 56 12
Time Complexity:
Insertion at the beginning of the circular linked list takes O(1) time complexity.
Traversing and printing all nodes in the circular linked list takes O(n) time complexity where n is the number of nodes in the linked list.
Therefore, the overall time complexity of the program is O(n).
Auxiliary Space:
The space required by the program depends on the number of nodes in the circular linked list.
In the worst-case scenario, when there are n nodes, the space complexity of the program will be O(n) as n new nodes will be created to store the data.
Additionally, some extra space is required for the temporary variables and the function calls.
Therefore, the auxiliary space complexity of the program is O(n).
A Doubly Circular linked list or a circular two-way linked list is a more complex type of linked list that contains a pointer to the next as well as the previous node in the sequence. The difference between the doubly linked and circular doubly list is the same as that between a singly linked list and a circular linked list. The circular doubly linked list does not contain null in the previous field of the first node. Below is the image for the same:
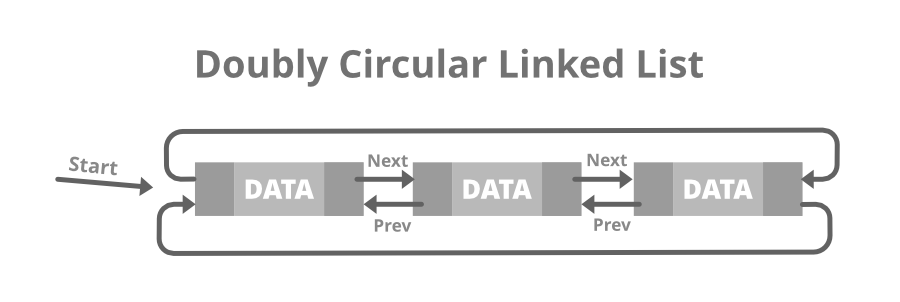
Below is the structure of the Doubly Circular Linked List:
C++
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
struct Node* prev;
};
|
Java
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
Node prev;
};
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.previous = None
self.data = data
self.next = None
|
C#
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node prev;
};
|
Javascript
<script>
var start = null;
class Node {
constructor() {
this.data = 0;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
}
</script>
|
Creation and Traversal of Doubly Circular Linked List:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
struct Node* prev;
};
void insertBegin(struct Node** start, int value)
{
if (*start == NULL) {
struct Node* new_node = new Node;
new_node->data = value;
new_node->next = new_node->prev = new_node;
*start = new_node;
return;
}
struct Node* last = (*start)->prev;
struct Node* new_node = new Node;
new_node->data = value;
new_node->next = *start;
new_node->prev = last;
last->next = (*start)->prev = new_node;
*start = new_node;
}
void display(struct Node* start)
{
struct Node* temp = start;
printf("\nTraversal in"
" forward direction \n");
while (temp->next != start) {
printf("%d ", temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
printf("%d ", temp->data);
printf("\nTraversal in "
"reverse direction \n");
Node* last = start->prev;
temp = last;
while (temp->prev != last) {
printf("%d ", temp->data);
temp = temp->prev;
}
printf("%d ", temp->data);
}
int main()
{
struct Node* start = NULL;
insertBegin(&start, 5);
insertBegin(&start, 4);
insertBegin(&start, 7);
printf("Created circular doubly"
" linked list is: ");
display(start);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node prev;
};
static Node start = null;
static void insertBegin(int value)
{
if (start == null) {
Node new_node = new Node();
new_node.data = value;
new_node.next = new_node.prev = new_node;
start = new_node;
return;
}
Node last = (start).prev;
Node new_node = new Node();
new_node.data = value;
new_node.next = start;
new_node.prev = last;
last.next = (start).prev = new_node;
start = new_node;
}
static void display()
{
Node temp = start;
System.out.printf("\nTraversal in"
+ " forward direction \n");
while (temp.next != start) {
System.out.printf("%d ", temp.data);
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.printf("%d ", temp.data);
System.out.printf("\nTraversal in "
+ "reverse direction \n");
Node last = start.prev;
temp = last;
while (temp.prev != last) {
System.out.printf("%d ", temp.data);
temp = temp.prev;
}
System.out.printf("%d ", temp.data);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
insertBegin(5);
insertBegin(4);
insertBegin(7);
System.out.printf("Created circular doubly"
+ " linked list is: ");
display();
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.previous = None
self.data = data
self.next = None
class DoublyLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.start_node = None
self.last_node = None
def append(self, data):
if self.last_node is None:
self.head = Node(data)
self.last_node = self.head
else:
new_node = Node(data)
self.last_node.next = new_node
new_node.previous = self.last_node
new_node.next = self.head
self.head.previous = new_node
self.last_node = new_node
def display(self, Type='Left_To_Right'):
if Type == 'Left_To_Right':
current = self.head
while current.next is not None:
print(current.data, end=' ')
current = current.next
if current == self.head:
break
print()
else:
current = self.last_node
while current.previous is not None:
print(current.data, end=' ')
current = current.previous
if current == self.last_node.next:
print(self.last_node.next.data, end=' ')
break
print()
if __name__ == '__main__':
L = DoublyLinkedList()
L.append(1)
L.append(2)
L.append(3)
L.append(4)
L.display('Left_To_Right')
L.display('Right_To_Left')
|
C#
using System;
public class GFG {
public
class Node {
public
int data;
public
Node next;
public
Node prev;
};
static Node start = null;
static void insertBegin(int value)
{
Node new_node = new Node();
if (start == null) {
new_node.data = value;
new_node.next = new_node.prev = new_node;
start = new_node;
return;
}
Node last = (start).prev;
new_node.data = value;
new_node.next = start;
new_node.prev = last;
last.next = (start).prev = new_node;
start = new_node;
}
static void display()
{
Node temp = start;
Console.Write("\nTraversal in"
+ " forward direction \n");
while (temp.next != start) {
Console.Write(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
Console.Write(temp.data + " ");
Console.Write("\nTraversal in "
+ "reverse direction \n");
Node last = start.prev;
temp = last;
while (temp.prev != last) {
Console.Write(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.prev;
}
Console.Write(temp.data + " ");
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
insertBegin(5);
insertBegin(4);
insertBegin(7);
Console.Write("Created circular doubly"
+ " linked list is: ");
display();
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
var start = null;
class Node {
constructor() {
this.data = 0;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
}
function insertEnd(value) {
var new_node;
if (start == null) {
new_node = new Node();
new_node.data = value;
new_node.next = new_node.prev = new_node;
start = new_node;
return;
}
var last = start.prev;
new_node = new Node();
new_node.data = value;
new_node.next = start;
start.prev = new_node;
new_node.prev = last;
last.next = new_node;
}
function insertBegin(value) {
var last = start.prev;
var new_node = new Node();
new_node.data = value;
new_node.next = start;
new_node.prev = last;
last.next = start.prev = new_node;
start = new_node;
}
function display() {
var temp = start;
document.write("<br>Traversal in forward direction <br>");
while (temp.next != start) {
document.write(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
document.write(temp.data);
document.write("<br>Traversal in reverse direction <br>");
var last = start.prev;
temp = last;
while (temp.prev != last) {
document.write(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.prev;
}
document.write(temp.data);
}
var start = null;
insertEnd(5);
insertBegin(4);
insertBegin(7);
document.write("Created circular doubly linked list is: ");
display();
</script>
|
Output
Created circular doubly linked list is:
Traversal in forward direction
7 4 5
Traversal in reverse direction
5 4 7
Time Complexity:
Insertion at the beginning of a doubly circular linked list takes O(1) time complexity.
Traversing the entire doubly circular linked list takes O(n) time complexity, where n is the number of nodes in the linked list.
Therefore, the overall time complexity of the program is O(n).
Auxiliary space:
The program uses a constant amount of auxiliary space, i.e., O(1), to create and traverse the doubly circular linked list.
The space required to store the linked list grows linearly with the number of nodes in the linked list.
Therefore, the overall auxiliary space complexity of the program is O(1).
A header linked list is a special type of linked list that contains a header node at the beginning of the list.
So, in a header linked list START will not point to the first node of the list but START will contain the address of the header node. Below is the image for Grounded Header Linked List:
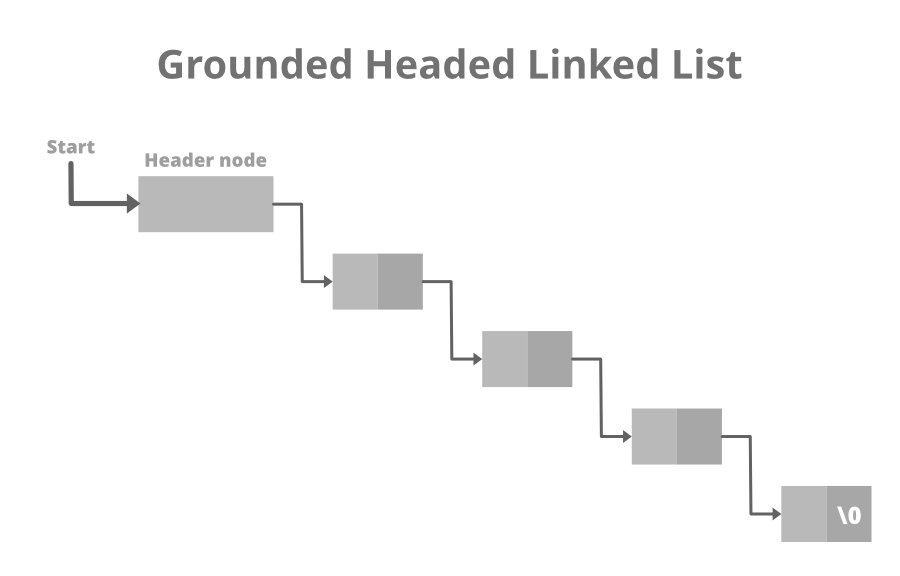
Below is the Structure of the Grounded Header Linked List:
C++
struct link {
int info;
struct link* next;
};
|
Java
static class link {
int info;
link next;
};
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
|
C#
public class link {
public int info;
public link next;
};
|
Javascript
<script>
class Node {
constructor() {
this.data = 0;
this.next = null;
}
}
</script>
|
Creation and Traversal of Header Linked List:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
struct link {
int info;
struct link* next;
};
struct link* start = NULL;
struct link* create_header_list(int data)
{
struct link *new_node, *node;
new_node = (struct link*)malloc(sizeof(struct link));
new_node->info = data;
new_node->next = NULL;
if (start == NULL) {
start = (struct link*)malloc(sizeof(struct link));
start->next = new_node;
}
else {
node = start;
while (node->next != NULL) {
node = node->next;
}
node->next = new_node;
}
return start;
}
struct link* display()
{
struct link* node;
node = start;
node = node->next;
while (node != NULL) {
printf("%d ", node->info);
node = node->next;
}
printf("\n");
return start;
}
int main()
{
create_header_list(11);
create_header_list(12);
create_header_list(13);
printf("List After inserting"
" 3 elements:\n");
display();
create_header_list(14);
create_header_list(15);
printf("List After inserting"
" 2 more elements:\n");
display();
return 0;
}
|
Java
class GFG {
static class link {
int info;
link next;
};
static link start = null;
static link create_header_list(int data)
{
link new_node, node;
new_node = new link();
new_node.info = data;
new_node.next = null;
if (start == null) {
start = new link();
start.next = new_node;
}
else {
node = start;
while (node.next != null) {
node = node.next;
}
node.next = new_node;
}
return start;
}
static link display()
{
link node;
node = start;
node = node.next;
while (node != null) {
System.out.printf("%d ", node.info);
node = node.next;
}
System.out.printf("\n");
return start;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
create_header_list(11);
create_header_list(12);
create_header_list(13);
System.out.printf("List After inserting"
+ " 3 elements:\n");
display();
create_header_list(14);
create_header_list(15);
System.out.printf("List After inserting"
+ " 2 more elements:\n");
display();
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = Node(0)
self.last_node = self.head
def append(self, data):
self.last_node.next = Node(data)
self.last_node = self.last_node.next
def display(self):
current = self.head.next
while current is not None:
print(current.data, end=' ')
current = current.next
print()
if __name__ == '__main__':
L = LinkedList()
L.append(1)
L.append(2)
L.append(3)
L.append(4)
L.display()
|
C#
using System;
public class GFG {
public class link {
public int info;
public link next;
};
static link start = null;
static link create_header_list(int data)
{
link new_node, node;
new_node = new link();
new_node.info = data;
new_node.next = null;
if (start == null) {
start = new link();
start.next = new_node;
}
else {
node = start;
while (node.next != null) {
node = node.next;
}
node.next = new_node;
}
return start;
}
static link display()
{
link node;
node = start;
node = node.next;
while (node != null) {
Console.Write("{0} ", node.info);
node = node.next;
}
Console.Write("\n");
return start;
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
create_header_list(11);
create_header_list(12);
create_header_list(13);
Console.Write("List After inserting"
+ " 3 elements:\n");
display();
create_header_list(14);
create_header_list(15);
Console.Write("List After inserting"
+ " 2 more elements:\n");
display();
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
class Link {
constructor(info, next) {
this.info = info;
this.next = next;
}
}
let start = null;
function createHeaderList(data) {
let newNode = new Link(data, null);
if (start == null) {
start = new Link(null, newNode);
} else {
let node = start;
while (node.next != null) {
node = node.next;
}
node.next = newNode;
}
return start;
}
function display() {
let node = start;
node = node.next;
while (node != null) {
document.write(node.info+" ");
node = node.next;
}
return start;
}
createHeaderList(11);
createHeaderList(12);
createHeaderList(13);
document.write("List After inserting 3 elements:<br>");
display();
createHeaderList(14);
createHeaderList(15);
document.write("<br>List After inserting 2 more elements:<br>");
display();
</script>
|
Output
List After inserting 3 elements:
11 12 13
List After inserting 2 more elements:
11 12 13 14 15
Time Complexity:
The time complexity of creating a new node and inserting it at the end of the linked list is O(1).
The time complexity of traversing the linked list to display its contents is O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the list.
Therefore, the overall time complexity of creating and traversing a header linked list is O(n).
Auxiliary Space:
The space complexity of the program is O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the linked list.
This is because we are creating n nodes, each with a fixed amount of space required for storing the node information and a pointer to the next node.
Therefore, the overall auxiliary space complexity of the program is O(n).
Additional Types:
- Multiply Linked List: Multiply Linked List is a data structure in which each node of the list contains multiple pointers. It is a type of linked list which has multiple linked lists in one list. Each node has multiple pointers which can point to different nodes in the list and can also point to nodes outside the list. The data stored in a Multiply Linked List can be easily accessed and modified, making it a very efficient data structure. The nodes in a Multiply Linked List can be accessed in any order, making it suitable for applications such as graphs, trees, and cyclic lists.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...