Convert given Binary Tree to Symmetric Tree by adding minimum number of nodes
Last Updated :
02 Jun, 2022
Given a Binary Tree, the task is to convert the given Binary Tree to the Symmetric Tree by adding the minimum number of nodes in the given Tree.
Examples:
Input:
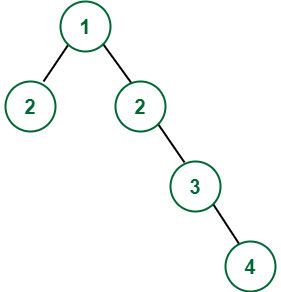
Output:
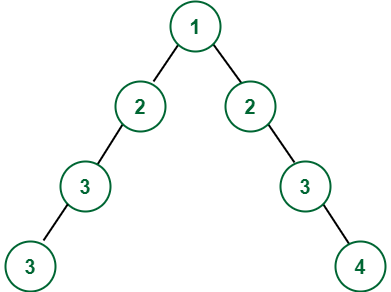
Input:
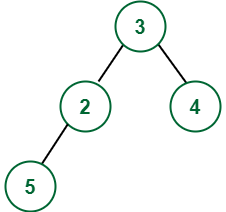
Output:
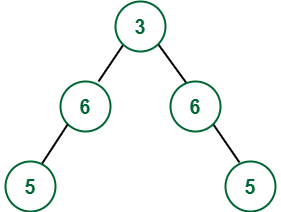
Approach: To solve this problem, follow the below steps:
- Make a function buildSymmetricTree which will accept two parameters root1 and root2.
- Here, root1 and root2, are the nodes that are at the symmetrical places of one another.
- So initially, both root1 and root2 will contain the value of the root and in each recursive call:
- If root1 exists but root2 doesn’t then create a new node with the value same as root1 and place it in the position of root2.
- Follow the above step also for root1 if root2 exists but root1 doesn’t.
- If the value of root1 and root2 is not the same, then change the value of both nodes to the sum of them.
- Now, make the next two recursive calls for the symmetrical positions at (root1->left, root2->right) and (root1->right, root2->left).
- The tree will become symmetrical after all recursive calls will be made.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node *left, *right;
Node(int val)
{
this->val = val;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
Node* buidSymmetricTree(Node* root1,
Node* root2)
{
if (root1 == NULL and root2 == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
if (root1 == NULL) {
Node* node = new Node(root2->val);
root1 = node;
}
if (root2 == NULL) {
Node* node = new Node(root1->val);
root2 = node;
}
if (root1->val != root2->val) {
int temp = root1->val + root2->val;
root1->val = temp;
root2->val = temp;
}
root1->left
= buidSymmetricTree(
root1->left, root2->right);
root1->right
= buidSymmetricTree(
root1->right, root2->left);
return root1;
}
void inorder(Node* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
inorder(root->left);
cout << root->val << " ";
inorder(root->right);
}
int main()
{
Node* root = new Node(3);
root->left = new Node(2);
root->right = new Node(4);
root->left->left = new Node(5);
buidSymmetericTree(root, root);
inorder(root);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static class Node {
int val;
Node left, right;
Node(int val)
{
this.val = val;
left = right = null;
}
};
static Node buidSymmetricTree(Node root1,
Node root2)
{
if (root1 == null && root2 == null) {
return null;
}
if (root1 == null) {
Node node = new Node(root2.val);
root1 = node;
}
if (root2 == null) {
Node node = new Node(root1.val);
root2 = node;
}
if (root1.val != root2.val) {
int temp = root1.val + root2.val;
root1.val = temp;
root2.val = temp;
}
root1.left
= buidSymmetricTree(
root1.left, root2.right);
root1.right
= buidSymmetricTree(
root1.right, root2.left);
return root1;
}
static void inorder(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
return;
inorder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.val+ " ");
inorder(root.right);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node root = new Node(3);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(4);
root.left.left = new Node(5);
buidSymmetericTree(root, root);
inorder(root);
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.left = self.right = None
def buidSymmetricTree(root1, root2):
if (root1 == None and root2 == None):
return None
if (root1 == None):
node = Node(root2.val)
root1 = node
if (root2 == None):
node = Node(root1.val)
root2 = node
if (root1.val != root2.val):
temp = root1.val + root2.val
root1.val = temp
root2.val = temp
root1.left = buidSymmetricTree( root1.left, root2.right)
root1.right = buidSymmetricTree(root1.right, root2.left)
return root1
def inorder(root):
if (root == None):
return
inorder(root.left)
print(root.val, end=" ")
inorder(root.right)
root = Node(3)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(4)
root.left.left = Node(5)
buidSymmetericTree(root, root)
inorder(root)
|
C#
using System;
public class GFG {
public class Node {
public int val;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
left = right = null;
}
};
static Node buidSymmetricTree(Node root1, Node root2)
{
if (root1 == null && root2 == null) {
return null;
}
if (root1 == null) {
Node node = new Node(root2.val);
root1 = node;
}
if (root2 == null) {
Node node = new Node(root1.val);
root2 = node;
}
if (root1.val != root2.val) {
int temp = root1.val + root2.val;
root1.val = temp;
root2.val = temp;
}
root1.left = buidSymmetricTree(root1.left, root2.right);
root1.right = buidSymmetricTree(root1.right, root2.left);
return root1;
}
static void inorder(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
return;
inorder(root.left);
Console.Write(root.val + " ");
inorder(root.right);
}
public static void Main(String[] args) {
Node root = new Node(3);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(4);
root.left.left = new Node(5);
buidSymmetericTree(root, root);
inorder(root);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.val = val;
this.left = this.right = null;
}
};
function buidSymmetricTree(root1,
root2) {
if (root1 == null && root2 == null) {
return null;
}
if (root1 == null) {
let node = new Node(root2.val);
root1 = node;
}
if (root2 == null) {
let node = new Node(root1.val);
root2 = node;
}
if (root1.val != root2.val) {
let temp = root1.val + root2.val;
root1.val = temp;
root2.val = temp;
}
root1.left
= buidSymmetricTree(
root1.left, root2.right);
root1.right
= buidSymmetricTree(
root1.right, root2.left);
return root1;
}
function inorder(root) {
if (root == null)
return;
inorder(root.left);
document.write(root.val + " ");
inorder(root.right);
}
let root = new Node(3);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(4);
root.left.left = new Node(5);
buidSymmetericTree(root, root);
inorder(root);
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...