Diagonal is a line segment that joins two corners of the polygon by skipping at least one corner in the polygon. We can also say that a diagonal is a line segment that joins two non-adjacent sides of any polygon. Diagonals meaning they are generally bigger in length than the sides of a polygon but it’s not always the case. We can also say that diagonals in maths are the line segment that joins two vertices of the polygon that are not adjacent.
Diagonals in math are defined only for lateral shapes, or the shapes that have corners, such as Squares, Rectangles, Pentagons, etc. but they are not defined for curved shapes such as Circles, and others. A diagonal can also be defined for 3-D shapes such as Cubes, Cuboids, etc. Now let’s learn more about diagonal line, their properties, diagonals of various shapes, and other things about diagonals in detail in this article.
What are Diagonals?
Diagonal is a straight line connecting opposite vertices of any polygon is called the diagonal of the polygon. The length of the diagonal of the polygon is always greater than the sides of the polygon. A polygon can have more than one diagonal and the number of diagonals in math a polygon have depends on the number of sides the polygon has, the simplest polygon with a diagonal is the quadrilateral and it has two diagonals. The image added below shows a square and a triangle in which the square has two diagonals and the triangle has no diagonal.

Note: A triangle is the simplest polygon with three sides but a triangle has no diagonals.
Diagonal Shape
As we have already learned that diagonal is a line segment that connects two vertices of the polygon that are not on the same edge. Thus, we can say that all the diagonals are the line segment.
Diagonal Formula
The formula that tells us how many diagonals a polygon has is called the diagonal formula. The number of diagonals of the polygon depends on the sides or the vertices of the polygon. Suppose there are “n” vertices of a polygon, then the number of diagonals in math of a polygon is found using the formula:
Number of Diagonals of a Polygon with “n” Vertices = [n(n-3)]/2
Let’s see an diagonal examples using the above formula.
Example: Find the diagonals of a pentagon using the diagonal formula discussed above.
Solution:
Given shape of is Pentagon
Number of vertices of the pentagon(n) = 5
Using the Diagonal Formula,
Number of Diagonals of a Polygon with “n” Vertices = [n(n-3)]/2
⇒ Number of Diagonal = [5(5-3)]/2
⇒ Number of Diagonal = 10/2 = 5
Thus, a pentagon has five diagonals.
Learn more about Diagonal Formula.
Diagonals of Shapes
A polygon has n vertices so the diagonals in a polygon are not fixed. A polygon can have zero to m (a very large natural number) diagonal shape in maths. Area of a polygon can be easily calculated using polygon formula. As we already know the diagonal of the polygon depends on the number of vertices the polygon has. Now let’s learn about the diagonal of various polygons below,
- Diagonals of a Triangle
- Diagonals of a Quadrilateral
- Diagonals of a Square
- Diagonals of a Rectangle
- Diagonals of a Rhombus
- Diagonals of a Trapezium
- Diagonals of a Kite
- Diagonals of a Pentagon
- Diagonals of a Hexagon
Read more about the Diagonal of a Polygon.
Diagonals of Triangle
A close figure made using three sides is called a triangle. A triangle has three sides, three angles, and three vertices. A triangle did not have any non-adjacent vertices, thus a triangle did not have any diagonals. Thus, a triangle has no diagonals.
Diagonals of Quadrilateral
A quadrilateral is a figure with four vertices and using the diagonal formula discussed above we know that a quadrilateral has 2 diagonals. A quadrilateral can be of various types, square, rectangle, rhombus, and others. Let’s learn about the diagonals of some quadrilaterals in detail.
Diagonals of Square
A square is a quadrilateral with all four sides equal and all four angles 90 degrees. A square has two diagonals and the length of the diagonals are equal. The diagonals of the square also bisect each other. The image added below shows the diagonal of the square

Diagonals of Rectangle
A rectangle is a quadrilateral with opposite pair of sides equal and parallel, and all four angles 90 degrees. A rectangle has two diagonals and the length of the diagonals are equal. The diagonals of the rectangle bisect each other. The image added below shows the diagonal of the rectangle,

Diagonals of Rhombus
A rhombus is a quadrilateral with all four sides equal but in the case of the Rhombus all four angles are not equal. A Rhombus has two diagonals and the length of the diagonals is not equal. The diagonals of the square are perpendicular bisectors of each other, i.e. they bisect each other at 90 degrees. The image added below shows the diagonal of the rhombus,

Note: For the Rhombus if the diagonals are a and b then its area is 1/2(ab)
Learn more about, Area of Rhombus
Diagonals of Trapezium
A quadrilateral with a pair of parallel sides is called the Trapezium. It only has a pair of parallel lines and the other pair is not parallel. A trapezium has two diagonals, the image added below shows a trapezium ABCD in which AC is the diagonal of the trapezium.

Learn more about, Area of Trapezium
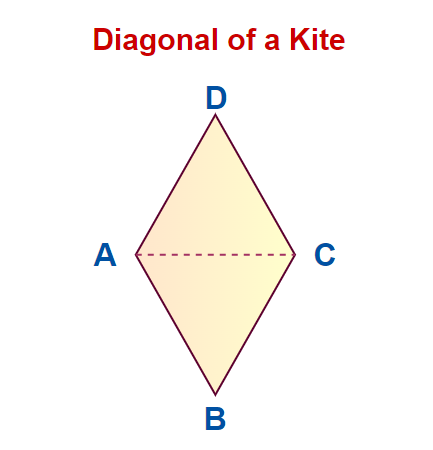
Diagonals of Kite
Kite is a quadrilateral in which the adjacent pair of sides are equal. The image added below shows a Kite ABCD in which the AC is the diagonal of the Kite.
Diagonals of Pentagon
A pentagon is a 2-D figure with five sides and five vertices. For a regular pentagon, all five sides are equal, and using the diagonal formula we can say that a pentagon has 5 diagonals. In the case of a regular pentagon, all five diagonals of the pentagon are equal. The image added below shows a pentagon and all its diagonals.

Diagonals of Hexagon
A hexagon is a 2-D figure with six sides and six vertices. For a regular hexagon, all six sides are equal, and using the diagonal formula we can say that a hexagon has 6 diagonals. In the case of a regular hexagon, all six diagonals of the hexagon are equal. The image added below shows a hexagon and all its diagonals.

Also, Read
Diagonals of 3D Shapes
Similar to the 2-D shapes, some 3-D shapes also have diagonals and the (body) diagonals in the 3-D shapes are the line that joins the vertices of the 3-D shape that are non-planer. The diagonal of 3-D shapes such as Cubes and Cubiod are discussed below,
Diagonals of Cube
A cube is a 3-D figure in which all three parameters length, breadth, and height are equal. It is a 3-D representation of a square. A cube has two types of diagonal body diagonal and face diagonals.
- The body diagonal of a cube is the line segment that cuts through its center, joining the opposite vertices.
- The face diagonal is the one joining the opposite vertices on every face.
A cube has two types of diagonals in maths, Body Diagonal and Face Diagonal. The image added below shows both the diagonals of the cube.

Read more about, Diagonal of a Cube.
Diagonals of Cuboid
A cuboid is a 3-D figure in which all three parameters length, breadth, and height are different. It is a 3-D representation of a rectangle. A cuboid has two types of diagonal body diagonal and face diagonals.
- The body diagonal of a cube is the line segment that cuts through its center, joining the opposite vertices.
- The face diagonal is the one joining the opposite vertices on every face.
A cuboid has two types of diagonals, Body Diagonal and Face Diagonal. The image added below shows both the diagonals of the cuboid.

Number of Diagonals in Polygons
The number of the diagonals in the polygon depends on the number of sides/vertices in the polygon and it is calculated using the number of the diagonals formula.
The table showing the number of diagonals of some polygons is discussed below,
| Number of Sides in Shape (n) |
Number of Diagonals |
| Triangle (3) |
0 |
| Quadrilateral (4) |
2 |
| Pentagon (5) |
5 |
| Hexagon (6) |
9 |
| Heptagon (7) |
14 |
| Octagon (8) |
20 |
| Nonagon (9) |
27 |
| Decagon (10) |
35 |
Length of Diagonal
Diagonal of any polygon is the line segment joining the vertices of the polygon that are not on the same edge. The length of the polygon depends on the type of polygon. We do not have a single formula to calculate the length of the diagonal and the length of the diagonal is calculated using the properties of the polygon.
Let’s learn the length of the diagonal of various figures as
- Length of Diagonal of Square
- Length of Diagonal of a Rectangle
Now let’s learn their formula as
Formula for Diagonal of Square
The diagonal of the square is calculated using the Pythagoras Theorem. Suppose we have a square of the side “a” then its length of diagonal(d) is calculated as
d = √(a2 + a2)
⇒ d = √(2a2)
⇒ d = 2√(a)
The length of the diagonal is calculated as,
Length of Diagonal of a Square(D) = a√2
where, a is the side of the square
Formula for Diagonal of Rectangle
The diagonal of the rectangle is calculated using the Pythagoras Theorem. The length of the diagonal is calculated as,
Length of Diagonal of a Rectangle(D) = √(l2 + b2)
Where,
- l is the length of Rectangle, and
- b is the length of Rectangle.
Length of a Diagonal of 3D Figures
A 3D figure also has diagonals and the diagonal of the 3D figure such as Cube and Cuboid is calculated below in the article.
Formula for Diagonal of a Cube
A cube is a 3D figure with all three sides equal and is a 3D representation of the square. It has two types of diagonals in math,
- Face Diagonals
- Body Diagonals
And both of their lengths are calculated using different formulas as,
Suppose we have a cube of the side “a” then its face diagonal is calculated using the Pythagoras Theorem as
Length of Face Diagonal = √2(a) units
Also for body diagonals, we use Pythagoras’ theorem two times then the resultant formula for the length of the body diagonal is,
Length of Body Diagonal = √3(a) units
Formula for Diagonal of a Cuboid
A cuboid is a 3D figure with all three sides different and is a 3D representation of the rectangle. It has two types of diagonals,
- Face Diagonals
- Body Diagonals
And both of their lengths are calculated using different formulas as,
Suppose we have a cuboid of sides “a”, “b”, and “c” respectively, then its face diagonal along the face with dimensions as a and b is calculated using the Pythagoras Theorem as,
Length of Face Diagonal = √(a2 + b2) units
Also for body diagonals, we use Pythagoras’ theorem two times then the resultant formula for the length of the body diagonal is,
Length of Body Diagonal = √(a2 + b2 + c2) units
Read More,
Solved Examples on Diagonals
Example 1: Find the diagonal of a square with a side 5 cm
Solution:
Given,
- Length of Side of Square(a) = 5 cm
Formula for the diagonal of a square,
Diagonal of a Square(d) = a√2
Substituting the value we get,
d = 5√2
⇒ d = 4 × 1.414 = 7.07 cm
Thus, the diagonal of a square is 7.07 cm.
Example 2: Find the diagonal of a rectangle with a side of 8 cm and 6 cm respectively.
Solution:
Given,
- Length of Rectangle(l) = 8 cm
- Breadth of Rectangle(b) = 6 cm
Formula for the diagonal of a rectangle,
Diagonal of a rectangle(d) = √(l2 + b2)
Substituting the value we get,
d = √(82 + 62)
⇒ d = √(100) = 10 cm
Thus, the diagonal of a square is 10 cm.
Example 3: Find one of the diagonals of a Rhombus is 10 cm and its area is 100 cm2
Solution:
Given,
- Area of a Rhombus(A) = 100 cm2
- Length of the diagonal of a rhombus(a) = 10 cm
using the formula,
Area(A) = 1/2(ab)
Substituting the value we get,
100 = 1/2(10b)
⇒ 200 = 10b
⇒ b = 200/10
⇒ b = 20
Thus, the other diagonal of the rhombus is 20 cm.
Example 4: Find the diagonals of a decagon using the diagonal formula discussed above.
Solution:
Given,
- Shape of a Decagon
- Number of vertices of the decagon(n) = 10
Using the Diagonal Formula,
Number of Diagonals of a Polygon with “n” Vertices = [n(n-3)]/2
⇒ Number of Diagonal = [10(10-3)]/2
⇒ Number of Diagonal = 70/2 = 35
Thus, a decagon has thirty-five diagonals.
Example 5: Find the diagonals of a heptagon using the diagonal formula discussed above.
Solution:
Given,
- Shape of Heptagon
- Number of vertices of the Heptagon(n) = 7
Using the Diagonal Formula,
Number of Diagonals of a Polygon with “n” Vertices = [n(n-3)]/2
⇒ Number of Diagonal = [7(7-3)]/2
⇒ Number of Diagonal = 28/2 = 14
Thus, a heptagon has fourteen diagonals.
FAQs on Diagonals
What is the Diagonals?
A diagonal is a line segment that joins the two vertices of the polygon that on not on the same edge.
How to Find the Number of Diagonals in a Polygon?
The formula to calculate how many diagonals a polygon has is,
Number of Diagonals of a Polygon with “n” Vertices = [n(n-3)]/2
How many Diagonals does a Triangle have?
Using the diagonal formula we can calculate the number of diagonals in a triangle as,
The diagonal formula is,
(N)Number of Diagonals of a Polygon with “n” Vertices = [n(n-3)]/2
For triangle n = 3, thus,
N = 3(3-3)/2 = 0
Thus, a triangle has zero(0) diagonals.
How many Diagonals does a Hexagon have?
Using the diagonal formula we can calculate the number of diagonals in a hexagon as,
The diagonal formula is,
(N)Number of Diagonals of a Polygon with “n” Vertices = [n(n-3)]/2
For hexagon n = 6, thus,
N = 6(6-3)/2 = 9
Thus, a hexagon has nine(9) diagonals.
What is the Length of Diagonal of a Square?
The length of the diagonal of the square is calculated using the formula,
Diagonal = a√2
where “a” is the length of side of a square.
Does Circle have a Diagonal?
As a circle is a curved figure, i.e. it does not have any vertices, thus it has no diagonals.
How many diagonals does a heptagon have?
With 7 vertices, a heptagon contains 14 diagonals.
How many diagonals dose a circle have?
No, a circle lacks diagonals due to its absence of vertices and sides.
How many diagonals in cuboid?
A cuboid has a total of six diagonals, including one space diagonal, two face diagonals on each of two adjacent faces, and one body diagonal.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...