Compare effect of different scalers on data with outliers in Scikit Learn
Last Updated :
05 Feb, 2023
Feature scaling is an important step in data preprocessing. Several machine learning algorithms like linear regression, logistic regression, and neural networks rely on the fine-tuning of weights and biases to generalize better. However, features with different scales could prevent such models from performing well as features with higher values dominate the ones with lower values. Scikit Learn offers a variety of scalers to perform feature scaling. This article briefly describes the effect of different scalers on data with outliers.
For demonstration purposes, the California Housing Dataset of Scikit Learn is considered. This dataset consists of 8 attributes and the task is to predict the median house value is $100,000.
Importing required libraries
Python3
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_california_housing
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from sklearn.preprocessing import MaxAbsScaler
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.preprocessing import RobustScaler
from sklearn.preprocessing import PowerTransformer
from sklearn.preprocessing import QuantileTransformer
from sklearn.preprocessing import Normalizer
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
from sklearn.linear_model import SGDRegressor
import seaborn as sns
|
Load the dataset
Python3
data = fetch_california_housing(as_frame=True)
df = data.frame
df.head()
|
Output:
| |
MedInc |
HouseAge |
AveRooms |
AveBedrms |
Population |
AveOccup |
Latitude |
Longitude |
MedHouseVal |
| 0 |
8.3252 |
41.0 |
6.984127 |
1.023810 |
322.0 |
2.555556 |
37.88 |
-122.23 |
4.526 |
| 1 |
8.3014 |
21.0 |
6.238137 |
0.971880 |
2401.0 |
2.109842 |
37.86 |
-122.22 |
3.585 |
| 2 |
7.2574 |
52.0 |
8.288136 |
1.073446 |
496.0 |
2.802260 |
37.85 |
-122.24 |
3.521 |
| 3 |
5.6431 |
52.0 |
5.817352 |
1.073059 |
558.0 |
2.547945 |
37.85 |
-122.25 |
3.413 |
| 4 |
3.8462 |
52.0 |
6.281853 |
1.081081 |
565.0 |
2.181467 |
37.85 |
-122.25 |
3.422 |
Data information
Output:
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 20640 entries, 0 to 20639
Data columns (total 9 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 MedInc 20640 non-null float64
1 HouseAge 20640 non-null float64
2 AveRooms 20640 non-null float64
3 AveBedrms 20640 non-null float64
4 Population 20640 non-null float64
5 AveOccup 20640 non-null float64
6 Latitude 20640 non-null float64
7 Longitude 20640 non-null float64
8 MedHouseVal 20640 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(9)
memory usage: 1.4 MB
Now, let us analyze the distribution of each feature.
Python3
plt.figure(figsize=(15,12))
cols = df.columns
for i in range(len(cols)):
plt.subplot(3,3,i+1)
sns.distplot(df[cols[i]], kde = False)
plt.show()
|
Output:

Distribution plots
We can observe that median income has a long tail distribution, while average occupants have a few large outliers. Hence, we consider these 2 features for studying the impact of different scalers on outliers. Furthermore, let us see the impact of latitude and longitude on the target variable.
Plot Median House value with respect to Latitude and longitude
Python3
lat_long_plot = sns.scatterplot(y = df['Latitude'],
x = df['Longitude'],
data = df,
size = df['MedHouseVal'],
hue = df['MedHouseVal'],
palette = 'viridis')
lat_long_plot.set_xlabel('Longitude')
lat_long_plot.set_ylabel('Latitude')
|
Output:

Effect of latitude and longitude on median house value
We can observe that houses from a particular region have high values. Hence, latitude and longitude are also considered for training the model. Ultimately, latitude, longitude, and median income are used to train the model. Now the dataset is split into training and test sets.
Split Train and Test Data
Python3
X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(df,
df['MedHouseVal'],
test_size = 0.25,
random_state=42)
|
Define the Joint Distribution Plot function
Here we define the function which can plot joint distributions plot for data.
Python3
def plot_dist(data):
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 5))
sns.jointplot(x =data[0:1000, 0], y = data[0:1000, 5], data = data)
plt.show()
|
Define the Regression model
Here we define the Stochastic Gradient Descent regressor to build the model, then fit the model and predict on X_test new data, then apply mean squared error to find the accuracy of the model.
Python3
def linear_reg(X_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test):
reg_model = SGDRegressor()
reg_model.fit(X_train, Y_train)
pred = reg_model.predict(X_test)
accuracy = mean_squared_error(Y_test, pred)
return accuracy
|
Without scaling the data
Python3
plot_dist(X_train.values)
acc = linear_reg(X_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test)
print(f'MSE : {acc}')
|
Output:

Without Scaling the data
MSE : 1.3528478529652859e+29
Effect of Standard Scaler
Scikit Learn offers StandardScaler() for performing standardization.
Python3
std_scaler = StandardScaler()
X_train_std_scaler = std_scaler.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test_std_scaler = std_scaler.transform(X_test)
plot_dist(X_train_std_scaler)
acc = linear_reg(X_train_std_scaler, Y_train, X_test_std_scaler, Y_test)
print(f'Accuracy with standard scaler : {acc}')
|
Output:

Effect of Standard Scaler
Accuracy with standard scaler : 2.927062092029926e-07
We can observe that the scales of the 2 features are quite different. The median income is ranging from -2 to 6, whereas the average occupants is ranging from -0.1 to 0.6. Therefore, standard scalers cannot guarantee balanced feature scales.
Effect of MinMax Scaler
Scikit Learn offers MinMaxScaler() for normalization.
Python3
min_max_scaler = MinMaxScaler()
X_train_min_max_scaler = min_max_scaler.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test_min_max_scaler = min_max_scaler.transform(X_test)
plot_dist(X_train_min_max_scaler)
acc = linear_reg(X_train_min_max_scaler, Y_train, X_test_min_max_scaler, Y_test)
print(f'Accuracy with minmax scaler : {acc}')
|
Output:
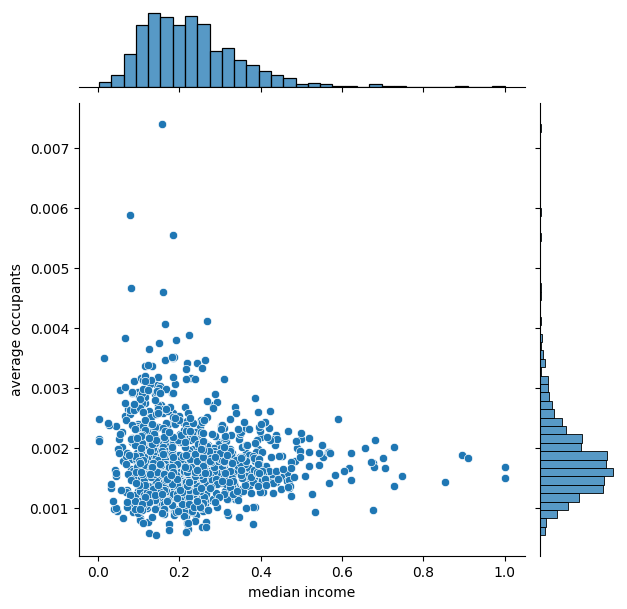
Effect of MinMax Scaler
Accuracy with minmax scaler : 0.005800840622553663
MinMax scaler reduces the range of feature values to [0, 1]. However, the range is quite different for the 2 features under consideration. Average occupants have a considerably smaller value compared to median income.
Effect of MaxAbs Scaler
MaxAbsScaler() is similar to MinMaxScaler(). However, the range of scaled values may vary depending on the feature values. The range is [0, 1] if only positive values are present, [-1, 0] if only negative values are present, and [-1, 1] if both values are present.
Python3
max_abs_scaler = MaxAbsScaler()
X_train_max_abs_scaler = max_abs_scaler.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test_max_abs_scaler = max_abs_scaler.transform(X_test)
plot_dist(X_train_max_abs_scaler)
acc = linear_reg(X_train_max_abs_scaler, Y_train, X_test_max_abs_scaler, Y_test)
print(f'Accuracy with maxabs scaler : {acc}')
|
Output:
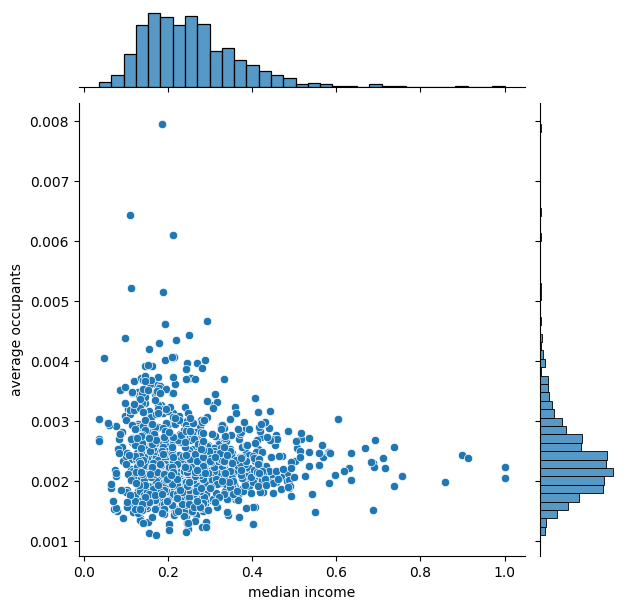
Effect of Max Absolute Scaler
Accuracy with maxabs scaler : 0.006259459937552328
In this case, it produces results similar to MinMaxScaler().
Effect of Robust Scaler
Scikit Learn provides RobustScaler() which makes use of inter-quartile range for feature scaling.
Python3
robust_scaler = RobustScaler()
X_train_robust_scaler = robust_scaler.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test_robust_scaler = robust_scaler.transform(X_test)
plot_dist(X_train_robust_scaler)
acc = linear_reg(X_train_robust_scaler, Y_train, X_test_robust_scaler, Y_test)
print(f'Accuracy with robust scaler : {acc}')
|
Output:
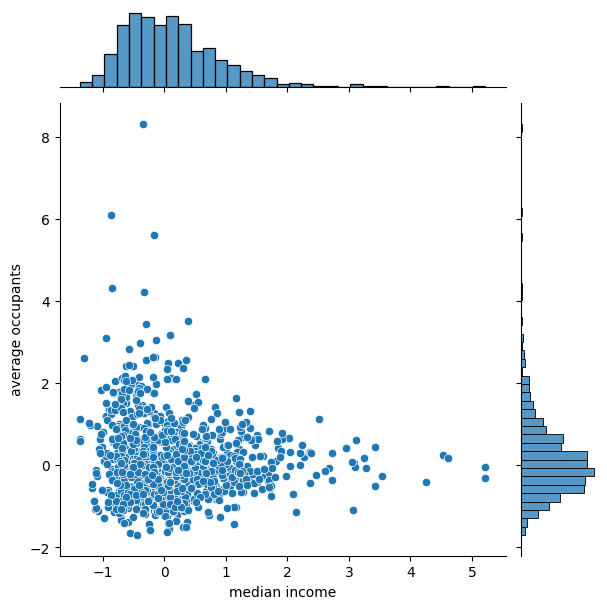
Effect of Robust Scaler
Accuracy with robust scaler : 1.931800745764342e+20
Effect of Power Transform
Python3
power_transform = PowerTransformer()
X_train_power_transform = power_transform.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test_power_transform = power_transform.transform(X_test)
plot_dist(X_train_power_transform)
acc = linear_reg(X_train_power_transform, Y_train, X_test_power_transform, Y_test)
print(f'Accuracy with power transform : {acc}')
|
Output:

Effect of Power Transform
Accuracy with power transform : 0.09313345304679063
Effect of Quantile Transformer
Python3
quantiles = QuantileTransformer(n_quantiles=23, random_state=0)
X_train_quantiles = quantiles.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test_quantiles = quantiles.transform(X_test)
plot_dist(X_train_quantiles)
acc = linear_reg(X_train_quantiles, Y_train, X_test_quantiles, Y_test)
print(f'Accuracy with QuantileTransformer: {acc}')
|
Output:

Effect of Quantile Transformer
Effect of Normalizer
Python3
from sklearn.preprocessing import Normalizer
normalize = Normalizer()
X_train_normalize = normalize.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test_normalize = normalize.transform(X_test)
plot_dist(X_train_normalize)
acc = linear_reg(X_train_normalize, Y_train, X_test_normalize, Y_test)
print(f'Accuracy with Normalizer : {acc}')
|
Output:

Effect of Normalizer
Accuracy with Normalizer : 1.3216531944583318
Model Accuracy
Let’s print the accuracy of each model
Python3
acc = linear_reg(X_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test)
print(f'General Accuracy : {acc}')
acc = linear_reg(X_train_std_scaler, Y_train, X_test_std_scaler, Y_test)
print(f'Accuracy with standard scaler : {acc}')
acc = linear_reg(X_train_min_max_scaler, Y_train, X_test_min_max_scaler, Y_test)
print(f'Accuracy with minmax scaler : {acc}')
acc = linear_reg(X_train_max_abs_scaler, Y_train, X_test_max_abs_scaler, Y_test)
print(f'Accuracy with maxabs scaler : {acc}')
acc = linear_reg(X_train_robust_scaler, Y_train, X_test_robust_scaler, Y_test)
print(f'Accuracy with robust scaler : {acc}')
acc = linear_reg(X_train_power_transform, Y_train, X_test_power_transform, Y_test)
print(f'Accuracy with power transform : {acc}')
acc = linear_reg(X_train_quantiles, Y_train, X_test_quantiles, Y_test)
print(f'Accuracy with QuantileTransformer: {acc}')
acc = linear_reg(X_train_normalize, Y_train, X_test_normalize, Y_test)
print(f'Accuracy with Normalizer : {acc}')
|
Output:
General Accuracy : 2.6731951662759754e+28
Accuracy with standard scaler : 6.1103137019148144e-06
Accuracy with minmax scaler : 0.005842587280784744
Accuracy with maxabs scaler : 0.006149996463712555
Accuracy with robust scaler : 1.0374102250716266e+23
Accuracy with power transform : 0.09243653923790224
Accuracy with QuantileTransformer: 0.12639279065095635
Accuracy with Normalizer : 1.322663822919674
It is evident that feature scaling improves accuracy significantly. In the current scenario, feature scaling with standard scaler and min-max scaler provides the best accuracy.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...