Current constitutes the basis of almost every electronic application. We use the current to turn on almost every appliance. We want it to heat water in an electric kettle, We want it to turn on the heater, and we want electric current to charge our devices. So we see current forms a large part of our life. In this article, we try to study what is this current. Electric current is the flow of one coulomb of electricity per second.
We talk about the definition of current, the symbol used to represent current. We study about charges that constitute, and we study the origin of the current. Not only this but we also study how current flows through an example. We try to differentiate between AC and DC. The article ends by mentioning some advantages, disadvantages, and some real-life applications of current. Solved examples have been added for a better understanding of the concepts.
What is a Charge?
To study about current we need to know about the fundamental quantity of electronics which is charge. Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. The fundamental unit of charge is Coulomb(C). Symbol: Q
It can be further divided into two types:
- Positive Charge: A positive charge occurs when an atom has more protons than electrons.
- Negative Charge: When an object has more electrons than protons is called a negative charge.
What is Electric Current?
Current is termed as the rate at which charge flows in a closed circuit. The scientific definition of current is the ‘rate of flow of charge’ so we can have current due to electrons and current due to protons. Basically , it is the flow rate of electrons in the electric circuit or we can say the flow of charges in the given space. Thus , this formula is derived from the ohm’s law:
I = V/R
where : V – electric voltage
I – Electric current
R- Resistance of wire
Symbol: I
I= q/T
where,
q = charge,
T = time
The symbol was first used by André-Marie Ampère, after whom the unit of electric current is named, in formulating Ampère’s force law (1820).
Origin of Current
Benjamin Franklin is given the credit for discovering electricity in the 1700s with his kite experiment, where he flew a kite with a metal key tied to it during a thunderstorm. Later various scientists discovered various phenomena’s related to electricity and many papers were published.
In 1826, André Ampère published his theories about electricity and magnetism, explaining the electro-dynamic theory. He was the first person to explain this theory. The unit for electrical currents, which is ampere, is named after him.
Example
Let us study a simple example to understand the current:

Current Circuit
This simple circuit consist of a cell which provides the power supply, it consist of a bulb which uses electrical energy to generate heat energy. The connecting wires provide a complete path for current to flow. As we can see in above diagram, the cell provides the necessary voltage required for charges to move. These charges in motion are called electric current. The positive carriers move from higher potential to direction of lower potential. Hence, from the diagram we can see the current due to positive charge in from positive terminal to negative terminal outside the cell.
Conventionally the direction of motion of electrons is opposite to direction of motion of current which can be seen in the above circuit.
Mathematical Derivation of Current
We try to derive the mathematical current formula. For this we take a simple circuit :
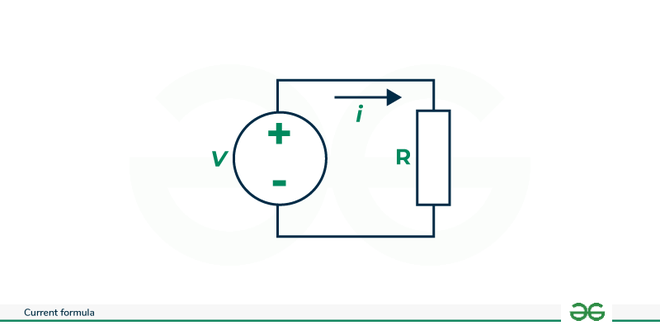
Current formula
where,
i= Electric Current
V= Electric voltage
R = Resistance of metal wire
Now we apply Kirchhoff’s law
V – iR=0
V = iR
V/R = i
So current(i) is the ratio of voltage to resistance in this circuit
Types Of Current
So basically , Electric current can be divided into two types:
- Alternating Current
- Direct Current
Alternating Current
Alternating Current is the current in which direction of flow of electrons changes at regular intervals of time. In this magnitude and direction of current are a property of time. The graph of AC shows that AC is a function of time and can be denoted by a sine wave, cos wave, a rectangular wave etc.
-660.png)
Alternating Current
This current is usually supplied in households since it can travel large distances with minimal loss of power.
Direct Current
Direct current is one-directional flow of current. It has a constant magnitude and flows in one direction during all time. As we can see from the graph below ,DC is unidirectional and is denoted by a straight line parallel to x-axis. DC is usually used for solar cells, electric vehicles which require large power supply.
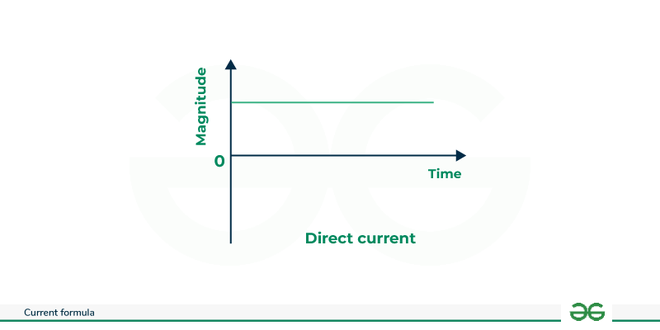
Direct Current
Generation of Current
The below diagram show how does current and electrons travel inside a circuit. In this section we will study how this current is generated with EMF.

Generation of Current
When an external voltage is applied at one of the ends of the conductor it generates an electric field on the negatively charged electrons that are attracted to the positive terminal of the external voltage.
For the electric current to be transmitted from one point to another, there must be materials with a high amount of free electrons located in the last orbit of their nucleus, which means they are highly susceptible to moving due to the weaker attractive force on them from their nucleus.
Properties Of Current
Electric current has certain properties like:
- There are two types of current- AC and DC. Direct current is unidirectional current that flows in one direction with constant magnitude while Alternating current is a variable current which changes direction in regular intervals of time and is generally used for operating household and industrial appliances.
- The unit of electric current is Ampere. 1 ampere represents the current generated when 1 coulomb of charge passes in 1 second.
- Conventional direction of current is assumed to be the direction in which positive charge flows. Hence in the circuit the direction of current is from the positive terminal of battery to the negative terminal.
- Electric current has a property called Electrical energy associated with it which is defined as the work done in moving electrons in the circuit. This electrical energy of current is potentially used to generate other forms of energy like heat energy and light energy in a bulb.
Solved Examples
1. Solve for the current generated and power wasted by a 2 ohm resistor in the given circuit.

Current Generation
We can apply ohm’s law to find current
Then,
V=IReq
Req=4ohms
On putting values :
20=4I
I=5A
Then energy wasted by one resistor :
E=I2R
E=25*2=50 J
2. Write down the equation for a sinusoidal voltage of 50 Hz and its peak value is 20 V. Draw the corresponding voltage versus time graph.
f=50Hz Vm=20V
Instantaneous voltage V=Vmsin(t)
V=20sin(t)
V=20sin(2π* 50t)
V=20sin(314t)
The waveform is given below :

V=20sin(314t)
Applications of Electric Current
- Electric current is used to run various appliances like household appliances (e.g refrigerator ,microwave) and industrial units(e.g heating fans).
- Electricity generates electrical energy which is converted into other forms of energy depending upon need of user .For example light energy in electric bulbs and mechanical energy in electric motors.
- Current is a major parameter in electronics and communication industry since it is used in fields of antenna, mobile phones and in other essential circuitries.
- The heating effect of electric current forms the basis of many appliances like geyser, heater, toasters.
- The chemical effect of electric current which states that when an electric current passes through a solution, the solution ionizes and breaks down into ion is also applied in various fields like electroplating.
Advantages of Electric Current
Advantages of electric current:
- Electric current is easily accessible and easy to produce making it an accessible resource.
- It is easy to manage and transport. AC current can be transmitted over long distances with minimal loss of power.
- The energy associated with electric current can be easily transformed into any other form of energy like electrical and heat energy. Thereby it can be utilized as per user need.
- It is much cleaner and environment friendly resource . The processes associated with current generation don’t emit greenhouse gases.
- It has lower maintenance . Once electric current is produced it requires minimal labor. Electric vehicles are cheaper to maintain since they don’t require regular oil change.
Disadvantages of Electric Current
Dis-advantages of electric current:
- Any carelessness while dealing with electric current can be dangerous. The human body already conducts electricity, and after meeting live electricity, an electric current flows through tissues that cause an electric shock, also called electrocution. We often hear about such incidents.
- It can cause other injuries like flame, lightning, flash, and true. These can cause fire-breakouts. Places having electric wiring are more prone to fires due to electric short circuit.
- Electric vehicles can cause electric emission. Electric vehicles are worse for the climate than gasoline, petrol, or diesel vehicles because of the power plant emission.
- Generation of electricity requires a cost. This cost is high and in addition to this cost we have a cost of maintenance too.
Conclusion
We have seen how phenomena’s like electrostatic induction, Generation of electric field , heating up of resistors occur due to one basic thing called ‘electronic current’. Current can be generated using various methods depending upon the user need. We have also seen various applications of current and how it is used in various fields of electronics like power plants, electroplating . Modern electronic industry is based largely on generation of current hence various methods are being employed for efficient current generation.
What are some examples of conductors of electric current?
Some popular examples of conductors of electric current are human body, aqueous solutions, metals like gold, silver, aluminium.
Define Ampere.
Ampere is defined as the unit of electric current that is equal to the flow of one Coulomb per second.
What is Coulomb’s Law?
Coulomb’s law states that the magnitude of the electrostatic force of attraction or repulsion between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of the magnitudes of charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...