Difference between WDM and SONET
Last Updated :
10 Oct, 2022
In this article, we are going to discuss the difference between Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) and Synchronous Optical Network (SONET). Let’s discuss them one by one.
1. Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM):
WDM stands for Wavelength Division Multiplexing. This is a fiber-optic transmission technique that facilitates the use of multiple light wavelengths (or colors) to send data over the same medium. On one fiber, two or more colors of light can travel and several signals can be transmitted in an optical waveguide at differing wavelengths or different frequencies on the optical spectrum.

2. Synchronous Optical Network (SONET):
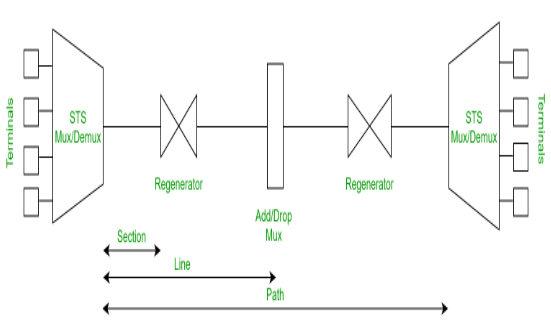
SONET stands for Synchronous Optical Network. This is a communication protocol, developed by Bellcore that is used to transmit a large amount of data over relatively larger distances by using optical fiber. By using this, multiple digital data streams are transferred at the same time over the optical fiber.
Difference between WDM and SONET :
| S. No. |
WDM |
SONET |
| 1. |
WDM uses a number of light sources, each emits the light of different wavelengths. |
SONET is a optical transmission interface. |
| 2. |
The optical multiplexer is used at the input side to multiplex these signals. |
SONET aggregates a number of optical signals into higher bit rate signal for transmission over a single fiber using a single wavelength. |
| 3. |
This improve the capability of optical cable in carrying data by multiplexing many channel of wavelengths. |
This are technologies that are used as a buffer (interfacing) layer for higher layers. |
| 4. |
All the signals arrive at the same time, rather of being distributed across time slots. |
It uses Time division multiplexing(TDM) or statistical TDM. |
| 5. |
The channel spacing is reduces to 1.6 nm or less. |
The channel spacing can be carried over WDM, but not vice versa. |
| 6. |
The number of channels delivered are 2. |
It is easy to isolate one channel from a multiplexed circuit. |
| 7. |
The best application is PON. |
The best application are ethernet cabling or public telephone network. |
| 8. |
The band used here are O and C. |
The band used here are STS-1 with fixed size frames. |
| 9. |
Advantages-
- There is possibility of transmission in full duplex mode.
- It offers more bandwidth.
- A simpler reconfiguration
- Extreme security
- This strategy might work best because it is straightforward to implement.
|
Advantages-
- Extreme effectiveness
- Allows all traffic types to be transported
- Easy demultiplexing
- It has out of band management system
- Decreased cost
- It provides network resilience capabilities.
- Both legacy and future networks can use it.
- Standard optical interference
- Capabilities for remote operation. remote testing, provisioning, inventorying, personalization, and reconfiguration
|
| 10. |
Disadvantages-
- Tuning of wavelengths is difficult
- Bandwidth is not efficiently utilized.
- The system becomes more expensive as optical components are added.
- When using WDM, lightwave transmission is only possible in a two-point circuit.
- The OLT (Optical Line Termination) must have a transmitter array with one transmitter for each ONU (Optical Network Unit), so scalability is an issue. A problem could arise if a new ONU is added unless the transmitter has been provisioned beforehand. Each ONU needs to have a laser with a certain wavelength.
- Problems with a cascaded topology
|
Disadvantages-
- At higher capacity, bandwidth efficiency is an issue.
- For tributary services, SONET mux services are required.
- Lack of an interoperable standard
- Additional overhead is needed.
- Low cost effective for low channel numbers.
- The SONET/SDH network management system is not well suited for managing and using the DWDM method.
|
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...