Indexing in MongoDB using Python
Last Updated :
16 Jun, 2022
By creating indexes in a MongoDB collection, query performance is enhanced because they store the information in such a manner that traversing it becomes easier and more efficient. There is no need for a full scan as MongoDB can search the query through indexes. Thus it restricts the number of documents that need to be checked for query criteria.
Syntax:
create_index([(str1, direction), (str1, direction).......], optional)
Parameters are:
- str : field to create index on.
- direction : can be one or many directions, it has to be one of these directions- descending, ascending, hashed, geosphere, geohaystack, geo2d or text
This function can accept either a key or a list of (key, direction) pairs.
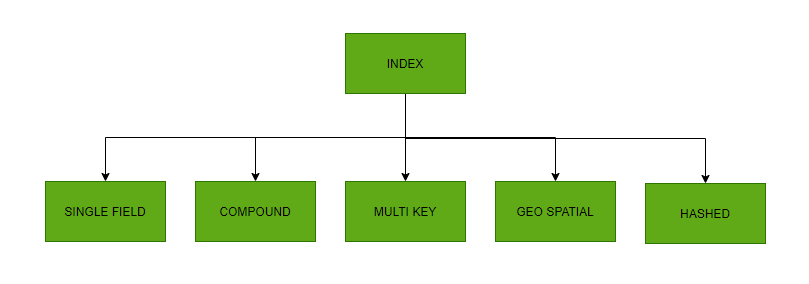
Example 1:
Python3
from pymongo import MongoClient
client = MongoClient('localhost', 27017)
db = client['GFG']
doc = db['Student']
res = doc.create_index("index_created")
print(res)
|
Output:
index_created_1
Example 2:
Python3
from pymongo import MongoClient
client = MongoClient('localhost', 27017)
db = client['GFG']
doc = db['Student']
res = doc.create_index([ ("index_descending", -1) ])
print(res)
|
Output:
index_descending_-1
Example 3:
Python3
from pymongo import MongoClient,, ASCENDING, DESCENDING
client = MongoClient('localhost', 27017)
db = client['GFG']
doc = db['Student']
res = doc.create_index(
[
("ascending_index", 1),
("second_descnding_indexed", DESCENDING)
]
)
print(res)
|
Output:
ascending_index_1
second_descnding_indexed_DESCENDING
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...