Components of IOT and relation with Cloud Computing
Last Updated :
25 May, 2022
In this blog I would to like explain the importance of IOT and Cloud Computing and How both are linked to each other.
What is IOT ?
Internet of Things (IoT) is an ecosystem of connected physical objects that are accessible through the Internet (formal definition). So, in simple terms IOT means anything that can be connected to internet and can be controlled / monitored using Internet from our smart devices or PCs.
The “things” specified here can be anything from small tracking chips to actual smart cars on road, all these can be categorized as IOT. All things that are connected to internet are assigned with IP to it so that it can be monitored uniquely using internet. The embedded systems and technology are the objects that help in realization of successful IOT.
Why to use IOT ?
Everything can be connected to internet and can be controlled from internet. Systems can be automated so that sensors upload data continuously to cloud and various algorithms (like Machine Learning Techniques) can be applied to this data so that we can analyse the data properly and produce efficient outputs. And based on results, the clouds can perform pre-defined actions in response to sensor data.
Security can be enhanced from our smart devices as we can keep an eye at our homes, work places etc. Automated rapid responses like in industries when certain parameters get disturbed automatically actions are triggered to counter the effect. (License plate recognition used in Traffic systems). Monitor places where surveillance is difficult.
- IOT in Agriculture, Health Care etc.
- Smart Wearables, Vehicles and cars.
- Smart Grids and Industries.
- Smart cities and Smart Grids.
Major Components of IOT:
These are explained as following below.
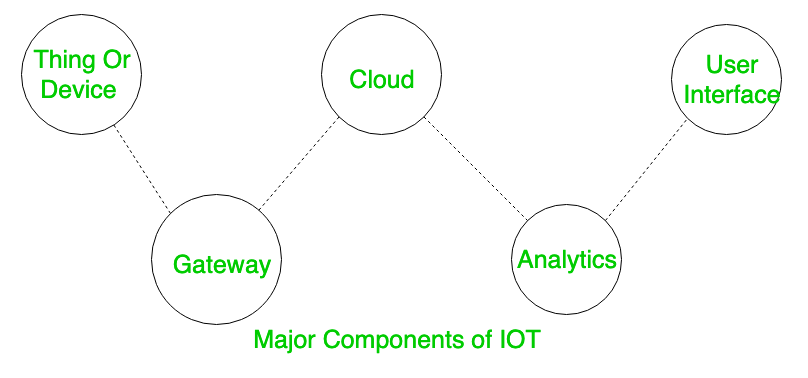
- Things or Device
These are fitted with sensors and actuators. Sensors collect data from the environment and give to gateway where as actuators performs the action (as directed after processing of data).
- Gateway
The sensors give data to Gateway and here some kind of pre-processing of data is even done. It also acts as a level of security for the network and for the transmitted data.
- Cloud
The data after being collected is uploaded to cloud. Cloud in simple terms is basically a set of servers connected to internet 24*7.
- Analytics
The data after being received in the cloud processing is done . Various algorithms are applied here for proper analysis of data (techniques like Machine Learning etc are even applied).
- User Interface
User end application where user can monitor or control the data.
Is the cloud necessary for IOT?
The answer is simply no because we can do the processing even locally instead of uploading the data into the cloud. These techniques are called as “Fog Computing ” or “Edge Computing ”. But then, why we associate cloud computing with IOT, the reason is also simple because cloud computing gives us scalability and low cost of operations.
If we stop using the Cloud resources then this would slow down the growth of the IOT career .
So, benefits of using the clouds are :-
- Decreased cost of setting up new infrastructure.
- Highly Scalable (we can use as much we want to).
- Pay as much we use (just like house electricity bills).
- Easily accessible just by internet.
What is exactly Cloud Computing ?
In simple terms, it is defined as storing and accessing of data and computing services over the internet rather than managing the files in a local storage. Cloud computing makes it possible to save these files(data)over internet. It’s like having a high performance computer some where in internet and we are only using the computing resources of that virtual high performance computer.
Essential characteristics of Cloud Computing:
- On-demand Self Service.
- Broad network access.
- Resource Pooling.
- On demand rapid expansion of resources.
- Pay as you use.
How to use Cloud ?
Cloud can be used as :-
- Infrastructure As A Service (IaaS):
It is the lowest level of cloud service. Here we just allocate the hardware as per the demand and rest everything is on our part that is starting from choosing OS to application programs.
- Platform As A Service (PaaS):
Here we don’t deal with the underlying hardware, Operating Systems etc. But here we have control over the applications that we want to use and put in our virtual system. In simple terms, it provides an environment for Development purpose.
- Software As A Service (SaaS):
Here consumers are allowed to use the licensed applications (that they have subscribed). Its like on-demand software. In simple terms, it means we take subscriptions of the services we want and after that we are to those applications hosted in the cloud.
Types of Cloud:
These are explained below:
- Public Cloud:
Cloud Infrastructure can be used by general public.
- Private Cloud:
Cloud Infrastructure to be used by specific organisation .
- Community Cloud:
Cloud Infrastructure to be used by specific community of consumers from organisation who may be working together. Example.: Healthcare industry
- Hybrid Cloud:
Here two or more cloud infrastructures are implemented and there is a switching between resources as per demand and need.
So, we discussed about importance of IOT and Cloud Computing. But what are the challenges in IOT ?
- Security:
As the number of devices connected to internet are increasing so as poorly designed devices are also getting more prone to security threats.
- Privacy:
The data of the user has to be protected from theft as almost all activities done by an individual can be monitored.
- Standards:
There are no proper standards and documentations discussing the best practices.
- Regulation:
Legal issues with Int involves cross border data flow, data retention and destruction policies etc.
- Development:
It should be expanded and implemented to even developing and under developed countries instead of focusing only on developed countries.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...