How To Create Custom AMI In AWS Using Terraform
Last Updated :
15 Mar, 2024
In the present cloud-centric software development landscape, the capacity to efficiently manage infrastructure resources is vital. Making custom Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) is a pivotal part of this process, permitting organizations to normalize their application environments and streamline sending work processes. Terraform, an open-source infrastructure as-code tool, gives a strong system to defining and managing infrastructure assets in cloud environments, including AWS (Amazon Web Services).
This guide centers around utilizing Terraform to make custom AMIs in AWS, enabling DevOps groups to really computerize and scale their foundation arrangements. By using Terraforms revelatory syntax and AWS supplier capacities, groups can classify their infrastructure prerequisites and accomplish consistency, reliability, and proficiency in their deployment processes.
All through this guide, we’ll dive into the complexities of utilizing Terraform to make custom AMIs, covering fundamental terminology, wording, and practical execution steps. From installation and setup to configuration asset determinations and managing conditions, perusers will acquire a thorough comprehension of how to tackle Terraforms capacities for AMI creation in AWS.
Understanding Of Primary Terminologies
- Amazon Machine Image (AMI): An AMI is a layout that contains the vital data to send off an example (virtual server) in the AWS cloud. It incorporates the operating system, software packages, setups, and different parts expected to run an application.
- Terraform: Terraform is an open-source infrastructure as-code device made by HashiCorp. It permits clients to characterize infrastructure resources utilizing a declarative configuration language and afterward arrangement and deal with those assets across different cloud providers, including AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
- Infrastructure as-Code (IaC): Infrastructure as-code is an act of overseeing Infrastructure resources through code as opposed to manual cycles or graphical points of interaction. With IaC, framework arrangements are written in code, empowering automation, version control, and consistency in infrastructure the executives.
- Provider: In Terraform, a provider is liable for cooperating with a particular cloud or service provider (e.g., AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud Platform). Every supplier offers a bunch of assets and APIs that Terraform uses to oversee infrastructure resources inside that supplier’s current circumstance.
- Resource: An resource in Terraform addresses a piece of infrastructure or a help presented by a provider. Instances of assets incorporate EC2 instances, S3 buckets, VPCs (Virtual Private Cloud), and IAM (Identity and Access Management) jobs.
- Declarative Configuration: Terraform utilizes a declarative way to deal with characterize infrastructure setups, where clients indicate the ideal condition of the infrastructure as opposed to the grouping of steps expected to accomplish that state. Terraform then decides the important activities to carry the infrastructure into the ideal state.
Create custom AMI In AWS Using Terraform: A Step-By-Step Guide
Step 1: Launch An Instance
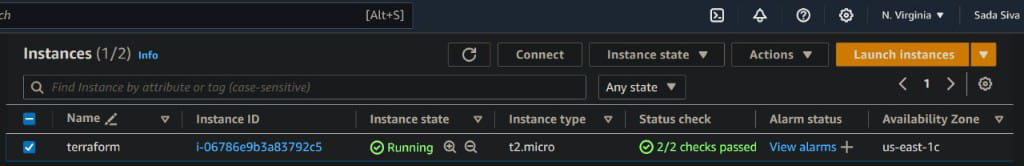
- Launch EC2 instance with Amazon Linux2 Kernel 5.10(AMI) along with port numbers set SSH – 22, HTTP 8o and select storage t2.micro.
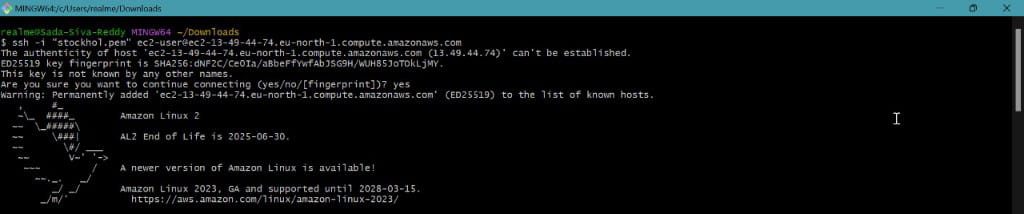
- Now connect with git bash terminal by using SSH Client
Step 2: Install Terraform
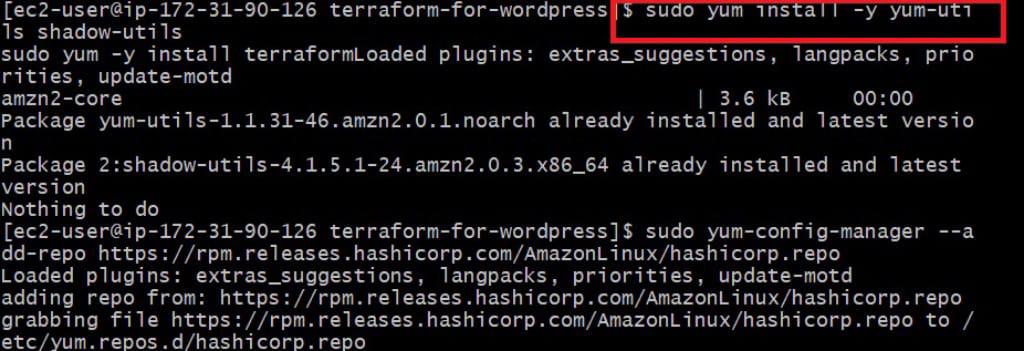
- Now install terraform from official site of hashicorp or follow below commands
sudo yum install -y yum-utils
sudo yum-config-manager --add-repo https://rpm.releases.hashicorp.com/AmazonLinux/hashicorp.repo
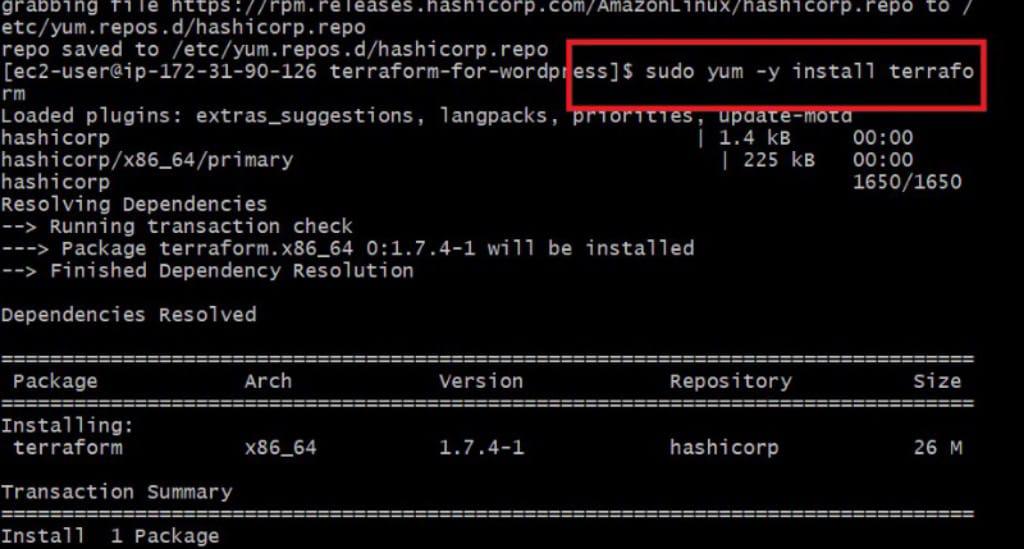
sudo yum -y install terraform
Step 3: Create A File And Write Terraform Script
- Create a file with .tf extension in that file write a script by using
vi <filename.tf>
Provider configuration
- This section specifies the AWS provider and sets the region to “us-east-1”. The provider block configures the authentication details and default settings for interacting with AWS.
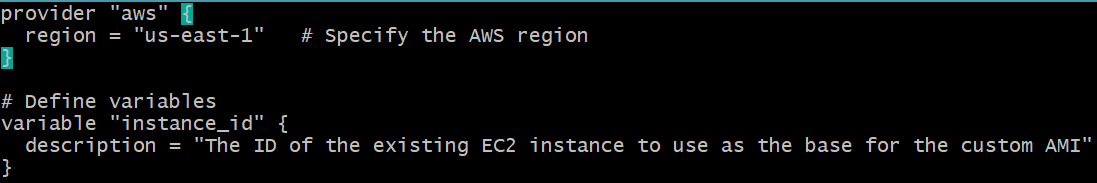
provider "aws" {
region = "us-east-1" # Specify the AWS region
}
Variable Section
- This section defines a variable named “instance_id” that represents the ID of the existing EC2 instance.
variable "instance_id" {
description = "The ID of the existing EC2 instance to use as the base for the custom AMI"
}
IAM Role Creation
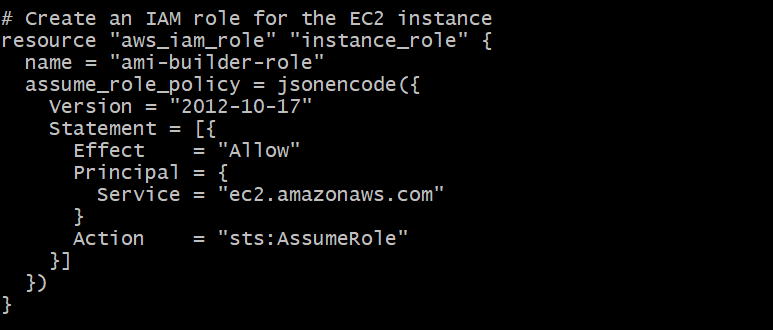
- This section creates an IAM (Identity and Access Management) role named “ami-builder-role” with a trust policy that allows EC2 instances to assume the role. IAM roles are used to grant permissions to entities in AWS.
resource "aws_iam_role" "instance_role" {
name = "ami-builder-role"
assume_role_policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012-10-17"
Statement = [{
Effect = "Allow"
Principal = {
Service = "ec2.amazonaws.com"
}
Action = "sts:AssumeRole"
}]
})
}
IAM Policy Attachment
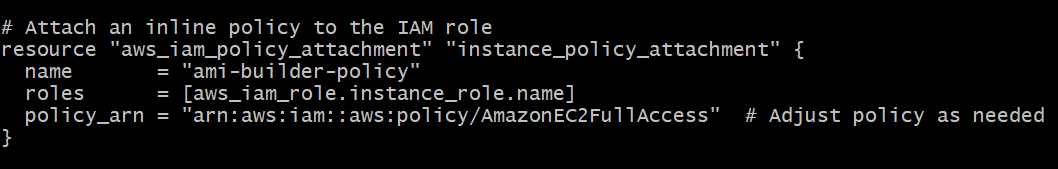
- This section attaches an IAM policy (AmazonEC2FullAccess) to the IAM role created earlier
resource "aws_iam_policy_attachment" "instance_policy_attachment" {
name = "ami-builder-policy"
roles = [aws_iam_role.instance_role.name]
policy_arn = "arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEC2FullAccess" # Adjust policy as needed
}
EC2 Instance Creation
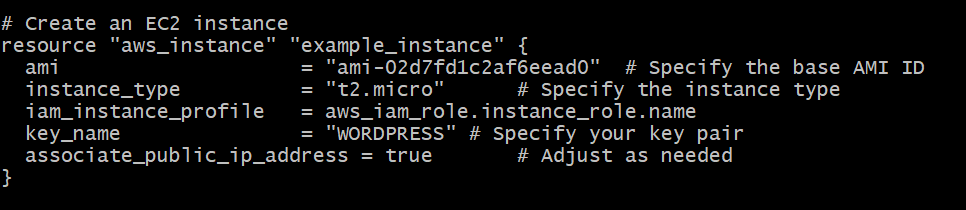
resource "aws_instance" "example_instance" {
ami = "ami-12345678" # Specify the base AMI ID
instance_type = "t2.micro" # Specify the instance type
iam_instance_profile = aws_iam_instance_profile.instance_profile.name
key_name = "your-key-pair" # Specify your key pair
associate_public_ip_address = true # Adjust as needed
}
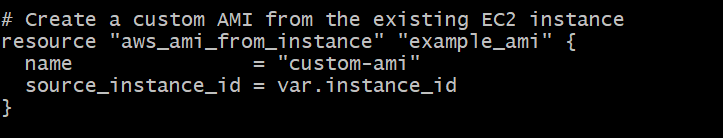
Custom AMI Creation
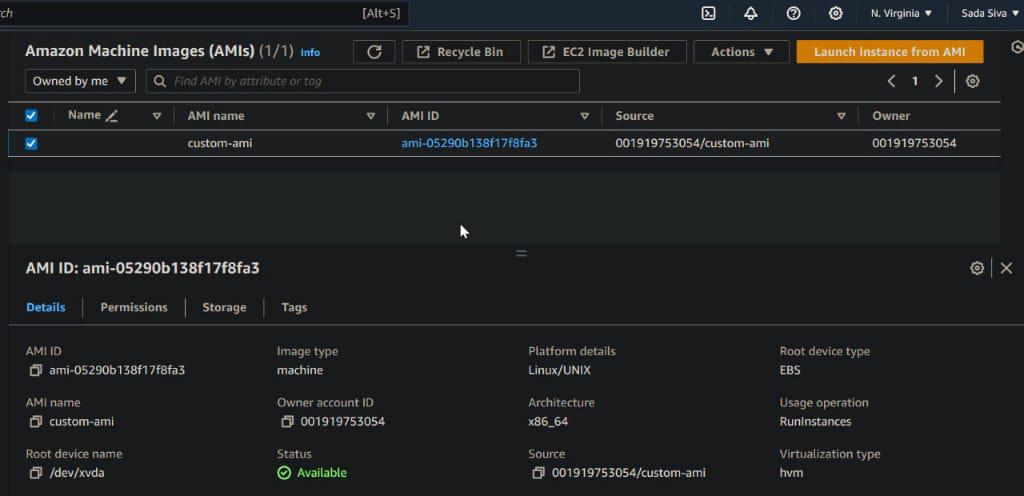
- This section creates a custom AMI named “custom-ami” from the existing EC2 instance specified by the “instance_id” variable.
resource "aws_ami_from_instance" "example_ami" {
name = "custom-ami"
source_instance_id = var.instance_id
}
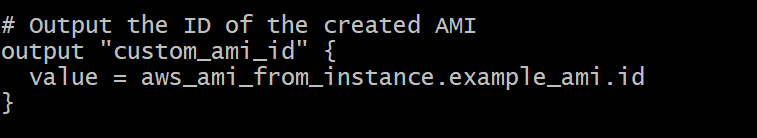
Output
- This section defines an output variable named “custom_ami_id” that retrieves the ID of the created custom AMI. Outputs provide visibility into the results of Terraform operations.
output "custom_ami_id" {
value = aws_ami_from_instance.example_ami.ami_id
}
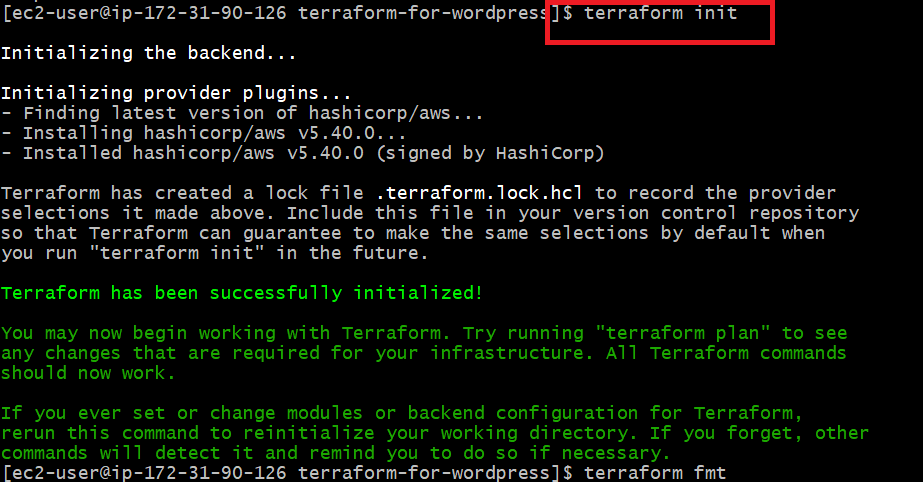
Step 4: Now Initialize Terraform And Execute Terraform Commands
- Now initialize terraform by using following command
terraform init
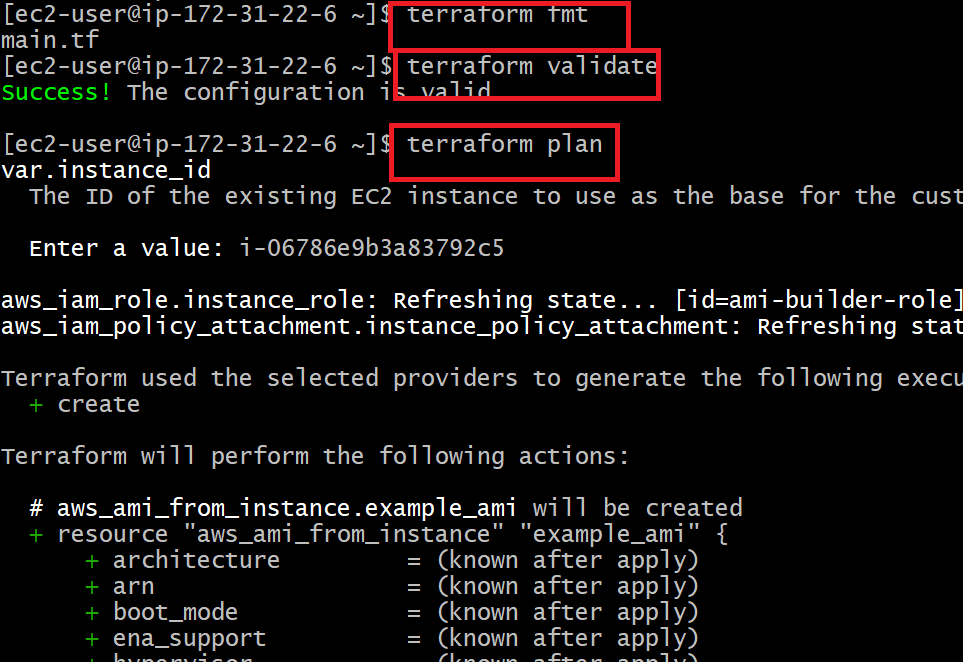
- Now execute terraform execution commands by using following commands
terraform fmt
terraform validate
terraform plan
- Now execute terraform apply command by using following command
terraform apply --auto-approve
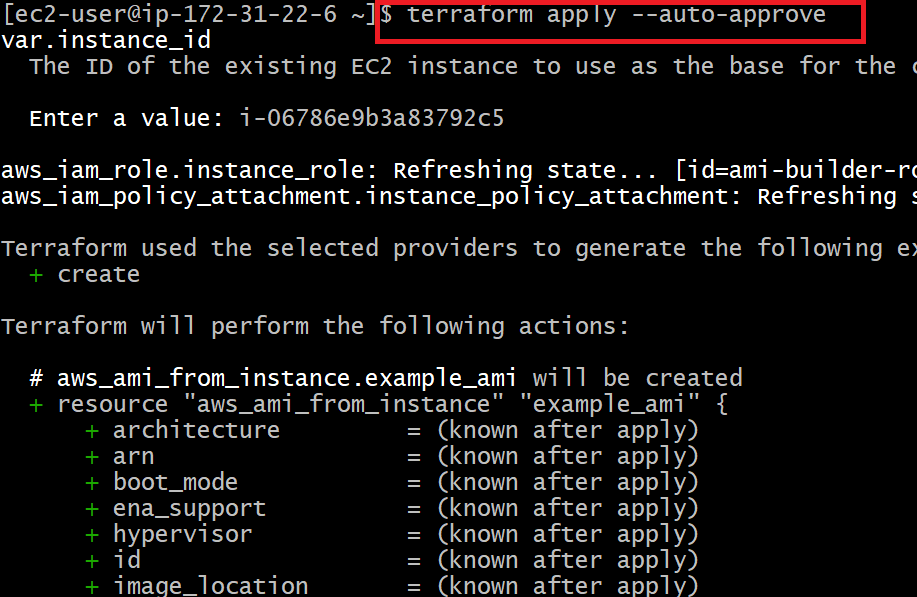
The following screenshot shows that we successfully created a custom AMI in AWS using Terraform.
Conclusion
In summary, this Terraform script gives a complete answer for automating the creation of custom Amazon Machine Image(AMIs) in AWS. By saddling the force of Terraforms infrastructure as-code approach, DevOps groups can productively deal with their infrastructure configurations, speed up, and ensure consistency across conditions.
Through the script, we’ve exhibited how Terraform empowers the consistent coordination of AWS resources and configurations, taking into account the production of custom AMIs from existing EC2 instances. This approach smoothes out the most common way of building standardized, reproducible images for deploying applications in AWS conditions.
AWS Custom AMI And Terraform – FAQs
Can I Utilize This Terraform Script To Make Custom AMIs In Various AWS Regions?
Yes, you can modify the content to different various districts in the provider block, permitting you to all the while make custom AMIs in different AWS regions .
How Might I Customize The Configurations Of The Ec2 Instance Prior To Creating The Custom AMI?
You can adjust the “aws_instance” resource block to incorporate additional configuration settings, for example, user data scripts, security group assignments, and labels, taking into consideration customization of the EC2 instance prior to making the custom AMI.
Is It Possible To Automate The Deletion Of The Ec2 Instance Subsequent To Making The Custom AMI?
Indeed, you can stretch out the Terraform content to incorporate a “null_resource” block with a provisioner that trigger an AWS Lambda capability or AWS Systems Manager Automation report to erase the EC2 instance after the custom AMI creation process is finished.
How Might I Deal With Errors Or Failures During The Custom Ami Creation Process?
Terraform provides error handling mechanisms, for example, lifecycle hooks, conditions, and conditional logic that can be utilized to deal with errors or failures during resource provisioning. You can execute retry rationale, rollback techniques, or making components aware of moderate issues and ensure the dependability of the custom AMI creation process.
Could I At Any Point Utilize This Terraform Script Related To Other Aws Services, Like AWS Lambda Or Amazon S3?
Yes, Terraform integrates consistently with different AWS services, permitting you to orchestrate complex infrastructure organizations that range various services. You can stretch out the script to incorporate assets, for example, Lambda functions, S3 buckets, CloudWatch alarms and more, to assemble complete infrastructure arrangements custom fitted to your particular prerequisites.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...