Difference between SONET and OTN
Last Updated :
10 Oct, 2022
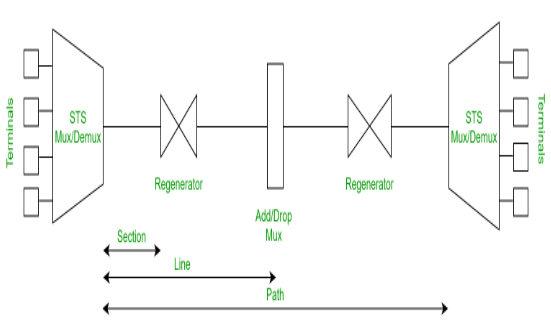
1. Synchronous Optical Network (SONET):
SONET stands for Synchronous Optical Network. This is a communication protocol, developed by Bellcore that is used to transmit a large amount of data over relatively larger distances by using optical fiber. By using this, multiple digital data streams are transferred at the same time over the optical fiber.
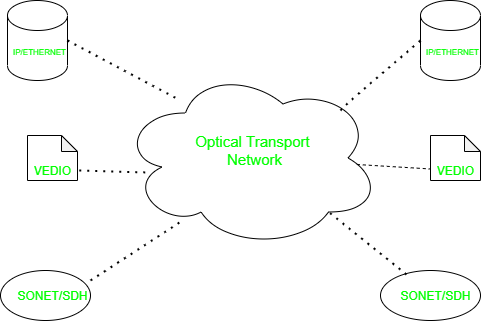
2. Optical Transport Network (OTN):
ON stands for Optical Transport Network. This is a protocol for sending network messaging over optical fiber networks. It is designed to address these issues by delivering a transparent framework to efficiently carry diverse traffic types. Two layers of switching are formed (TDM and WSON) and functions of transport, management, supervision, multiplexing, routing, and survivability are defined.
Difference between SONET and OTN :
| S. No. |
SONET |
OTN |
| 1. |
Synchronous mapping of payloads. |
Asynchronous mapping of payloads. |
| 2. |
It is designed to operates on multiple wavelength. |
It is designed to operates on multiple wavelength(DWDM). |
| 3. |
It requires right timing distribution across network. |
It does not require timing distribution. |
| 4. |
It was defined with fixed frame rates. |
It was defined with fixed frame sizes. |
| 5. |
It is less efficiently than OTN. |
It is much more efficiently than SONET. |
| 6. |
It performs multi stage multiplexing. |
It performs single stage multiplexing. |
| 7. |
It scales to maximum of 40Gb/s. |
It scales to 100Gb/s (or beyond). |
| 8. |
It does not has any standard FEC. |
It has FEC size for error correction to correct 16 blocks per frames. |
| 9. |
Why SONET?
- Fault Tolerant – protected rings recover in 50 milliseconds from node and span failures.
- Mature Technology as it is an established technology and provisioning model.
- Price/performance – one of the most affordable architectures for up to 10 Gbps
- Multi-service Capable – capable of carrying both TDM and packet-based traffic such as ATM, Ethernet, and MPLS.
- Standards -based – ensures cross-span and cross-vendor compatibility
- Deterministic and predictable – a strong, voice-centric heritage ensures a high level of service to all traffic.
|
Why OTN?
- More effective forward error correction
- Additional Tandem Connection Monitoring Levels (TCM)
- Transparent Client Signal Transport
- Change in Scalability
|
| 10. |
Disadvantages-
- At higher capacity, bandwidth efficiency is an issue.
- Lack of an interoperable standard
- Low cost effective for low channel numbers.
- For tributary services, SONET mux services are required.
- Additional overhead is needed.
- The SONET/SDH network management system is not well suited for managing and using the DWDM method.
|
Disadvantages-
- New hardware and a management system are necessary.
|
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...