In the past days, the process of metal welding should be possible by heating the metals and pressed jointly which is known as the forge welding method. In any case, as of now, the welding innovation has been changed by the arrival of electricity. In the nineteenth century, resistance, gas, and arc welding was invented. After this, there are various types of welding technologies have been imagined like friction, ultrasonic, plasma, laser, and electron beam welding. However, the uses of welding technology essentially include different industries.
In this article, we will be going through Resistance Wielding, We will start our Article with the Introduction of Resistance Wielding, Then we will go through the Working Principle of Resistance welding and With its Types, Then We will through its Specification, At last, we will conclude our article with its Advantages, Disadvantages, Applications, Comparison Between Resistance and Electric wield and Some FAQs.
What is Resistance Welding?
Resistance Welding can be defined as; it is a fluid state welding technique where the metal-to-metal joint can be shaped inside a fluid state in any case molten state. Here intensity can be produced at the It is a thermo-electric cycle in which intensity is created at the edge planes of welding plates as a result of electric resistance and a weld joint can be made by applying low-strain to these plates. This type of welding utilizes electric resistance from produce heat. Despite its high efficiency and pollution-free nature, this method has few applications due to limitations in material thickness and equipment costs.
Electric-Resistance-Welding
Working Principle of Resistance Welding
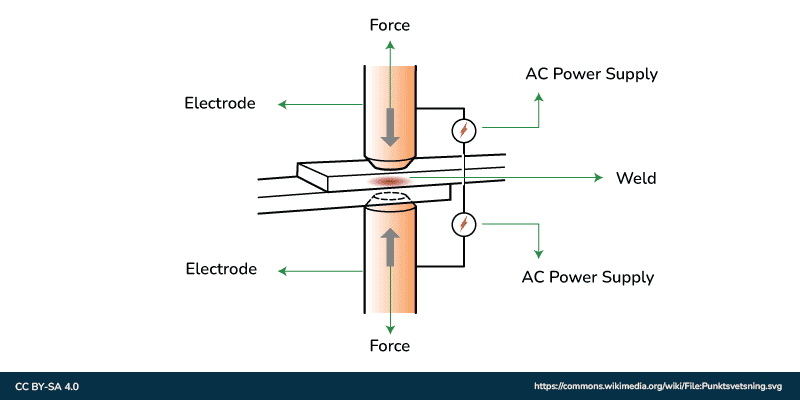
The cycle begins with the metal parts being carried into contact with one another, sandwiched between two electrode tips. These electrodes are responsible for applying the requisite pressure to ensure optimal contact and to firmly hold the parts intact during welding.
When the components are set up, an electric current is brought into the workpieces by energizing the electrodes. This current flow through the workpieces, experiencing resistance at the connection point where they meet.
As the current encounters this resistance, it delivers a lot of intensity at a sped up pace. The Joule heating effect is a way electrical energy is effectively turned into intense heat. The intensity created by the resistance causes the metal at the contact point to rapidly soften and eventually melt.
This heat generation happens due to the energy change from electric to thermal. The resistance welding equation for heat generation is
H = I 2 RT
Where,
I = Current flowing through the electrodes,
R = is the contact resistance of the point of interaction, and
t = is the time at which the current flows
Types of Resistance Welding
Different types of resistance welding are discussed below.
- Spot Welding
- Seam Welding
- Projection Welding
- Flash Butt Welding
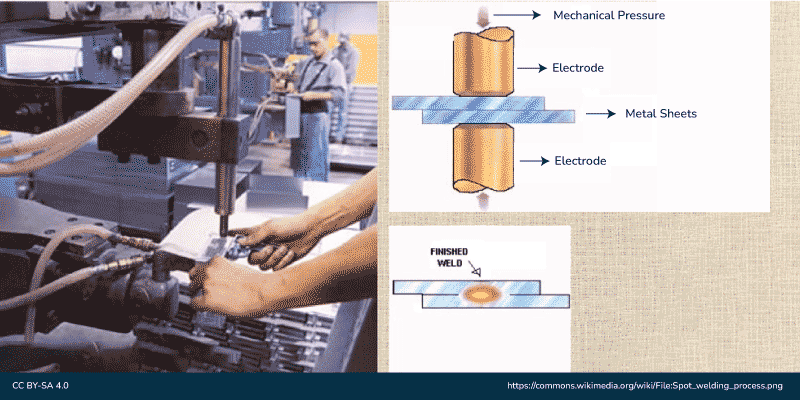
Spot Welding
The simplest form of welding is spot welding, in which the workpieces are held together by the anvil face’s force. The copper (Cu) terminals will connect with the work segment and the progression of current through it. The work portion material applies a couple of protections inside current stream which will cause restricted heat creation. The opposition is high at the edge surfaces on account of the air gap. The current starts to supply through it, then, at that point, it will decrease the edge surface.
Spot-Welding
The current supply and the time should be enough for the right dissolving of edge faces. Presently the progression of current will be halted anyway the power applied with terminal went on briefly, while the weld immediately cooled. However, the terminals take out as well as reach out to new detect to make a round piece. The piece size predominantly depends upon electrode size (4-7 mm).
Advantages of Spot Welding
- Spot welding has high similarity with effectiveness and consistency.
- Spot welding is economical.
- Spot welding gives a significantly more efficient approach to using electrical energy for welding process.
- Spot welding is a quick welding process.
Disadvantages of Spot Welding
- Spot welding requires an large working area.
- Spot welding uses a heavy welding gun that requires a lot of strength to operate. Subsequently, spot welding might be extremely hazardous to the matured welders.
- The thicker materials are not suitable for spot welding.
Applications of Spot Welding
- Spot welding is utilized in different ventures, for example, auto, aviation, metal furnishings, hardware, building development, and so on.
- Spot welding is utilized in high volume creation applications.
- It is used to weld thin sheets together.
- Spot welding is likewise utilized for manufacturing a wide range of sheet metal designs where high mechanical strength is required.
- Spot welding can likewise be applied to a wide range of boxes, centers and encasing cases, and so on.
Seam Welding
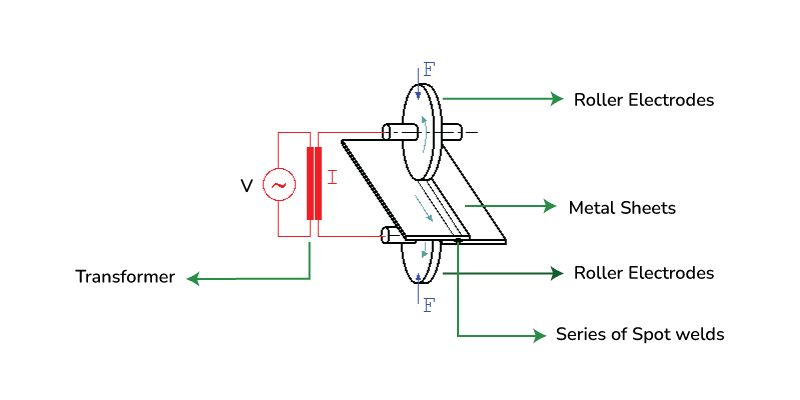
This type of welding is also called continuous spot welding where a roller form electrode can be used to supply current all through work parts. At first, the roller electrodes are getting out to the work part. These electrode rollers can carry a high current, melting the edge surfaces and shaping a weld joint.
Seam Welding
The electrode rollers will start moving on work plates to make a super durable weld joint. The weld timing and cathode development can be controlled to ensure that the weld cross-over and work part doesn’t get excessively warm. When seam welding is used to create airtight joints, the speed of the welding can be about 60 inches per minute.
Advantages of Seam Welding
- The welds created by the seam welding are impenetrable and water-tight.
- Seam welding is a quick welding interaction and it tends to be computerized utilizing mechanical machines.
- It does not require any filler or flux materials.
Disadvantages of Seam Welding
- The resistance seam welding process has a few drawbacks, including the fact that it uses roller electrodes and can only produce welds in straight lines or uniformly curved lines.
- It isn’t appropriate for metal sheets of thickness more than 3 mm per sheet.
Applications of Seam Welding
- Resistance seam welding is utilized for a number of purposes, including the creation of lap joints.
- It is utilized in assembling cycle of different kinds of strain tight or sealed tanks, for example, gas tanks, oil switches, transformer tanks, airplane tanks, and so on.
- Utilized for welding parts of vessels that should to be air tight and water tight.
- For welding of pipes and tubes.
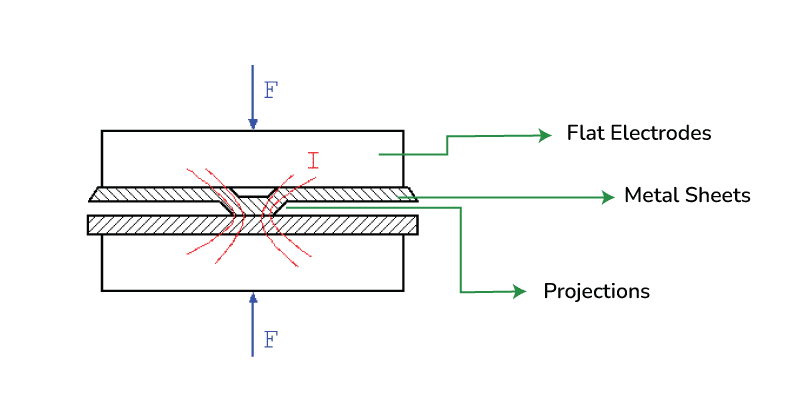
Projection Welding
Projection welding is like spot welding separated from a dimple can be generated on work parts at the spot any place weld is liked. At present the work parts held among cathode as well as a gigantic amount of current course through it. A little amount of strain can be applied all through the cathode on welding safeguards. The progression of current all through dimple which disintegrate it and the power reasons the dimple level and shape a weld.
Projection-welding
Advantages of Projection Welding
- There is no limitation on the metal thickness, i.e., metal of any thickness can be welded with the projection welding.
- Multiple welds can be made at once with projection welding. Subsequently, more result is acquired.
- In the projection welding, less current is gone through the terminals and low strain is applied. Hence, the anode life is expanded.
- Projection welding gives great intensity balance while welding process.
- The projection welding method results in a weld with a polished appearance.
Disadvantages of Projection Welding
- The course of projection development is complicated and time consuming.
- It requires highly skilled welders.
- Projection welding can’t be applied to a wide range of workpieces.
- Hardware utilized for projection welding are costly.
Applications of Projection Welding
- Projection welding is used for welding studs, nuts to plates, etc.
- Projection welding is also used in the shipbuilding, automotive, and sheet metal industries.
- It is moreover used for welding the bits of cooler, condensers, etc.
Flash Butt Welding
Flash butt welding is a type of resistance welding that is used in the steel industry to weld both tubes and rods. In this strategy, two work parts are welded which will be held tightly during the terminal holders as well as a high pulsed flow of current inside the 1,00,000 ampere range can be provided toward the work part material.
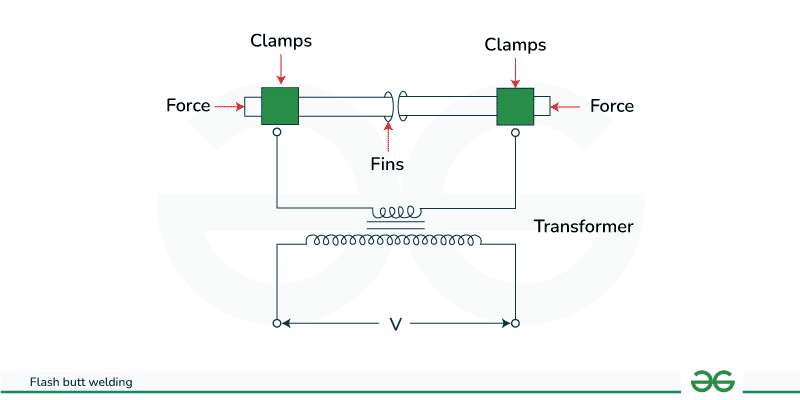
Flash Butt Welding
In the two electrode holders, one is long-lasting and other is variable. At first, current can be supplied, and a spark will be produced when the changeable clamp is pressed against the permanent clamp due to contact between the two parts at high current. At the point when the edge surface methodologies into plastic shape, the progression of current will be halted too as hub power can be improved to make joint. Due to plastic deformation, the weld can be formed using this method.
Advantages of Flash Butt Welding
- It is a faster process.
- Preparation of weld surface isn’t needed.
- Power necessity is less.
- Numerous dissimilar metals with various melting temperatures can be flash welded.
- The process is cheap.
- It offers strength factor up-to 100 percent.
Disadvantages of Flash Butt Welding
- More possibilities of fire hazards.
- Metal is lost during flashing and disturbing.
- Concentricity and straightness of the work pieces during welding process is frequently challenging to keep up with.
Applications of Flash Butt Welding
- It is utilized for welding metal sheets, bars, rods fittings and so on.
- Flash welding finds applications in car and air craft products.
- It is additionally utilized in home devices, coolers and farm implements.
Successful Welding Process
Three things are crucial for an effective welding process, and they are:
- Time for welding.
- Welding current.
- Welding pressure.
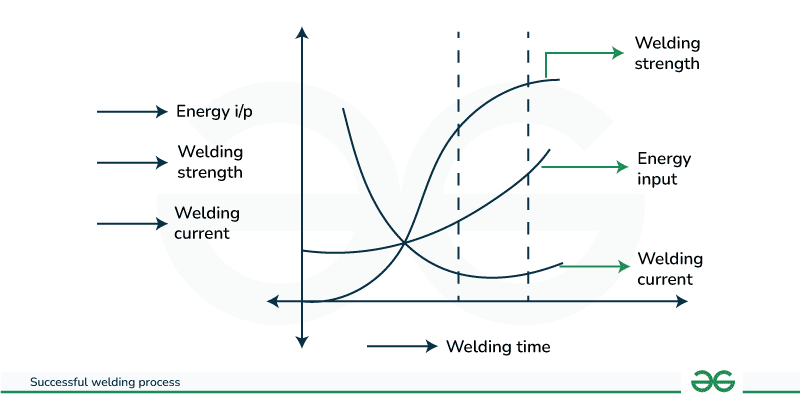
Successful Welding Process
The Figure shows how the energy input to the welding process, welding strength, and welding current differ with welding time.
The choice of welding time depends upon a few factors, such as, the type of welding, the thickness and piece of the material being welded, the size of the weld, and the required welding quality and efficiency. The welder should likewise consider the type of electrode, welding power source, and ambient circumstances. A longer welding time might be important for thicker material.
Specifications for Resistance Welding
The specifications for resistance welding can vary depending upon the type of welding being performed and the materials being welded. The amount of electrical current used to heat and fuse the metal parts is known as welding current, and it is one of the most common specifications.
- Welding Current: The welding current is a major parameter in welding. It is commonly in the range of 1,000 to 200,000 amperes, depending upon the material and thickness.
- Electrode Force: The force applied to the terminals during welding is basic for accomplishing a proper weld. It makes it easier for current to flow through the workpieces and ensures good contact between the metals.
- Anode Material: Materials that can conduct electricity well and withstand the high temperatures generated by welding are required for electrodes. Common terminal materials incorporate copper and its alloys.
- Cooling System: Resistance welding creates heat, So for cooling purpose we need a cooling system . Water cooling is used for this purpose.
- Welding Machine Control System: Modern resistance welding machines are equipped with control systems that allow exact change of welding parameters and high-quality welds.
- Welding Transformer: In welding system transformer plays a major role because for welding purpose we need more current. So we need a transformer that should be matched to the specific requirements of the welding application.
- Safety Measures: In any welding process safety is more important. For this purpose require a proper ventilation, personal protective equipment (PPE), safety interlocks on machinery are essential.
Advantages of Resistance Welding
- This method is simple and does not require a lot of skilled labor.
- The resistance welding metal is 20 millimeters thick and 0.1 millimeters thin
- Automated simply
- The production rate is high Both related and distinct metals can be welded.
- Welding speed will be high
- It needn’t bother with any flux, filler metal and protecting gases.
Disadvantages of Resistance Welding
- Instruments cost will be high.
- The work segment thickness is limited because of the current requirement.
- When used with high-conductive equipment, it is less effective.
- It consumes high electric-power.
- Weld joints contain small tensile and fatigue Strength.
Applications of Resistance Welding
- The applications of Resistance welding incorporate the following.
- This kind of welding can be generally used inside automotive industries, making of nut as well as a bolt.
- Seam welding can be used to produce spill demonstrate joint vital inside little tanks, boilers, and so on.
- Flash welding can be utilized for welding cylinders and lines.
Comparison Between Resistance Welding and Electric Arc Welding
|
Features
|
Resistance Welding
|
Electric Arc Welding
|
|
Supply
|
For the most part, AC supply is utilized for resistance welding
|
Both AC and DC supply can be utilized in the arc welding.
|
|
Power Factor
|
In resistance welding, the power factor is low.
|
In arc welding, the power factor is poor
|
|
Requirement of External Pressure
|
In resistance welding, outer tension is expected for joining the metals.
|
In arc welding, no outside pressure is required. Subsequently, the hardware is straightforward and simple to control.
|
|
Requirement of Filler Material
|
With the resistance welding, no filler material is included any structure for joining the two metal pieces.
|
Filler metal rod is required for arc welding to ensure that the joint has sufficient strength.
|
|
Voltage
|
Resistance welding requires an extremely low voltage.
|
In the event of arc welding, the striking voltage is high. Hence, it needs voltage control.
|
|
Temperature
|
In resistance welding process the temperature raise isn’t exceptionally high.
|
In arc welding, the arc segment temperature is extremely high. On the off chance that it isn’t dealt with as expected, it might harm the work-piece.
|
|
Production of Heat
|
In the resistance welding, the intensity is delivered because of the progression of current primarily through the contact resistance.
|
In the circular segment welding, the intensity is delivered because of the curve made between the electrode and the work-piece.
|
|
Suitability
|
Resistance welding is generally appropriate for large scale manufacturing and furthermore for fix work.
|
Arc welding is appropriate for fix work. However, it is incompatible with mass production.
|
Conclusion
In conclusion, resistance heating stands as a fundamental and flexible technique inside the domain of industrial processes, giving significant arrangements across a myriad of uses. This heating procedure, established in the principle of electrical resistance, has exhibited its adequacy in producing controlled and exact intensity for different purposes.
One of the striking qualities of resistance heating lies in its productivity, changing over electrical energy into heat with a high degree of effectiveness. The technique considers adjusted temperature control, going with it an ideal decision in situations where accuracy is foremost, for example, in hardware assembling and material handling. Metalworking, electronics, ceramics, and polymers are just a few of the many fields in which resistance heating can be used. Its significance in modern manufacturing processes is emphasized by its adaptability to various materials. Besides, the technique’s expense viability, combined with its ecological kind disposition, upgrades its allure in modern settings.
While resistance heating has lot of benefits, it must be taken into account for large-scale operations due to issues like power consumption and scalability. Nonetheless, progressing innovative headways and exploration endeavors plan to address these difficulties, guaranteeing that opposition warming remaining parts a significant and developing answer for what’s to come. Fundamentally, obstruction warming’s mix of productivity, accuracy, and flexibility highlights its getting through significance in molding the scene of modern cycles, adding to headways and advancements across different areas.
Electric Resistance Welding – FAQs
What is the purpose of resistance heating?
Resistance heating is utilized for different modern applications, including metalworking, materials handling, hardware assembling, and warming components in apparatuses.
What are the workings of resistance heating?
When an electric current passes through a material, resistance heating uses that material’s electrical resistance to generate heat. The opposition makes the material intensity up because of the energy dissemination.
Is resistance heating energy-proficient?
Resistance heating can be energy-effective, particularly in applications where exact temperature control is vital. In any case, proficiency relies upon variables, for example, the material being warmed and the general framework plan.
What are the benefits of resistance heating?
Benefits incorporate exact temperature control, versatility to different materials, cost-viability for explicit applications, and natural neighborliness contrasted with some elective warming strategies.
What kinds of things can be heated with resistance heat?
Resistance heating can be applied to many materials, including metals, ceramics, polymers, and composites.
Are there any limits to resistance heating?
Constraints might incorporate power utilization, especially in huge scope applications, and difficulties in accomplishing uniform warming for specific materials.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...