Find N fractions that sum upto a given fraction N/D
Last Updated :
23 May, 2022
Given a fraction N/D, the task is to split this fraction into N parts such that their sum is equal to the fraction N/D, i.e.,
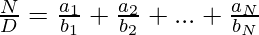
Note: Represents the terms in terms of fractions, instead of floating point numbers.
Input: N = 4, D = 2
Output: 4/5, 1/5, 1/3, 4/6
Explanation:
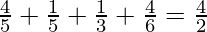
Therefore, it is a valid set of fractions such that their sum is 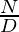
Input: N = 3, D = 4
Output: 1/2, 1/10, 3/20
Explanation:
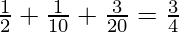
Therefore, it is a valid set of fractions such that their sum is 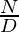
Approach: The key observation in the problem is that the first fraction numerator can be 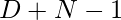 and then further
and then further 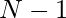 denominators can be using the below recurrence relation.
denominators can be using the below recurrence relation.
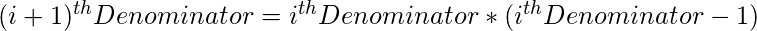
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void splitFraction(int n, int d)
{
int ar[n];
int first = d + n - 1;
ar[0] = first;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
int temp = --first;
first++;
ar[i] = first * temp;
--first;
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (ar[i] % n == 0)
{
cout << "1/" << ar[i] / n << ", ";
}
else
{
cout << n << "/" << ar[i] << ", ";
}
}
}
int main()
{
int N = 4;
int D = 2;
splitFraction(N, D);
}
|
Java
import java.util.Scanner;
class Solution {
public static void
splitFraction(int n, int d)
{
long ar[] = new long[n];
long first = d + n - 1;
ar[0] = first;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
ar[i] = first * (--first);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (ar[i] % n == 0) {
System.out.print(
"1/" + ar[i] / n
+ ", ");
}
else {
System.out.print(
n + "/" + ar[i]
+ ", ");
}
}
}
public static void main(
String[] args) throws Exception
{
int N = 4;
int D = 2;
splitFraction(N, D);
}
}
|
Python3
def splitFraction(n, d):
ar = []
for i in range(0, n):
ar.append(0)
first = d + n - 1
ar[0] = first
for i in range(1, n):
temp = first - 1
ar[i] = first * temp
first -= 1
for i in range(0, n):
if ar[i] % n == 0:
print("1/", int(ar[i] / n),
"," , end = " ")
else:
print(n, "/", ar[i], ",", end = " ")
N = 4
D = 2
splitFraction(N, D)
|
C#
using System;
class GFG{
public static void splitFraction(int n, int d)
{
long []ar = new long[n];
long first = d + n - 1;
ar[0] = first;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
ar[i] = first * (--first);
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (ar[i] % n == 0)
{
Console.Write("1/" + ar[i] / n + ", ");
}
else
{
Console.Write(n + "/" + ar[i] + ", ");
}
}
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int N = 4;
int D = 2;
splitFraction(N, D);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function splitFraction(n, d) {
var ar = new Array(n);
var first = d + n - 1;
ar[0] = first;
for (var i = 1; i < n; i++) {
ar[i] = first * --first;
}
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (ar[i] % n === 0) {
document.write("1/" + ar[i] / n + ", ");
} else {
document.write(n + "/" + ar[i] + ", ");
}
}
}
var N = 4;
var D = 2;
splitFraction(N, D);
</script>
|
Output: 4/5, 1/5, 1/3, 4/6,
Time Complexity: O(n), where n is the given integer.
Auxiliary Space: O(n), where n is the given integer.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...