Empathy Mapping: What is an Empathy Map?
Last Updated :
17 Dec, 2023
The idea of empathy mapping has evolved as a critical tool for comprehending and addressing user requirements, desires, and obstacles in the constantly changing world of design and user-centric innovation. An Empathy Map essentially acts as a compass for designers to navigate the complex landscape of human emotions, thoughts, and behaviors. This approach, which is based on the principles of empathy, gives designers a systematic framework to enter the user’s environment and get insights that go beyond simple demographics and statistics.

It’s a visual representation that helps teams understand and empathize with their target audience or users by focusing on their feelings, thoughts, behaviors, and needs. Essentially, an empathy map helps you get inside the minds and hearts of your users to create products, services, or content that truly resonates with them.
What is an Empathy Map?
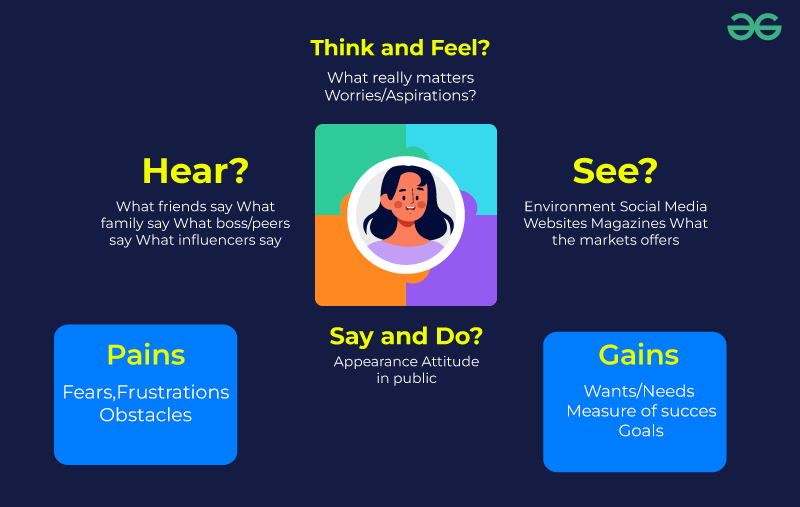
An Empathy Map is a visual framework that helps UX designers and teams gain a deeper understanding of their users by immersing themselves in the users’ perspectives, thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. It allows designers to step into the shoes of their users and create a comprehensive view of their experiences, needs, and motivations. Empathy Mapping gives designers the ability to create experiences that connect on a very human level. In this investigation, the essence of empathy mapping is uncovered, along with its components and the transforming power it may have on a variety of creative projects.
Typically, the empathy map is organized into four quadrants, each of which focuses on a different element of the user’s experience.
These four sections are:
- Says: This quadrant focuses on the user’s statements, whether made orally or in writing. It covers their declarations, quotations, and catchphrases that shed light on their ideas and perspectives.
- Thinks: In this section, designers delve into the user’s inner thoughts and considerations. Understanding the user’s hopes, concerns, and expectations in relation to the good or service is necessary for this.
- Feels: Investigating the user’s feelings and emotions falls under this quadrant. Designers try to understand the user’s feelings and emotional responses as they interact with the good or service.
- Does: The user’s actions, behaviors, and perceptible behaviors are the focus of the “Does” quadrant. The goal of design is to comprehend how people interact with the product, what they do, and how they move through the experience.
Let’s try to understand the Empathy Map with the help of an example of Making an Empathy Map for a Fitness App.
Consider a UX design team developing a fitness app. They want to comprehend the motivations and experiences of their intended audience.
The information could be filled out the Empathy Map in the following ways:
- Says: (User quotes) from interviews “I want a workout app that fits my busy schedule.” “I’m looking for a way to track my progress easily.”
- Thinks: (User aspirations) “I want to get in shape and feel confident.” User concerns: “I’m worried about injuring myself with incorrect exercises.”
- Feels: (User emotions) Excited about the possibility of a healthier lifestyle, frustrated by previous failed attempts at fitness.
- Does: (User actions) Follows fitness influencers on social media, uses a variety of fitness apps but struggles to stick to a routine.
How to Create an Empathy Map?
1. Establish Your Target Audience
Decide which particular user group or persona you want to target. To make sure your Empathy Map is suited to their experiences, precisely outline the traits, requirements, and objectives of this group.
2. Fill in the Quadrants
Starting with the information you’ve learned from your investigation, fill in each quadrant of the empathy map.
- Says: Quotes, assertions, or expressions that users have made in comments or during interviews should be filled in.
- Thinks: Write down the ideas, goals, worries, and expectations that users have expressed.
- Feels: Record the attitudes, thoughts, and feelings that customers have regarding the good or service.
- Does: Keep track of user interactions with the product or service, including their behaviors, actions, and perceptible actions.

3. Identify Opportunities and Pain Points
Pay close attention to any problems, obstacles, or unmet needs that the empathy map reveals. Your design choices will be guided by these as you solve user issues.
4. Set Priorities and Come Up with Ideas
Prioritize the biggest potential or pain points based on the findings from the empathy map. Make advantage of these data to generate suggestions for design enhancements, features, or products that directly respond to consumer wants.
5. Update the Empathy Map Frequently
User tastes and needs can change over time. By performing regular research and updating the map with fresh ideas, you can keep your empathy map current.
Use of an Empathy Map?
Empathy Maps are an effective tool that designers and teams can use to develop more user-centered and effective solutions. Here is a thorough explanation of how empathy maps are used in design:
- Understanding User Needs and Pain Points: Empathy Maps give designers a thorough understanding of the user’s ideas, feelings, actions, and goals. Designers can pinpoint user wants, problems, and concerns that may not be obvious from quantitative data alone thanks to this deeper insight. Designers can produce solutions that directly address users’ actual experiences by discovering these insights.
- Human-Centered Design: Empathy Maps are a key component of human-centered design because they force designers to put themselves in the users’ shoes. This strategy promotes human-centered design that appeals to the target market by shifting the focus from abstract ideas to the actual experiences of real people.
- Idea Generation and Conceptualisation: Idea development and conceptualization are sparked by the knowledge obtained through empathy maps. The insights can be used by designers to come up with features, functionality, and design ideas that are in line with user requirements and preferences.
- Informed Design Decisions: Empathy Maps serve as a compass during the design process, allowing for educated design decisions. The map can be used by designers to make sure that each design choice they make is based on a thorough grasp of the user’s perspective. This leads to design decisions that are more pertinent and successful.
- Prioritising products: The pain points and difficulties noted in the empathy map assist designers in putting a higher priority on products and enhancements that directly address these problems. By doing this, feature bloat is avoided and the most important user needs are fulfilled.
- Testing and Validation: Design ideas produced from empathy maps can be put to the test with users to verify presumptions and get feedback. Through an iterative process, users’ demands are effectively met and the final result is one that resonates with them.
Key Takeaways from Empathy Map
After looking into what an empathy map is, how to create and use one while designing a feature or app or website. Now let’s look into some major takeaways that can be derived from creating and analyzing an Empathy Map:
- Data-Driven Insights: Empathy Maps provide design decisions a data-driven foundation by rooting them in actual user behavior and emotions.
- Design for Emotional Impact: By being aware of user emotions, designers can develop interactions that arouse a sense of well-being.
- Holistic Understanding: Empathy Maps combine several user experience dimensions to create a more accurate and comprehensive understanding.
- Iterative Design: To ensure continuing alignment with user wants and sentiments, keep returning to the empathy map while you iterate on designs.
- Design Alignment: Ensure that design choices correspond to users’ expectations and experiences in the real world.
- Idea generation: Create innovative design solutions, features, and functionalities that directly address user needs using the information from the empathy map.
- Deeper insight: Go beyond simple demographics to gain a deeper insight of user needs, desires, issues, and motivations.
- Persona Enrichment: By incorporating emotional and behavioral characteristics, empathy maps help to create user personas that are more relatable and believable.
- Identification of Pain Points: Identify obstacles, annoyances, and pain points that people experience when using a product or service.
- User-Centered Insights: Empathy maps offer a user-centric perspective by showing the feelings, thoughts, and behaviors of the intended audience.
- Prioritisation Focus: Give top priority to design elements and advancements that solve the biggest problems and difficulties encountered by users.
- Communication Tool: Empathy Maps serve as a visible and practical tool for teams to exchange user insights, which improves communication and cooperation.
- Testing and Validation: Design solutions based on empathy maps can be put to the test with users to verify presumptions and collect input for improvement.
- User Engagement: Empathy-driven design solutions are more effective in resonating with users, increasing both user engagement and satisfaction.
- Meaningful Experiences: At the end of the day, empathy maps help to produce more powerful, relevant, and meaningful user experiences.
- Building Empathy: Designers develop empathy for users, promoting a human-centered design philosophy.
- Bridge the Gap: Empathy maps help to close the gap between user expectations and design outcomes, resulting in products that have real emotional resonance.
Conclusion
So we’re at the end of this article, hope this article helps you understand fundamental and essential concepts of UX design such as empathy map. The Empathy Map emerges as a guiding light, illuminating the complex world of user experiences, in the dynamic landscape of user-centric design. This potent tool empowers designers to create solutions that resonate deeply by probing consumers’ thoughts, feelings, behaviors, and aspirations. Empathy Maps create relationships that are meaningful by bridging the gap between user expectations and design outcomes. The adoption of these findings by designers ushers in a new era of design that is not just practical but also profoundly empathic, producing goods and experiences that have a lasting impact on consumers’ lives.
FAQs on Empathy Mapping
1. What is Empathy Map?
An Empathy Map is a visual tool used for understanding a target audience’s thoughts and experiences to improve product or service design. It helps teams gain insights into users’ perspectives and needs.
2. What tools are used to create empathy map?
Whiteboards and sticky notes are used for physical brainstorming sessions, or digital tools like Miro, MURAL for virtual collaboration and documentation.
3. Why is empathy important in UX?
Empathy allow designer to understand the needs and wants of users and according to that UX designers can create or modify their product so that user can build trust on that.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...