Data Science Interview Questions – Explore the Data Science Interview Questions and Answers for beginners and experienced professionals looking for new opportunities in data science.

We all know that data science is a field where data scientists mine raw data, analyze it, and extract useful insights from it. The article outlines the frequently asked questionas during the data science interview. Practising all the below questions will help you to explore your career as a data scientist.
What is Data Science?
Data science is a field that extracts knowledge and insights from structured and unstructured data by using scientific methods, algorithms, processes, and systems. It combines expertise from various domains, such as statistics, computer science, machine learning, data engineering, and domain-specific knowledge, to analyze and interpret complex data sets.
Furthermore, data scientists use a combination of multiple languages, such as Python and R. They are also frequent users of data analysis tools like pandas, NumPy, and scikit-learn, as well as machine learning libraries.
After exploring the brief of data science, let’s dig into the data science interview questions and answers.
Basic Data Science Interview Questions For Fresher
Q.1 What is marginal probability?
A key idea in statistics and probability theory is marginal probability, which is also known as marginal distribution. With reference to a certain variable of interest, it is the likelihood that an event will occur, without taking into account the results of other variables. Basically, it treats the other variables as if they were “marginal” or irrelevant and concentrates on one.
Marginal probabilities are essential in many statistical analyses, including estimating anticipated values, computing conditional probabilities, and drawing conclusions about certain variables of interest while taking other variables’ influences into account.
Q.2 What are the probability axioms?
The fundamental rules that control the behaviour and characteristics of probabilities in probability theory and statistics are referred to as the probability axioms, sometimes known as the probability laws or probability principles.
There are three fundamental axioms of probability:
- Non-Negativity Axiom
- Normalization Axiom
- Additivity Axiom
Q.3 What is conditional probability?
The event or outcome occurring based on the existence of a prior event or outcome is known as conditional probability. It is determined by multiplying the probability of the earlier occurrence by the increased lprobability of the later, or conditional, event.
Q.4 What is Bayes’ Theorem and when is it used in data science?
The Bayes theorem predicts the probability that an event connected to any condition would occur. It is also taken into account in the situation of conditional probability. The probability of “causes” formula is another name for the Bayes theorem.
In data science, Bayes’ Theorem is used primarily in:
- Bayesian Inference
- Machine Learning
- Text Classification
- Medical Diagnosis
- Predictive Modeling
When working with ambiguous or sparse data, Bayes’ Theorem is very helpful since it enables data scientists to continually revise their assumptions and come to more sensible conclusions.
Q.5 Define variance and conditional variance.
A statistical concept known as variance quantifies the spread or dispersion of a group of data points within a dataset. It sheds light on how widely individual data points depart from the dataset’s mean (average). It assesses the variability or “scatter” of data.
Conditional Variance
A measure of the dispersion or variability of a random variable under certain circumstances or in the presence of a particular event, as the name implies. It reflects a random variable’s variance that is dependent on the knowledge of another random variable’s variance.
Q.6 Explain the concepts of mean, median, mode, and standard deviation.
Mean: The mean, often referred to as the average, is calculated by summing up all the values in a dataset and then dividing by the total number of values.
Median: When data are sorted in either ascending or descending order, the median is the value in the middle of the dataset. The median is the average of the two middle values when the number of data points is even.
In comparison to the mean, the median is less impacted by extreme numbers, making it a more reliable indicator of central tendency.
Mode: The value that appears most frequently in a dataset is the mode. One mode (unimodal), several modes (multimodal), or no mode (if all values occur with the same frequency) can all exist in a dataset.
Standard deviation: The spread or dispersion of data points in a dataset is measured by the standard deviation. It quantifies the variance between different data points.
Q.7 What is the normal distribution and standard normal distribution?
The normal distribution, also known as the Gaussian distribution or bell curve, is a continuous probability distribution that is characterized by its symmetric bell-shaped curve. The normal distribution is defined by two parameters: the mean (μ) and the standard deviation (σ). The mean determines the center of the distribution, and the standard deviation determines the spread or dispersion of the distribution. The distribution is symmetric around its mean, and the bell curve is centered at the mean. The probabilities for values that are further from the mean taper off equally in both directions. Similar rarity applies to extreme values in the two tails of the distribution. Not all symmetrical distributions are normal, even though the normal distribution is symmetrical.
The standard normal distribution, also known as the Z distribution, is a special case of the normal distribution where the mean (μ) is 0 and the standard deviation (σ) is 1. It is a standardized form of the normal distribution, allowing for easy comparison of scores or observations from different normal distributions.
Q.8 What is SQL, and what does it stand for?
SQL stands for Structured Query Language.It is a specialized programming language used for managing and manipulating relational databases. It is designed for tasks related to database management, data retrieval, data manipulation, and data definition.
Q.9 Explain the differences between SQL and NoSQL databases.
Both SQL (Structured Query Language) and NoSQL (Not Only SQL) databases, differ in their data structures, schema, query languages, and use cases. The following are the main variations between SQL and NoSQL databases.
|
SQL databases are relational databases, they organise and store data using a structured schema with tables, rows, and columns.
| NoSQL databases use a number of different types of data models, such as document-based (like JSON and BSON), key-value pairs, column families, and graphs.
|
SQL databases have a set schema, thus before inserting data, we must establish the structure of our data.The schema may need to be changed, which might be a difficult process.
| NoSQL databases frequently employ a dynamic or schema-less approach, enabling you to insert data without first creating a predetermined schema.
|
SQL is a strong and standardised query language that is used by SQL databases. Joins, aggregations, and subqueries are only a few of the complicated processes supported by SQL queries.
| The query languages or APIs used by NoSQL databases are frequently tailored to the data model.
|
Q.10 What are the primary SQL database management systems (DBMS)?
Relational database systems, both open source and commercial, are the main SQL (Structured Query Language) database management systems (DBMS), which are widely used for managing and processing structured data. Some of the most popular SQL database management systems are listed below:
- MySQL
- Microsoft SQL Server
- SQLite
- PostgreSQL
- Oracle Database
- Amazon RDS
Q.11 What is the ER model in SQL?
The structure and relationships between the data entities in a database are represented by the Entity-Relationship (ER) model, a conceptual framework used in database architecture. The ER model is frequently used in conjunction with SQL for creating the structure of relational databases even though it is not a component of the SQL language itself.
Q.12 What is data transformation?
The process of transforming data from one structure, format, or representation into another is referred to as data transformation. In order to make the data more suited for a given goal, such as analysis, visualisation, reporting, or storage, this procedure may involve a variety of actions and changes to the data. Data integration, cleansing, and analysis depend heavily on data transformation, which is a common stage in data preparation and processing pipelines.
Q.13 What are the main components of a SQL query?
A relational database’s data can be retrieved, modified, or managed via a SQL (Structured Query Language) query. The operation of a SQL query is defined by a number of essential components, each of which serves a different function.
- SELECT
- FROM
- WHERE
- GROUP BY
- HAVING
- ORDER BY
- LIMIT
- JOIN
Q.14 What is a primary key?
A relational database table’s main key, also known as a primary keyword, is a column that is unique for each record. It is a distinctive identifier.The primary key of a relational database must be unique. Every row of data must have a primary key value and none of the rows can be null.
Q.15 What is the purpose of the GROUP BY clause, and how is it used?
In SQL, the GROUP BY clause is used to create summary rows out of rows that have the same values in a set of specified columns. In order to do computations on groups of rows as opposed to individual rows, it is frequently used in conjunction with aggregate functions like SUM, COUNT, AVG, MAX, or MIN. we may produce summary reports and perform more in-depth data analysis using the GROUP BY clause.
Q.16 What is the WHERE clause used for, and how is it used to filter data?
In SQL, the WHERE clause is used to filter rows from a table or result set according to predetermined criteria. It enables us to pick only the rows that satisfy particular requirements or follow a pattern. A key element of SQL queries, the WHERE clause is frequently used for data retrieval and manipulation.
Q.17 How do you retrieve distinct values from a column in SQL?
Using the DISTINCT keyword in combination with the SELECT command, we can extract distinct values from a column in SQL. By filtering out duplicate values and returning only unique values from the specified column, the DISTINCT keyword is used.
Q.18 What is the HAVING clause?
To filter query results depending on the output of aggregation functions, the HAVING clause, a SQL clause, is used along with the GROUP BY clause. The HAVING clause filters groups of rows after they have been grouped by one or more columns, in contrast to the WHERE clause, which filters rows before they are grouped.
Q.19 How do you handle missing or NULL values in a database table?
Missing or NULL values can arise due to various reasons, such as incomplete data entry, optional fields, or data extraction processes.
- Replace NULL with Placeholder Values
- Handle NULL Values in Queries
- Use Default Values
Q.20 What is the difference between supervised and unsupervised machine learning?
The difference between Supervised Learning and Unsupervised Learning are as follow:
|
Supervised learning refers to that part of machine learning where we know what the target variable is and it is labeled.
| Unsupervised Learning is used when we do not have labeled data and we are not sure about our target variable
|
The objective of supervised learning is to predict an outcome or classify the data
| The objective here is to discover patterns among the features of the dataset and group similar features together
|
Some of the algorithm types are:
- Regression (Linear, Logistic, etc.)
- Classification (Decision Tree Classifier, Support Vector Classifier, etc.)
| Some of the algorithms are :
- Dimensionality reduction (Principle Component Analysis, etc.)
- Clustering (KMeans, DBSCAN, etc.)
|
Supervised learning uses evaluation metrics like:
- Mean Squared Error
- Accuracy
| Unsupervised Learning uses evaluation metrics like:
- Silhouette
- Inertia
|
Predictive modeling, Spam detection
| Anomaly detection, Customer segmentation
|
Q.21 What is linear regression, and What are the different assumptions of linear regression algorithms?
Linear Regression – It is type of Supervised Learning where we compute a linear relationship between the predictor and response variable. It is based on the linear equation concept given by:
[Tex]\hat{y} = \beta_1x+\beta_o
[/Tex], where
- [Tex]\hat{y}
[/Tex] = response / dependent variable
- [Tex]\beta_1
[/Tex] = slope of the linear regression
- [Tex]\beta_o
[/Tex] = intercept for linear regression
- [Tex]x
[/Tex] = predictor / independent variable(s)
There are 4 assumptions we make about a Linear regression problem:
- Linear relationship : This assumes that there is a linear relationship between predictor and response variable. This means that, which changing values of predictor variable, the response variable changes linearly (either increases or decreases).
- Normality : This assumes that the dataset is normally distributed, i.e., the data is symmetric about the mean of the dataset.
- Independence : The features are independent of each other, there is no correlation among the features/predictor variables of the dataset.
- Homoscedasticity : This assumes that the dataset has equal variance for all the predictor variables. This means that the amount of independent variables have no effect on the variance of data.
Q.22 Logistic regression is a classification technique, why its name is regressions, not logistic classifications?
While logistic regression is used for classification, it still maintains a regression structure underneath. The key idea is to model the probability of an event occurring (e.g., class 1 in binary classification) using a linear combination of features, and then apply a logistic (Sigmoid) function to transform this linear combination into a probability between 0 and 1. This transformation is what makes it suitable for classification tasks.
In essence, while logistic regression is indeed used for classification, it retains the mathematical and structural characteristics of a regression model, hence the name.
Q.23 What is the logistic function (sigmoid function) in logistic regression?
Sigmoid Function: It is a mathematical function which is characterized by its S- shape curve. Sigmoid functions have the tendency to squash a data point to lie within 0 and 1. This is why it is also called Squashing function, which is given as:

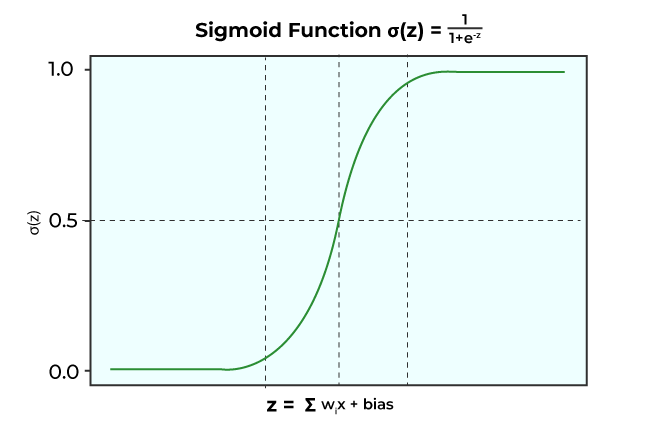
Some of the properties of Sigmoid function is:
Q.24 What is overfitting and how can be overcome this?
Overfitting refers to the result of analysis of a dataset which fits so closely with training data that it fails to generalize with unseen/future data. This happens when the model is trained with noisy data which causes it to learn the noisy features from the training as well.
To avoid Overfitting and overcome this problem in machine learning, one can follow the following rules:
- Feature selection : Sometimes the training data has too many features which might not be necessary for our problem statement. In that case, we use only the necessary features that serve our purpose
- Cross Validation : This technique is a very powerful method to overcome overfitting. In this, the training dataset is divided into a set of mini training batches, which are used to tune the model.
- Regularization : Regularization is the technique to supplement the loss with a penalty term so as to reduce overfitting. This penalty term regulates the overall loss function, thus creating a well trained model.
- Ensemble models : These models learn the features and combine the results from different training models into a single prediction.
Q.25 What is a support vector machine (SVM), and what are its key components?
Support Vector machines are a type of Supervised algorithm which can be used for both Regression and Classification problems. In SVMs, the main goal is to find a hyperplane which will be used to segregate different data points into classes. Any new data point will be classified based on this defined hyperplane.
Support Vector machines are highly effective when dealing with high dimensionality space and can handle non linear data very well. But if the number of features are greater than number of data samples, it is susceptible to overfitting.
The key components of SVM are:
- Kernels Function: It is a mapping function used for data points to convert it into high dimensionality feature space.
- Hyperplane: It is the decision boundary which is used to differentiate between the classes of data points.
- Margin: It is the distance between Support Vector and Hyperplane
- C: It is a regularization parameter which is used for margin maximization and misclassification minimization.
Q.26 Explain the k-nearest neighbors (KNN) algorithm.
The k-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) algorithm is a simple and versatile supervised machine learning algorithm used for both classification and regression tasks. KNN makes predictions by memorizing the data points rather than building a model about it. This is why it is also called “lazy learner” or “memory based” model too.
KNN relies on the principle that similar data points tend to belong to the same class or have similar target values. This means that, In the training phase, KNN stores the entire dataset consisting of feature vectors and their corresponding class labels (for classification) or target values (for regression). It then calculates the distances between that point and all the points in the training dataset. (commonly used distance metrics are Euclidean distance and Manhattan distance).
(Note : Choosing an appropriate value for k is crucial. A small k may result in noisy predictions, while a large k can smooth out the decision boundaries. The choice of distance metric and feature scaling also impact KNN’s performance.)
Q.27 What is the Naïve Bayes algorithm, what are the different assumptions of Naïve Bayes?
The Naïve Bayes algorithm is a probabilistic classification algorithm based on Bayes’ theorem with a “naïve” assumption of feature independence within each class. It is commonly used for both binary and multi-class classification tasks, particularly in situations where simplicity, speed, and efficiency are essential.
The main assumptions that Naïve Bayes theorem makes are:
- Feature independence – It assumes that the features involved in Naïve Bayes algorithm are conditionally independent, i.e., the presence/ absence of one feature does not affect any other feature
- Equality – This assumes that the features are equal in terms of importance (or weight).
- Normality – It assumes that the feature distribution is Normal in nature, i.e., the data is distributed equally around its mean.
Q.28 What are decision trees, and how do they work?
Decision trees are a popular machine learning algorithm used for both classification and regression tasks. They work by creating a tree-like structure of decisions based on input features to make predictions or decisions. Lets dive into its core concepts and how they work briefly:
- Decision trees consist of nodes and edges.
- The tree starts with a root node and branches into internal nodes that represent features or attributes.
- These nodes contain decision rules that split the data into subsets.
- Edges connect nodes and indicate the possible decisions or outcomes.
- Leaf nodes represent the final predictions or decisions.
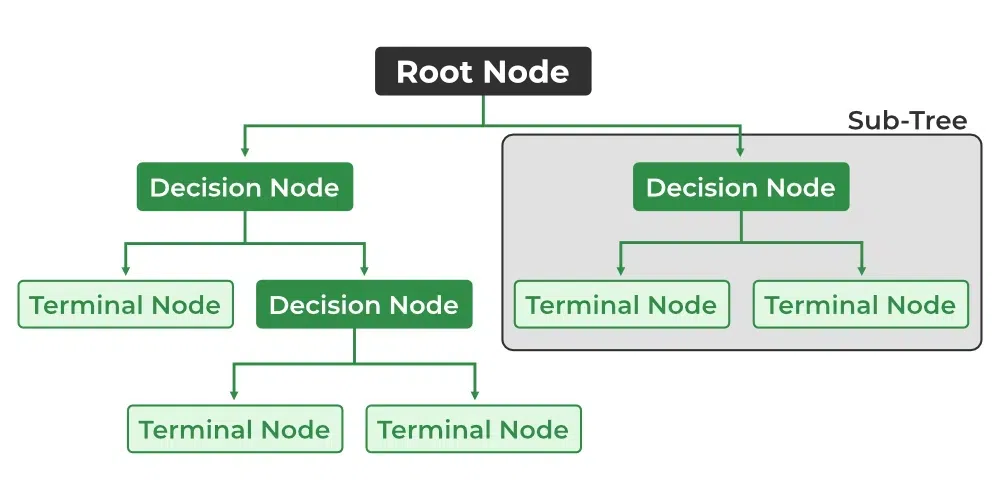
The objective is to increase data homogeneity, which is often measured using standards like mean squared error (for regression) or Gini impurity (for classification). Decision trees can handle a variety of attributes and can effectively capture complex data relationships. They can, however, overfit, especially when deep or complex. To reduce overfitting, strategies like pruning and restricting tree depth are applied.
Q.29 Explain the concepts of entropy and information gain in decision trees.
Entropy: Entropy is the measure of randomness. In terms of Machine learning, Entropy can be defined as the measure of randomness or impurity in our dataset. It is given as:
 , where
, where
 = probability of an event “i”.
= probability of an event “i”.
Information gain: It is defined as the change in the entropy of a feature given that there’s an additional information about that feature. If there are more than one features involved in Decision tree split, then the weighted average of entropies of the additional features is taken.
Information gain =  , where
, where
E = Entropy
Q.30 What is the difference between the bagging and boosting model?
|
Bagging, or Bootstrap aggregating, is an ensemble modelling method where predictions from different models are combined together to give the aggregated result
| Boosting method is where multiple weak learners are used together to get a stronger model with more robust predictions.
|
This is used when dealing with models that have high variance (overfitting).
| This is used when dealing with models with high bias (underfitting) and variance as well.
|
This is more robust due to averaging and this makes it less sensitive
| It is more sensitive to presence of outliers and that makes it a bit less robust as compared to bagging models
|
The models are run in parallel and are typically independent
| The models are run in sequential method where the base model is dependent.
|
Random Forest, Bagged Decision Trees
| AdaBoost, Gradient Boosting, XGBoost
|
Q.31 Describe random forests and their advantages over single-decision trees.
Random Forests are an ensemble learning technique that combines multiple decision trees to improve predictive accuracy and reduce overfitting. The advantages it has over single decision trees are:
- Improved Generalization: Single decision trees are prone to overfitting, especially when they become deep and complex. Random Forests mitigate this issue by averaging predictions from multiple trees, resulting in a more generalized model that performs better on unseen data
- Better Handling of High-Dimensional Data : Random Forests are effective at handling datasets with a large number of features. They select a random subset of features for each tree, which can improve the performance when there are many irrelevant or noisy features
- Robustness to Outliers: Random Forests are more robust to outliers because they combine predictions from multiple trees, which can better handle extreme cases
Q.32 What is K-Means, and how will it work?
K-Means is an unsupervised machine learning algorithm used for clustering or grouping similar data points together. It aims to partition a dataset into K clusters, where each cluster represents a group of data points that are close to each other in terms of some similarity measure. The working of K-means is as follow:
- Choose the number of clusters K
- For each data point in the dataset, calculate its distance to each of the K centroids and then assign each data point to the cluster whose centroid is closest to it
- Recalculate the centroids of the K clusters based on the current assignment of data points.
- Repeat the above steps until a group of clusters are formed.
Q.33 What is a confusion matrix? Explain with an example.
Confusion matrix is a table used to evaluate the performance of a classification model by presenting a comprehensive view of the model’s predictions compared to the actual class labels. It provides valuable information for assessing the model’s accuracy, precision, recall, and other performance metrics in a binary or multi-class classification problem.
A famous example demonstration would be Cancer Confusion matrix:
|
Cancer
| Not Cancer
|
Cancer
| True Positive (TP)
| False Positive (FP)
|
Not Cancer
| False Negative (FN)
| True Negative (TN)
|
- TP (True Positive) = The number of instances correctly predicted as the positive class
- TN (True Negative) = The number of instances correctly predicted as the negative class
- FP (False Positive) = The number of instances incorrectly predicted as the positive class
- FN (False Negative) = The number of instances incorrectly predicted as the negative class
Q.34 What is a classification report and explain the parameters used to interpret the result of classification tasks with an example.
A classification report is a summary of the performance of a classification model, providing various metrics that help assess the quality of the model’s predictions on a classification task.
The parameters used in a classification report typically include:
- Precision: Precision is the ratio of true positive predictions to the total predicted positives. It measures the accuracy of positive predictions made by the model.
Precision = TP/(TP+FP)
- Recall (Sensitivity or True Positive Rate): Recall is the ratio of true positive predictions to the total actual positives. It measures the model’s ability to identify all positive instances correctly.
Recall = TP / (TP + FN)
- Accuracy: Accuracy is the ratio of correctly predicted instances (both true positives and true negatives) to the total number of instances. It measures the overall correctness of the model’s predictions.
Accuracy = (TP + TN) / (TP + TN + FP + FN)
- F1-Score: The F1-Score is the harmonic mean of precision and recall. It provides a balanced measure of both precision and recall and is particularly useful when dealing with imbalanced datasets.
F1-Score = 2 * (Precision * Recall) / (Precision + Recall)
where,
- TP = True Positive
- TN = True Negative
- FP = False Positive
- FN = False Negative
Q.35 Explain the uniform distribution.
A fundamental probability distribution in statistics is the uniform distribution, commonly referred to as the rectangle distribution. A constant probability density function (PDF) across a limited range characterises it. In simpler terms, in a uniform distribution, every value within a specified range has an equal chance of occurring.
Q.36 Describe the Bernoulli distribution.
A discrete probability distribution, the Bernoulli distribution is focused on discrete random variables. The number of heads you obtain while tossing three coins at once or the number of pupils in a class are examples of discrete random variables that have a finite or countable number of potential values.
Q.37 What is the binomial distribution?
The binomial distribution is a discrete probability distribution that describes the number of successes in a fixed number of independent Bernoulli trials, where each trial has only two possible outcomes: success or failure. The outcomes are often referred to as “success” and “failure,” but they can represent any dichotomous outcome, such as heads or tails, yes or no, or defective or non-defective.
The fundamental presumptions of a binomial distribution are that each trial has exactly one possible outcome, each trial has an equal chance of success, and each trial is either independent of the others or mutually exclusive.
Q.38 Explain the exponential distribution and where it’s commonly used.
The probability distribution of the amount of time between events in the Poisson point process is known as the exponential distribution. The gamma distribution is thought of as a particular instance of the exponential distribution. Additionally, the geometric distribution’s continuous analogue is the exponential distribution.
Common applications of the exponential distribution include:
- Reliability Engineering
- Queueing Theory
- Telecommunications
- Finance
- Natural Phenomena
- Survival Analysis
Q.39 Describe the Poisson distribution and its characteristics.
The Poisson distribution is a probability distribution that describes the number of events that occur within a fixed interval of time or space when the events happen at a constant mean rate and are independent of the time since the last event.
Key characteristics of the Poisson distribution include:
- Discreteness: The Poisson distribution is used to model the number of discrete events that occur within a fixed interval.
- Constant Mean Rate: The events occur at a constant mean rate per unit of time or space.
- Independence: The occurrences of events are assumed to be independent of each other. The probability of multiple events occurring in a given interval is calculated based on the assumption of independence.
Q40. Explain the t-distribution and its relationship with the normal distribution.
The t-distribution, also known as the Student’s t-distribution, is used in statistics for inferences about population means when the sample size is small and the population standard deviation is unknown. The shape of the t-distribution is similar to the normal distribution, but it has heavier tails.
Relationship between T-Distribution and Normal Distribution: The t-distribution converges to the normal distribution as the degrees of freedom increase. In fact, when the degrees of freedom become very large, the t-distribution approaches the standard normal distribution (normal distribution with mean 0 and standard deviation 1). This is a result of the Central Limit Theorem.
Q.41 Describe the chi-squared distribution.
The chi-squared distribution is a continuous probability distribution that arises in statistics and probability theory. It is commonly denoted as χ2 (chi-squared) and is associated with degrees of freedom. The chi-squared distribution is particularly used to model the distribution of the sum of squared independent standard normal random variables.It is also used to determine if data series are independent, the goodness of fit of a data distribution, and the level of confidence in the variance and standard deviation of a random variable with a normal distribution.
Q.42 What is the difference between z-test, F-test, and t-test?
The z-test, t-test, and F-test are all statistical hypothesis tests used in different situations and for different purposes. Here’s a overview of each test and the key differences between them.
|
When we want to compare a sample mean to a known population mean and we know the population standard deviation, we use the z-test.
| When we want to compare a sample mean to a known or assumed population mean but don’t know what the population standard deviation is we use the t-test.
| The F-test is used to compare the variances of two or more samples. It is commonly used in analysis of variance (ANOVA) and regression analysis.
|
When we dealing with large sample sizes or when we known the population standard deviation it is most frequently used.
| The t-test follows a t-distribution, which has different shapes depending on the degrees of freedom.
| The two-sample F-test, which analyses the variances of two independent samples, is the most popular of the F-test’s variants.
|
The z-test follows a standard normal distribution when certain assumptions are met.
| The sample standard deviation (s) determines the test statistic for the t-test.
| One set of degrees of freedom corresponds to each sample’s degrees of freedom in the F-distribution.
|
In summary, the choice between a z-test, t-test, or F-test depends on the specific research question and the characteristics of the data.
Q.43 What is the central limit theorem, and why is it significant in statistics?
The Central Limit Theorem states that, regardless of the shape of the population distribution, the distribution of the sample means approaches a normal distribution as the sample size increases.This is true even if the population distribution is not normal. The larger the sample size, the closer the sampling distribution of the sample mean will be to a normal distribution.
Q.44 Describe the process of hypothesis testing, including null and alternative hypotheses.
Hypothesis testing is a statistical method used to make inferences about population parameters based on sample data.It is a systematic way of evaluating statements or hypotheses about a population using observed sample data.To identify which statement is best supported by the sample data, it compares two statements about a population that are mutually exclusive.
- Null hypothesis(H0): The null hypothesis (H0) in statistics is the default assumption or assertion that there is no association between any two measured cases or any two groups. In other words, it is a fundamental assumption or one that is founded on knowledge of the problem.
- Alternative hypothesis(H1): The alternative hypothesis, or H1, is the null-hypothesis-rejecting hypothesis that is utilised in hypothesis testing.
Q.45 How do you calculate a confidence interval, and what does it represent?
A confidence interval (CI) is a statistical range or interval estimate for a population parameter, such as the population mean or population proportion, based on sample data. to calculate confidence interval these are the following steps.
- Collect Sample Data
- Choose a Confidence Level
- Select the Appropriate Statistical Method
- Calculate the Margin of Error (MOE)
- Calculate the Confidence Interval
- Interpret the Confidence Interval
Confidence interval represents a range of values within which we believe, with a specified level of confidence (e.g., 95%), that the true population parameter lies.
Q.46 What is a p-value in Statistics?
The term “p-value,” which stands for “probability value,” is a key one in statistics and hypothesis testing. It measures the evidence contradicting a null hypothesis and aids in determining whether a statistical test’s findings are statistically significant. Here is a definition of a p-value and how it is used in hypothesis testing.
Q.47 Explain Type I and Type II errors in hypothesis testing.
Rejecting a null hypothesis that is actually true in the population results in a type I error (false-positive); failing to reject a null hypothesis that is actually untrue in the population results in a type II error (false-negative).
type I and type II mistakes cannot be completely avoided, the investigator can lessen their risk by increasing the sample size (the less likely it is that the sample will significantly differ from the population).
Q.48 What is the significance level (alpha) in hypothesis testing?
A crucial metric in hypothesis testing that establishes the bar for judging whether the outcomes of a statistical test are statistically significant is the significance level, which is sometimes indicated as (alpha). It reflects the greatest possible chance of committing a Type I error, or mistakenly rejecting a valid null hypothesis.
The significance level in hypothesis testing.
- Setting the Significance Level
- Interpreting the Significance Level
- Hypothesis Testing Using Significance Level
- Choice of Significance Level
Q.49 How can you calculate the correlation coefficient between two variables?
The degree and direction of the linear link between two variables are quantified by the correlation coefficient. The Pearson correlation coefficient is the most widely used method for determining the correlation coefficient. The Pearson correlation coefficient can be calculated as follows.
- Collect Data
- Calculate the Means
- Calculate the Covariance
- Calculate the Standard Deviations
- Calculate the Pearson Correlation Coefficient (r)
- Interpret the Correlation Coefficient.
Q.50 What is covariance, and how is it related to correlation?
Both covariance and correlation are statistical metrics that show how two variables are related to one another.However, they serve slightly different purposes and have different interpretations.
- Covariance :Covariance measures the degree to which two variables change together. It expresses how much the values of one variable tend to rise or fall in relation to changes in the other variable.
- Correlation : A standardised method for measuring the strength and direction of a linear relationship between two variables is correlation. It multiplies the standard deviations of the two variables to scale the covariance.
Q.51 Explain how to perform a hypothesis test for comparing two population means.
When comparing two population means, a hypothesis test is used to determine whether there is sufficient statistical support to claim that the means of the two distinct populations differ significantly. Tests we can commonly use for include “paired t-test” or “two -sample t test”. The general procedures for carrying out such a test are as follows.
- Formulate Hypotheses
- Choose the Significance Level
- Collect Data
- Define Test Statistic
- Draw a Conclusion
- Final Results
Q.52 Explain the concept of normalization in database design.
By minimising data duplication and enhancing data integrity, normalisation is a method in database architecture that aids in the effective organisation of data. It include dividing a big, complicated table into smaller, associated tables while making sure that connections between data elements are preserved. The basic objective of normalisation is to reduce data anomalies, which can happen when data is stored in an unorganised way and include insertion, update, and deletion anomalies.
Q.53 What is database normalization?
Database denormalization is the process of intentionally introducing redundancy into a relational database by merging tables or incorporating redundant data to enhance query performance. Unlike normalization, which minimizes data redundancy for consistency, denormalization prioritizes query speed. By reducing the number of joins required, denormalization can improve read performance for complex queries. However, it may lead to data inconsistencies and increased maintenance complexity. Denormalization is often employed in scenarios where read-intensive operations outweigh the importance of maintaining a fully normalized database structure. Careful consideration and trade-offs are essential to strike a balance between performance and data integrity.
Q.54 Define different types of SQL functions.
SQL functions can be categorized into several types based on their functionality.
- Scalar Functions
- Aggregate Functions
- Window Functions
- Table-Valued Functions
- System Functions
- User-Defined Functions
- Conversion Functions
- Conditional Functions
Q.55 Explain the difference between INNER JOIN and LEFT JOIN.
INNER JOIN and LEFT JOIN are two types of SQL JOIN operations used to combine data from multiple tables in a relational database. Here are the some main differences between them.
|
Only rows with a match in the designated columns between the two tables being connected are returned by an INNER JOIN.
| LEFT JOIN returns all rows from the left table and the matching rows from the right table.
|
A row is not included in the result set if there is no match for it in either of the tables.
| Columns from the right table’s rows are returned with NULL values if there is no match for that row.
|
When we want to retrieve data from both tables depending on a specific criterion, INNER JOIN can be helpful.
| It makes sure that every row from the left table appears in the final product, even if there are no matches for that row in the right table.
|
Q.56 What is a subquery, and how can it be used in SQL?
A subquery is a query that is nested within another SQL query, also referred to as an inner query or nested query. On the basis of the outcomes of another query, we can use it to get data from one or more tables. SQL’s subqueries capability is employed for a variety of tasks, including data retrieval, computations, and filtering.
Q.57 How do you perform mathematical calculations in SQL queries?
In SQL, we can perform mathematical calculations in queries using arithmetic operators and functions. Here are some common methods for performing mathematical calculations.
- Arithmetic Operators
- Mathematical Functions
- Aggregate Functions
- Custom Expressions
Q.58 What is the purpose of the CASE statement in SQL?
The SQL CASE statement is a flexible conditional expression that may be used to implement conditional logic inside of a query. we can specify various actions or values based on predetermined criteria.
Q.59 What is the difference between a database and a data warehouse?
Database: Consistency and real-time data processing are prioritised, and they are optimised for storing, retrieving, and managing structured data. Databases are frequently used for administrative functions like order processing, inventory control, and customer interactions.
Data Warehouse: Data warehouses are made for processing analytical data. They are designed to facilitate sophisticated querying and reporting by storing and processing massive amounts of historical data from various sources. Business intelligence, data analysis, and decision-making all employ data warehouses.
Q.60 What is regularization in machine learning, State the differences between L1 and L2 regularization
Regularization: Regularization is the technique to restrict the model overfitting during training by inducing a penalty to the loss. The penalty imposed on the loss function is added so that the complexity of the model can be controlled, thus overcoming the issue of overfitting in the model.
The following are the differences between L1 and L2 regularization:
|
L1 regularization is the technique where the induced penalty term changes some of the terms to be exactly zero
| L2 regularization is the technique where the induced penalty term changes some of the terms to be as near to zero as possible.
|
Selects a subset of most important ones while eliminating less important ones.
| Selects all the features but assigns less weights to less important features.
|

where,
L1 = Lasso Loss function
 = Model loss = Model loss
 = regularization controlling parameter = regularization controlling parameter
w = weights of the model
| 
where,
L2 = Ridge Loss function
 = Model loss = Model loss
 = regularization controlling parameter = regularization controlling parameter
w = weights of the model
|
Sensitive to outliers and noisy data as it can eliminate them
| More robust to the presence of Outliers and noisy data
|
Computationally more expensive
| Computationally less expensive.
|
Q.61 Explain the concepts of bias-variance trade-off in machine learning.
When creating predictive models, the bias-variance trade-off is a key concept in machine learning that deals with finding the right balance between two sources of error, bias and variance. It plays a crucial role in model selection and understanding the generalization performance of a machine learning algorithm. Here’s an explanation of these concepts:
- Bias:Bias is simply described as the model’s inability to forecast the real value due of some difference or inaccuracy. These differences between actual or expected values and the predicted values are known as error or bias error or error due to bias.
- Variance: Variance is a measure of data dispersion from its mean location. In machine learning, variance is the amount by which a predictive model’s performance differs when trained on different subsets of the training data. More specifically, variance is the model’s variability in terms of how sensitive it is to another subset of the training dataset, i.e. how much it can adapt on the new subset of the training dataset.
|
Best fit (Ideal Scenario )
| Underfitting
|
Overfitting
| Not capture the underlying patterns
(Worst Case)
|
As a Data Science Professional, Our focus should be to achieve the the best fit model i.e Low Bias and Low Variance. A model with low bias and low variance suggests that it can capture the underlying patterns in the data (low bias) and is not overly sensitive to changes in the training data (low variance). This is the perfect circumstance for a machine learning model, since it can generalize effectively to new, previously unknown data and deliver consistent and accurate predictions. However, in practice, this is not achievable.
.png)
If the algorithm is too simplified (hypothesis with linear equation), it may be subject to high bias and low variance, making it error-prone. If algorithms fit too complicated a hypothesis (hypothesis with a high degree equation), it may have a large variance and a low bias. In the latter case, the new entries will underperform. There is, however, something in between these two situations called as a Trade-off or Bias Variance Trade-off. So, that An algorithm can’t be more complex and less complex at the same time.
Q.62 How do we choose the appropriate kernel function in SVM?
A kernel function is responsible for converting the original data points into a high dimensionality feature space. Choosing the appropriate kernel function in a Support Vector Machine is a crucial step, as it determines how well the SVM can capture the underlying patterns in your data. Below mentioned are some of the ways to choose the suitable kernel function:
- If the dataset exhibits linear relationship
In this case, we should use Linear Kernel function. It is simple, computationally efficient and less prone to overfitting. For example, text classification, sentiment analysis, etc.
- If the dataset requires probabilistic approach
The sigmoid kernel is suitable when the data resembles a sigmoid function or when you have prior knowledge suggesting this shape. For example, Risk assessment, Financial applications, etc.
- If the dataset is Simple Non Linear in nature
In this case, use a Polynomial Kernel Function. Polynomial functions are useful when we are trying to capture moderate level of non linearity. For example, Image and Speech Recognition, etc.
- If the dataset is Highly Non-Linear in Nature/ we do not know about the underlying relationship
In that case, a Radial basis function is the best choice. RBF kernel can handle highly complex dataset and is useful when you’re unsure about the data’s underlying distribution. For example, Financial forecasting, bioinformatics, etc.
Q.63 How does Naïve Bayes handle categorical and continuous features?
Naive Bayes is probabilistic approach which assumes that the features are independent of each other. It calculates probabilities associated with each class label based on the observed frequencies of feature values within each class in the training data. This is done by finding the conditional probability of Feature given a class. (i.e., P(feature | class)). To make predictions on categorical data, Naive Bayes calculates the posterior probability of each class given the observed feature values and selects the class with the highest probability as the predicted class label. This is called as “maximum likelihood” estimation.
Q.64 What is Laplace smoothing (add-one smoothing) and why is it used in Naïve Bayes?
In Naïve Bayes, the conditional probability of an event given a class label is determined as P(event| class). When using this in a classification problem (let’s say a text classification), there could a word which did not appear in the particular class. In those cases, the probability of feature given a class label will be zero. This could create a big problem when getting predictions out of the training data.
To overcome this problem, we use Laplace smoothing. Laplace smoothing addresses the zero probability problem by adding a small constant (usually 1) to the count of each feature in each class and to the total count of features in each class. Without smoothing, if any feature is missing in a class, the probability of that class given the features becomes zero, making the classifier overly confident and potentially leading to incorrect classifications
Q.65 What are imbalanced datasets and how can we handle them?
Imbalanced datasets are datasets in which the distribution of class labels (or target values) is heavily skewed, meaning that one class has significantly more instances than any other class. Imbalanced datasets pose challenges because models trained on such data can have a bias toward the majority class, leading to poor performance on the minority class, which is often of greater interest. This will lead to the model not generalizing well on the unseen data.
To handle imbalanced datasets, we can approach the following methods:
- Resampling (Method of either increasing or decreasing the number of samples):
- Up-sampling: In this case, we can increase the classes for minority by either sampling without replacement or generating synthetic examples. Some of the popular examples are SMOTE (Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique), etc.
- Down-sampling: Another case would be to randomly cut down the majority class such that it is comparable to minority class.
- Ensemble methods (using models which are capable of handling imbalanced dataset inherently:
- Bagging : Techniques like Random Forests, which can mitigate the impact of class imbalance by constructing multiple decision trees from bootstrapped samples
- Boosting: Algorithms like AdaBoost and XGBoost can give more importance to misclassified minority class examples in each iteration, improving their representation in the final model
Q.66 What are outliers in the dataset and how can we detect and remove them?
An Outlier is a data point that is significantly different from other data points. Usually, Outliers are present in the extremes of the distribution and stand out as compared to their out data point counterparts.
For detecting Outliers we can use the following approaches:
- Visual inspection: This is the easiest way which involves plotting the data points into scatter plot/box plot, etc.
- statistics: By using measure of central tendency, we can determine if a data point falls significantly far from its mean, median, etc. making it a potential outlier.
- Z-score: if a data point has very high Z-score, it can be identified as Outlier
For removing the outliers, we can use the following:
- Removal of outliers manually
- Doing transformations like applying logarithmic transformation or square rooting the outlier
- Performing imputations wherein the outliers are replaced with different values like mean, median, mode, etc.
Q.67 What is the curse of dimensionality And How can we overcome this?
When dealing with a dataset that has high dimensionality (high number of features), we are often encountered with various issues and problems. Some of the issues faced while dealing with dimensionality dataset are listed below:
- Computational expense: The biggest problem with handling a dataset with vast number of features is that it takes a long time to process and train the model on it. This can lead to wastage of both time and monetary resources.
- Data sparsity: Many times data points are far from each other (high sparsity). This makes it harder to find the underlying patterns between features and can be a hinderance in proper analysis
- Visualising issues and overfitting: It is rather easy to visualize 2d and 3d data. But beyond this order, it is difficult to properly visualize our data. Furthermore, more data features can be correlated and provide misleading information to the model training and cause overfitting.
These issues are what are generally termed as “Curse of Dimensionality”.
To overcome this, we can follow different approaches – some of which are mentioned below:
- Feature Selection: Many a times, not all the features are necessary. It is the user’s job to select out the features that would be necessary in solving a given problem statement.
- Feature engineering: Sometimes, we may need a feature that is the combination of many other features. This method can, in general, reduces the features count in the dataset.
- Dimensionality Reduction techniques: These techniques reduce the number of features in a dataset while preserving as much useful information as possible. Some of the famous Dimensionality reduction techniques are: Principle component analysis (PCA), t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding (t-SNE), etc.
- Regularization: Some regularization techniques like L1 and L2 regularizations are useful when deciding the impact each feature has on the model training.
Q.68 How does the random forest algorithm handle feature selection?
Mentioned below is how Random forest handles feature selection
- When creating individual trees in the Random Forest ensemble, a subset of features is assigned to each tree which is called Feature Bagging. Feature Bagging introduces randomness and diversity among the trees.
- After the training, the features are assigned a “importance score” based on how well those features performed by reducing the error of the model. Features that consistently contribute to improving the model’s accuracy across multiple trees are deemed more important
- Then the features are ranked based on their importance scores. Features with higher importance scores are considered more influential in making predictions.
Q.69 What is feature engineering? Explain the different feature engineering methods.
Feature Engineering: It can be defined as a method of preprocessing of data for better analysis purpose which involves different steps like selection, transformation, deletion of features to suit our problem at hand. Feature Engineering is a useful tool which can be used for:
- Improving the model’s performance and Data interpretability
- Reduce computational costs
- Include hidden patterns for elevated Analysis results.
Some of the different methods of doing feature engineering are mentioned below:
- Principle Component Analysis (PCA) : It identifies orthogonal axes (principal components) in the data that capture the maximum variance, thereby reducing the data features.
- Encoding – It is a technique of converting the data to be represented a numbers with some meaning behind it. It can be done in two ways :
- One-Hot Encoding – When we need to encode Nominal Categorical Data
- Label Encoding – When we need to encode Ordinal Categorical Data
- Feature Transformation: Sometimes, we can create new columns essential for better modelling just by combining or modifying one or more columns.
Q.70 How we will deal with the categorical text values in machine learning?
Often times, we are encountered with data that has Categorical text values. For example, male/female, first-class/second-class/third-class, etc. These Categorical text values can be divided into two types and based on that we deal with them as follows:
- If it is Categorical Nominal Data: If the data does not have any hidden order associated with it (e.g., male/female), we perform One-Hot encoding on the data to convert it into binary sequence of digits
- If it is Categorical Ordinal Data : When there is a pattern associated with the text data, we use Label encoding. In this, the numerical conversion is done based on the order of the text data. (e.g., Elementary/ Middle/ High/ Graduate,etc.)
Q.71 What is DBSCAN and How we will use it?
Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise (DBSCAN), is a density-based clustering algorithm used for grouping together data points that are close to each other in high-density regions and labeling data points in low-density regions as outliers or noise. Here is how it works:
- For each data point in the dataset, DBSCAN calculates the distance between that point and all other data points
- DBSCAN identifies dense regions by connecting core points that are within each other’s predefined threshold (eps) neighborhood.
- DBSCAN forms clusters by grouping together data points that are density-reachable from one another.
Q.72 How does the EM (Expectation-Maximization) algorithm work in clustering?
The Expectation-Maximization (EM) algorithm is a probabilistic approach used for clustering data when dealing with mixture models. EM is commonly used when the true cluster assignments are not known and when there is uncertainty about which cluster a data point belongs to. Here is how it works:
- First, the number of clusters K to be formed is specified.
- Then, for each data point, the likelihood of it belonging to each of the K clusters is calculated. This is called the Expectation (E) step
- Based on the previous step, the model parameters are updated. This is called Maximization (M) step.
- Together it is used to check for convergence by comparing the change in log-likelihood or the parameter values between iterations.
- If it converges, then we have achieved our purpose. If not, then the E-step and M-step are repeated until we reach convergence.
Q.73 Explain the concept of silhouette score in clustering evaluation.
Silhouette score is a metric used to evaluate the quality of clusters produced by a clustering algorithm. Here is how it works:
- the average distance between the data point and all other data points in the same cluster is first calculated. Let us call this as (a)
- Then for the same data point, the average distance (b) between the data point and all data points in the nearest neighboring cluster (i.e., the cluster to which it is not assigned)
- silhouette coefficient for each data point is calculated, which given by: S = (b – a) / max(a, b)
- if -1<S<0, it signifies that data point is closer to a neighboring cluster than to its own cluster.
- if S is close to zero, data point is on or very close to the decision boundary between two neighboring clusters.
- if 0<S<1, data point is well within its own cluster and far from neighboring clusters.
Q.74 What is the relationship between eigenvalues and eigenvectors in PCA?
In Principal Component Analysis (PCA), eigenvalues and eigenvectors play a crucial role in the transformation of the original data into a new coordinate system. Let us first define the essential terms:
- Eigen Values: Eigenvalues are associated with each eigenvector and represent the magnitude of the variance (spread or extent) of the data along the corresponding eigenvector
- Eigen Vectors: Eigenvectors are the directions or axes in the original feature space along which the data varies the most or exhibits the most variance
The relationship between them is given as:
[Tex]AV = \lambda{V}
[/Tex], where
A = Feature matrix
V = eigen vector
[Tex]\lambda
[/Tex] = Eigen value.
A larger eigenvalue implies that the corresponding eigenvector captures more of the variance in the data.The sum of all eigenvalues equals the total variance in the original data. Therefore, the proportion of total variance explained by each principal component can be calculated by dividing its eigenvalue by the sum of all eigenvalues
Q.75 What is the cross-validation technique in machine learning?
Cross-validation is a resampling technique used in machine learning to assess and validate the performance of a predictive model. It helps in estimating how well a model is likely to perform on unseen data, making it a crucial step in model evaluation and selection. Cross validation is usually helpful when avoiding overfitting the model. Some of the widely known cross validation techniques are:
- K-Fold Cross-Validation: In this, the data is divided into K subsets, and K iterations of training and testing are performed.
- Stratified K-Fold Cross-Validation: This technique ensures that each fold has approximately the same proportion of classes as the original dataset (helpful in handling data imbalance)
- Shuffle-Split Cross-Validation: It randomly shuffles the data and splits it into training and testing sets.
Q.76 What are the ROC and AUC, explain its significance in binary classification.
Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) is a graphical representation of a binary classifier’s performance. It plots the true positive rate (TPR) vs the false positive rate (FPR) at different classification thresholds.
True positive rate (TPR) : It is the ratio of true positive predictions to the total actual positives.
Recall = TP / (TP + FN)
False positive rate (FPR) : It is the ratio of False positive predictions to the total actual positives.
FPR= FP / (TP + FN)
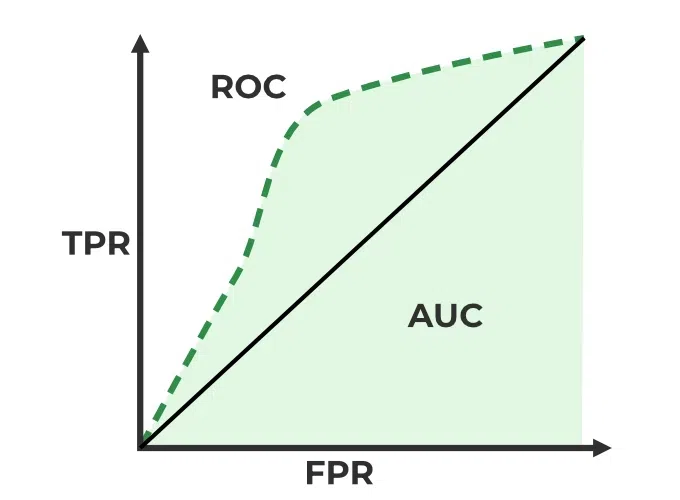
Area Under the Curve (AUC) as the name suggests is the area under the ROC curve. The AUC is a scalar value that quantifies the overall performance of a binary classification model and ranges from 0 to 1, where a model with an AUC of 0.5 indicates random guessing, and an AUC of 1 represents a perfect classifier.
Q.77 Describe gradient descent and its role in optimizing machine learning models.
Gradient descent is a fundamental optimization algorithm used to minimize a cost or loss function in machine learning and deep learning. Its primary role is to iteratively adjust the parameters of a machine learning model to find the values that minimize the cost function, thereby improving the model’s predictive performance. Here’s how Gradient descent help in optimizing Machine learning models:
- Minimizing Cost functions: The primary goal of gradient descent is to find parameter values that result in the lowest possible loss on the training data.
- Convergence: The algorithm continues to iterate and update the parameters until it meets a predefined convergence criterion, which can be a maximum number of iterations or achieving a desired level of accuracy.
- Generalization: Gradient descent ensure that the optimized model generalizes well to new, unseen data.
Q.78 Describe batch gradient descent, stochastic gradient descent, and mini-batch gradient descent.
Batch Gradient Descent: In Batch Gradient Descent, the entire training dataset is used to compute the gradient of the cost function with respect to the model parameters (weights and biases) in each iteration. This means that all training examples are processed before a single parameter update is made. It converges to a more accurate minimum of the cost function but can be slow, especially in a high dimensionality space.
Stochastic Gradient Descent: In Stochastic Gradient Descent, only one randomly selected training example is used to compute the gradient and update the parameters in each iteration. The selection of examples is done independently for each iteration. This is capable of faster updates and can handle large datasets because it processes one example at a time but high variance can cause it to converge slower.
Mini-Batch Gradient Descent: Mini-Batch Gradient Descent strikes a balance between BGD and SGD. It divides the training dataset into small, equally-sized subsets called mini-batches. In each iteration, a mini-batch is randomly sampled, and the gradient is computed based on this mini-batch. It utilizes parallelism well and takes advantage of modern hardware like GPUs but can still exhibits some level of variance in updates compared to Batch Gradient Descent.
Q.79 Explain the Apriori — Association Rule Mining
Association Rule mining is an algorithm to find relation between two or more different objects. Apriori association is one of the most frequently used and most simple association technique. Apriori Association uses prior knowledge of frequent objects properties. It is based on Apriori property which states that:
“All non-empty subsets of a frequent itemset must also be frequent”
Data Science Interview Questions for Experienced
Q.80 Explain multivariate distribution in data science.
A vector with several normally distributed variables is said to have a multivariate normal distribution if any linear combination of the variables likewise has a normal distribution. The multivariate normal distribution is used to approximatively represent the features of specific characteristics in machine learning, but it is also important in extending the central limit theorem to several variables.
Q.81 Describe the concept of conditional probability density function (PDF).
In probability theory and statistics, the conditional probability density function (PDF) is a notion that represents the probability distribution of a random variable within a certain condition or constraint. It measures the probability of a random variable having a given set of values given a set of circumstances or events.
Q.82 What is the cumulative distribution function (CDF), and how is it related to PDF?
The probability that a continuous random variable will take on particular values within a range is described by the Probability Density Function (PDF), whereas the Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF) provides the cumulative probability that the random variable will fall below a given value. Both of these concepts are used in probability theory and statistics to describe and analyse probability distributions. The PDF is the CDF’s derivative, and they are related by integration and differentiation.
Q.83 What is ANOVA? What are the different ways to perform ANOVA tests?
The statistical method known as ANOVA, or Analysis of Variance, is used to examine the variation in a dataset and determine whether there are statistically significant variations between group averages. When comparing the means of several groups or treatments to find out if there are any notable differences, this method is frequently used.
There are several different ways to perform ANOVA tests, each suited for different types of experimental designs and data structures:
- One-Way ANOVA
- Two-Way ANOVA
- Three-Way ANOVA
When conducting ANOVA tests we typically calculate an F-statistic and compare it to a critical value or use it to calculate a p-value.
Q.84 How can you prevent gradient descent from getting stuck in local minima?
Ans: The local minima problem occurs when the optimization algorithm converges a solution that is minimum within a small neighbourhood of the current point but may not be the global minimum for the objective function.
To mitigate local minimal problems, we can use the following technique:
- Use initialization techniques like Xavier/Glorot and He to model trainable parameters. This will help to set appropriate initial weights for the optimization process.
- Set Adam or RMSProp as optimizer, these adaptive learning rate algorithms can adapt the learning rates for individual parameters based on historical gradients.
- Introduce stochasticity in the optimization process using mini-batches, which can help the optimizer to escape local minima by adding noise to the gradient estimates.
- Adding more layers or neurons can create a more complex loss landscape with fewer local minima.
- Hyperparameter tuning using random search cv and grid search cv helps to explore the parameter space more thoroughly suggesting right hyperparameters for training and reducing the risk of getting stuck in local minima.
Q.85 Explain the Gradient Boosting algorithms in machine learning.
Gradient boosting techniques like XGBoost, and CatBoost are used for regression and classification problems. It is a boosting algorithm that combines the predictions of weak learners to create a strong model. The key steps involved in gradient boosting are:
- Initialize the model with weak learners, such as a decision tree.
- Calculate the difference between the target value and predicted value made by the current model.
- Add a new weak learner to calculate residuals and capture the errors made by the current ensemble.
- Update the model by adding fraction of the new weak learner’s predictions. This updating process can be controlled by learning rate.
- Repeat the process from step 2 to 4, with each iteration focusing on correcting the errors made by the previous model.
Q.86 Explain convolutions operations of CNN architecture?
In a CNN architecture, convolution operations involve applying small filters (also called kernels) to input data to extract features. These filters slide over the input image covering one small part of the input at a time, computing dot products at each position creating a feature map. This operation captures the similarity between the filter’s pattern and the local features in the input. Strides determine how much the filter moves between positions. The resulting feature maps capture patterns, such as edges, textures, or shapes, and are essential for image recognition tasks. Convolution operations help reduce the spatial dimensions of the data and make the network translation-invariant, allowing it to recognize features in different parts of an image. Pooling layers are often used after convolutions to further reduce dimensions and retain important information.
Q.87 What is feed forward network and how it is different from recurrent neural network?
Deep learning designs that are basic are feedforward neural networks and recurrent neural networks. They are both employed for different tasks, but their structure and how they handle sequential data differ.
Feed Forward Neural Network
- In FFNN, the information flows in one direction, from input to output, with no loops
- It consists of multiple layers of neurons, typically organized into an input layer, one or more hidden layers, and an output layer.
- Each neuron in a layer is connected to every neuron in the subsequent layer through weighted connections.
- FNNs are primarily used for tasks such as classification and regression, where they take a fixed-size input and produce a corresponding output
Recurrent Neural Network
- A recurrent neural network is designed to handle sequential data, where the order of input elements matters. Unlike FNNs, RNNs have connections that loop back on themselves, allowing them to maintain a hidden state that carries information from previous time steps.
- This hidden state enables RNNs to capture temporal dependencies and context in sequential data, making them well-suited for tasks like natural language processing, time series analysis, and sequence generation.
- However, standard RNNs have limitations in capturing long-range dependencies due to the vanishing gradient problem.
Q.88 Explain the difference between generative and discriminative models?
Generative models focus on generating new data samples, while discriminative models concentrate on classification and prediction tasks based on input data.
Generative Models:
- Objective: Model the joint probability distribution P(X, Y) of input X and target Y.
- Use: Generate new data, often for tasks like image and text generation.
- Examples: Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs).
Discriminative Models:
- Objective: Model the conditional probability distribution P(Y | X) of target Y given input X.
- Use: Classify or make predictions based on input data.
- Examples: Logistic Regression, Support Vector Machines, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for image classification.
Q.89 What is the forward and backward propogations in deep learning?
Forward and backward propagations are key processes that occur during neural network training in deep learning. They are essential for optimizing network parameters and learning meaningful representations from input.
The process by which input data is passed through the neural network to generate predictions or outputs is known as forward propagation. The procedure begins at the input layer, where data is fed into the network. Each neuron in a layer calculates the weighted total of its inputs, applies an activation function, and sends the result to the next layer. This process continues through the hidden layers until the final output layer produces predictions or scores for the given input data.
The technique of computing gradients of the loss function with regard to the network’s parameters is known as backward propagation. It is utilized to adjust the neural network parameters during training using optimization methods such as gradient descent.
The process starts with the computation of the loss, which measures the difference between the network’s predictions and the actual target values. Gradients are then computed by using the chain rule of calculus to propagate this loss backward through the network. This entails figuring out how much each parameter contributed to the error. The computed gradients are used to adjust the network’s weights and biases, reducing the error in subsequent forward passes.
Q.90 Describe the use of Markov models in sequential data analysis?
Markov models are effective methods for capturing and modeling dependencies between successive data points or states in a sequence. They are especially useful when the current condition is dependent on earlier states. The Markov property, which asserts that the future state or observation depends on the current state and is independent of all prior states. There are two types of Markov models used in sequential data analysis:
- Markov chains are the simplest form of Markov models, consisting of a set of states and transition probabilities between these states. Each state represents a possible condition or observation, and the transition probabilities describe the likelihood of moving from one state to another.
- Hidden Markov Models extend the concept of Markov chains by introducing a hidden layer of states and observable emissions associated with each hidden state. The true state of the system (hidden state) is not directly observable, but the emissions are observable.
Applications:
- HMMs are used to model phonemes and words in speech recognition systems, allowing for accurate transcription of spoken language
- HMMs are applied in genomics for gene prediction and sequence alignment tasks. They can identify genes within DNA sequences and align sequences for evolutionary analysis.
- Markov models are used in modeling financial time series data, such as stock prices, to capture the dependencies between consecutive observations and make predictions.
Q.91 What is generative AI?
Generative AI is an abbreviation for Generative Artificial Intelligence, which refers to a class of artificial intelligence systems and algorithms that are designed to generate new, unique data or material that is comparable to, or indistinguishable from, human-created data. It is a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on the creative component of AI, allowing machines to develop innovative outputs such as writing, graphics, audio, and more. There are several generative AI models and methodologies, each adapted to different sorts of data and applications such as:
- Generative AI models such as GPT (Generative Pretrained Transformer) can generate human-like text.” Natural language synthesis, automated content production, and chatbot responses are all common uses for these models.
- Images are generated using generative adversarial networks (GANs).” GANs are made up of a generator network that generates images and a discriminator network that determines the authenticity of the generated images. Because of the struggle between the generator and discriminator, high-quality, realistic images are produced.
- Generative AI can also create audio content, such as speech synthesis and music composition.” Audio content is generated using models such as WaveGAN and Magenta.
Q.92 What are different neural network architecture used to generate artificial data in deep learning?
Various neural networks are used to generate artificial data. Here are some of the neural network architectures used for generating artificial data:
- GANs consist of two components – generator and discriminator, which are trained simultaneously through adversarial training. They are used to generating high-quality images, such as photorealistic faces, artwork, and even entire scenes.
- VAEs are generative models that learn a probabilistic mapping from the data space to a latent space. They also consist of encoder and decoder. They are used for generating images, reconstructing missing parts of images, and generating new data samples. They are also applied in generating text and audio.
- RNNs are a class of neural networks with recurrent connections that can generate sequences of data. They are often used for sequence-to-sequence tasks. They are used in text generation, speech synthesis, music composition.
- Transformers are a type of neural network architecture that has gained popularity for sequence-to-sequence tasks. They use self-attention mechanisms to capture dependencies between different positions in the input data. They are used in natural language processing tasks like machine translation, text summarization, and language generation.
- Autoencoders are neural networks that are trained to reconstruct their input data. Variants like denoising autoencoders and contractive autoencoders can be used for data generation. They are used for image denoising, data inpainting, and generating new data samples.
Q.93 What is deep reinforcement learning technique?
Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) is a cutting-edge machine learning technique that combines the principles of reinforcement learning with the capability of deep neural networks. Its ability to enable machines to learn difficult tasks independently by interacting with their environments, similar to how people learn via trial and error, has garnered significant attention.
DRL is made up of three fundamental components:
- The agent interacts with the environment and takes decision.
- The environment is the outside world with which the agent interacts and receives feedback.
- The reward signal is a scalar value provided by the environment after each action, guiding the agent toward maximizing cumulative rewards over time.
Applications:
- In robotics, DRL is used to control robots, manipulation and navigation.
- DRL plays a role in self-driving cars and vehicle control
- Can also be used for customized recommendations
Q.94 What is transfer learning, and how is it applied in deep learning?
Transfer learning is a strong machine learning and deep learning technique that allows models to apply knowledge obtained from one task or domain to a new, but related. It is motivated by the notion that what we learn in one setting can be applied to a new, but comparable, challenge.
Benefits of Transfer Learning:
- We may utilize knowledge from a large dataset by starting with a pretrained model, making it easier to adapt to a new task with data.
- Training a deep neural network from scratch can be time-consuming and costly in terms of compute. Transfer learning enables us to bypass the earliest phases of training, saving both time and resources.
- Pretrained models frequently learn rich data representations. Models that use these representations can generalize better, even when the target task has a smaller dataset.
Transfer Learning Process:
- Feature Extraction
- It’s a foundation step in transfer learning. The pretrained data is already trained on large and diverse dataset for a related task.
- To leverage the knowlege, output layers of the pretrained model are removed leaving the layers responsible for feature extraction. The target data is passed through these layers to extract feature information.
- using these extracted features, the model captures patterns and representations from the data.
- Fine Tuning
- After the feature extraction process, the model is fine-tuned for the specific target task.
- Output layers are added to the model and these layer are designed to produce the desired output for the target task.
- Backpropagation is used to iteratively update the model’s weights during fine-tuning. This method allows the model to tailor its representations and decision boundaries to the specifics of the target task.
- Even as the model focuses in the target task, the knowledge and features learned from the pre-trained layers continue to contribute to its understanding. This dual learning process improves the model’s performance and enables it to thrive in tasks that require little data or resources.
Q.95 What is difference between object detections and image segmentations.
Object detection and Image segmentation are both computer vision tasks that entail evaluating and comprehending image content, but they serve different functions and give different sorts of information.
Object Detection:
- goal of object detection is to identify and locate objects and represent the object in bounding boxes with their respective labels.
- used in applications like autonomous driving for detecting pedestrians and vehicle
Image Segmentation:
- focuses on partitioning an image into multiple regions, where each segment corresponding to a coherent part of the image.
- provide pixel level labeling of the entire image
- used in applications that require pixel level understanding such as medical image analysis for organ and tumor delineation.
Q.96 Explain the concept of word embeddings in natural language processing (NLP).
In NLP, the concept of word embedding is use to capture semantic and contextual information. Word embeddings are dense representations of words or phrases in continuous-valued vectors in a high-dimensional space. Each word is mapped to a vector with the real numbers, these vectors are learned from large corpora of text data.
Word embeddings are based on the Distributional Hypothesis, which suggests that words that appear in similar context have similar meanings. This idea is used by word embedding models to generate vector representations that reflect the semantic links between words depending on how frequently they co-occur with other words in the text.
The most common word embeddings techniques are-
- Bag of Words (BOW)
- Word2Vec
- Glove: Global Vector for word representation
- Term frequency-inverse document frequency (TF-IDF)
- BERT
Q.97 What is seq2seq model?
A neural network architecture called a Sequence-to-Sequence (Seq2Seq) model is made to cope with data sequences, making it particularly helpful for jobs involving variable-length input and output sequences. Machine translation, text summarization, question answering, and other tasks all benefit from its extensive use in natural language processing.
The Seq2Seq consists of two main components: encoder and decoder. The encoder takes input sequence and converts into fixed length vector . The vector captures features and context of the sequence. The decoder takes the vector as input and generated output sequence. This autoregressive technique frequently entails influencing the subsequent prediction using the preceding one.
Q.98 What is artificial neural networks.
Artificial neural networks take inspiration from structure and functioning of human brain. The computational units in ANN are called neurons and these neurons are responsible to process and pass the information to the next layer.
ANN has three main components:
- Input Layer: where the network receives input features.
- Hidden Layer: one or more layers of interconnected neurons responsible for learning patterns in the data
- Output Layer: provides final output on processed information.
Q.99 What is marginal probability?
A key idea in statistics and probability theory is marginal probability, which is also known as marginal distribution. With reference to a certain variable of interest, it is the likelihood that an event will occur, without taking into account the results of other variables. Basically, it treats the other variables as if they were “marginal” or irrelevant and concentrates on one.
Marginal probabilities are essential in many statistical analyses, including estimating anticipated values, computing conditional probabilities, and drawing conclusions about certain variables of interest while taking other variables’ influences into account.
Q.100 What are the probability axioms?
The fundamental rules that control the behaviour and characteristics of probabilities in probability theory and statistics are referred to as the probability axioms, sometimes known as the probability laws or probability principles.
There are three fundamental axioms of probability:
- Non-Negativity Axiom
- Normalization Axiom
- Additivity Axiom
Conclusion
We all know that data science is growing career and if you are looking a future in data science, then explore this detailed article on data science interview questions.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...