Diagonal of a Cuboid is a line segment that joins two opposite vertices of the cuboid. It can pass through either the body or the face of the diagonal of the cuboid. Cuboid, in 3D, is an elongated version of a cube, i.e., a box-like shape with three different sides.
The length of the diagonal of a cuboid can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem. In this article, we will discuss the diagonal of a cuboid, including its types, formula, and some solved examples for the same.
.webp)
What is Cuboid?
Cuboid is a three-dimensional geometric shape characterized by six rectangular faces, where each face meets another at a right angle.
Cuboid is often referred to as a rectangular prism due to its rectangular faces. The cuboid is a type of parallelepiped, which is a six-faced figure with each pair of opposite faces being identical rectangles.
Cuboid has several defining properties:
- Faces: All six faces of a cuboid are rectangles.
- Edges: A cuboid has 12 edges, where each edge is the intersection of two adjacent faces.
- Vertices: There are eight vertices (corners) where the edges meet.
Diagonal of Cuboid Definition
Diagonal of a cuboid is a line segment connecting two opposite corners or vertices of the cuboid.
In simpler terms, it is the longest possible straight line that can be drawn within the cuboid, passing through its interior as well as surface.
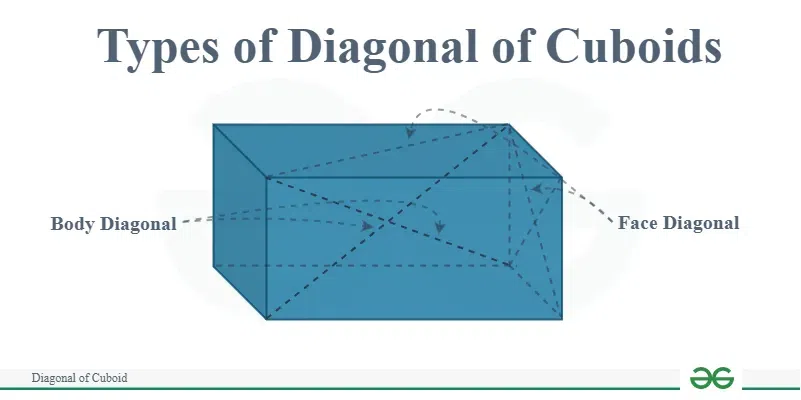
Types of Diagonal of Cuboid
In a cuboid, which is a three-dimensional geometric shape with six rectangular faces, the diagonals can be classified into two types:
- Face Diagonals
- Body Diagonals
Let’s discuss these types in detail as follows:
Face Diagonal
Face diagonal of a cuboid is a line segment that connects two opposite corners of one of the faces of the cuboid. In other words, it is a diagonal that lies entirely within one of the cuboid’s faces.
It is also called as Surface Diagonal. There are 12 Face diagonals as each face contains 2 diagonals.
Body Diagonal
These diagonals connect two vertices that are not on the same face or edge.
In Other words, The line segment connecting two opposite corners or vertices of the cuboid. It passes through the interior of the cuboid
A cuboid has four body diagonals.
The formula to calculate the diagonal (d) of a cuboid is given by the Pythagoras theorem:
d = √(l2 + b2 + h2)
Where,
- l is the length of the cuboid,
- b is the breadth/width of the cuboid, and
- h is the height of the cuboid.
Derivation Diagonal of Cuboid Formula
The derivation of the diagonal formula involves applying the Pythagorean theorem to a right-angled triangle formed by the length, width, and height of the cuboid.

The square of the diagonal (d2) is equal to the sum of the squares of the length, breadth, and height
d = √ (l2 + b2+ h2)
Here, For calculating the Body Diagonal D , Firstly we have to calculate the Surface Diagonal.
For Finding the surface diagonal , we use Pythagoras theorem
So, d12 = l2 + b2
and for finding D, Again we use Pythagoras Theorem,
D2 = h2 + d12
D2 = l2 + b2 + h2
SO, D = √ l2 + b2 + h2
Relationship between Diagonal Length and Sides
Relationship between diagonal lengths and sides are given as:
|
Length of Face Diagonal
|
Length of Body Diagonal
|
|
D2 = l2 + b2
|
D2 = l2+ b2 + h2
|
Where,
- D = Face Diagonal of Cuboid
- l = length of cuboid
- b = breadth of cuboid
- h = height of cuboid
Read More about Diagonal Formulas.
How to Find the Length of Diagonal of Cuboid?
To calculate the length of diagonal of cuboid we can use the following steps:
Step 1: Identify the three edges of Cuboid i.e., l, b, and h.
Step 2: For Body diagonal, use D2 = l2+ b2 + h2 and for face diagonal, use D2 = l2 + b2 to calculate the length.
Let’s consider an example for the same.
Example: Find the length of body diagonal of cuboid with dimensions 6 cm × 8 cm × 10 cm.
Solution:
Given: l = 6cm, b = 8 cm and h = 10 cm.
Length of Body Diagonal = √(l2+ b2 + h2 )
⇒ Length of Body Diagonal = √(62+ 82 + 102 )
⇒ Length of Body Diagonal = √(36+ 64 + 100)
⇒ Length of Body Diagonal = √(200)
⇒ Length of Body Diagonal = 14.142 . .
Thus, length of Body diagonal is 14.14 cm.
Diagonal of Cuboid and Cube
The key difference between diagonal of Cube and Cuboid are:
| Property |
Cuboid |
Cube |
| Definition |
A rectangular solid with six faces, where each face is a rectangle. |
A special case of a cuboid where all six faces are squares. |
| Shape |
Rectangular |
Perfectly symmetrical, all sides are equal |
| Faces |
Rectangular faces |
Square faces |
| Edge Lengths |
Unequal lengths on each dimension |
Equal lengths on each dimension |
| Formula for Diagonal Length |
√(l2+ b2 + h2) |
a√ 3 |
| Number of Diagonals |
Number of Body Diagonals: 04
Number of Face Diagonals: 12 |
Number of Body Diagonals: 04
Number of Face Diagonals: 12 |
Where,
- l is the length of cuboid,
- b is the breadth of cuboid,
- h is the height of cuboid, and
- a is the edge of cuboid.
Read More about Diagonal of Cube.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the diagonal of a cuboid is the longest length inside the cuboid, which can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem in the right-angled triangles formed inside the cuboid. In this article, we have discussed the formula as well as the derivation for the cuboid’s diagonal.
Read More,
Solved Problems:
Problem 1: Given a cuboid with length l = 4, breadth b = 3 and height h = 5 , find the diagonal d.
Solution:
Here, l = 4, b = 3 , h = 5
Thus, length of diagonal d is:
d = √(2 + b2+ h2)
⇒ d = √(42 + 32 + 52)
⇒ d = √(16 + 9 + 25)
⇒ d = √(50)
⇒ d ≈ 7.07
Therefore, the diagonal of the cuboid is approximately 7.07 units.
Example 2: Find the length of face diagonals of cuboid with dimensions 6 cm × 8 cm × 10 cm.
Solution:
Given: l = 6cm, b = 8 cm and h = 10 cm.
There are three lengths associated with face diagonals i.e.,
d1 = √(l2 + b2), d2 = √(l2 + h2), d3 = √(b2 + h2)
⇒ d1 = √(62 + 82) = √(36 + 64) = √(100) = 10 cm
⇒ d2 = √(62 + 102) = √(36 + 100) = √(136) ≈ 11.662 cm
⇒ d3 = √(82 + 102) = √(64 + 100) = √(164) ≈ 12.806 cm
Thus, the length of all face diagonals are 10 cm, 11.66 cm, and 12.81 cm.
Problem 3: For a cube with side length a = 6, find the diagonal d of the cube.
Solution:
As we know, Length of Body diagonal of Cube is given as a√3, where a is the side of cube.
Given: a = 6
Thus, d = √3 × 6 [As √3 ≈ 1. 73]
⇒ d ≈ 1.73 × 6
⇒ d ≈ 10.38
The diagonal of the cube is approximately 10.38 units.
Practice Questions: Diagonal of Cuboid
Question 1: Calculate the length of the face diagonal for a cuboid with dimensions: length = 9 cm, width = 5 cm.
Question 2: Find the length of the body diagonal for a cuboid with dimensions: length = 12 m, width = 7 m, height = 10 m.
Question 3: Determine the length of the body diagonal for a cuboid with dimensions: length = 8 m, width = 6 m, height = 4 m.
Question 4: Find the length of the longest diagonal for a cuboid with dimensions: length = 12 ft, width = 16 ft, height = 9 ft.
Question 5: Calculate the length of the body diagonal for a cuboid with dimensions: length = 15 m, width = 11 m, height = 6 m.
FAQs on Diagonal of Cuboid
What is Diagonal?
A diagonal in mathematics refers to a line segment connecting two non-adjacent vertices of a polygon.
How many Diagonals are there in Cuboid?
There are total of 4 body diagonals and 12 face diagonals of cuboid.
What is the Formula for Diagonal of Cube?
The formula is d = √(l2+ b2+ h2), where l = length, b= breadth or width and h = height of the cuboid.
How to Derive the Formula for Diagonal of Cuboid?
The diagonal of a cuboid can be found using the Pythagorean theorem.
Can the Diagonal be longer than any side of the Cuboid?
Yes, it’s possible. The diagonal is a measure of the space diagonal within the cuboid, and it may be longer than any individual side.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...