Reversal algorithm for Array rotation
Last Updated :
06 Apr, 2023
Given an array arr[] of size N, the task is to rotate the array by d position to the left.
Examples:
Input: arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}, d = 2
Output: 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1, 2
Explanation: If the array is rotated by 1 position to the left,
it becomes {2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1}.
When it is rotated further by 1 position,
it becomes: {3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1, 2}
Input: arr[] = {1, 6, 7, 8}, d = 3
Output: 8, 1, 6, 7
Approach: We have already discussed several methods in this post. The ways discussed there are:
- Using another temporary array.
- Rotating one by one.
- Using a juggling algorithm.
Another Approach (The Reversal Algorithm): Here we will be discussing another method which uses the concept of reversing a part of array. The intuition behind the idea is mentioned below:
Intuition:
If we observe closely, we can see that a group of array elements is changing its position. For example see the following array:
arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7} and d = 2. The rotated array is {3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1, 2}
The group having the first two elements is moving to the end of the array. This is like reversing the array.
- But the issue is that if we only reverse the array, it becomes {7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1}.
- After rotation the elements in the chunks having the first 5 elements {7, 6, 5, 4, 3} and the last 2 elements {2, 1} should be in the actual order as of the initial array [i.e., {3, 4, 5, 6, 7} and {1, 2}]but here it gets reversed.
- So if those blocks are reversed again we get the desired rotated array.
So the sequence of operations is:
- Reverse the whole array
- Then reverse the last ‘d’ elements and
- Then reverse the first (N-d) elements.
As we are performing reverse operations it is also similar to the following sequence:
- Reverse the first ‘d’ elements
- Reverse last (N-d) elements
- Reverse the whole array.
Algorithm: The algorithm can be described with the help of the below pseudocode:
Pseudocode:
Algorithm reverse(arr, start, end):
mid = (start + end)/2
loop from i = start to mid:
swap (arr[i], arr[end-(mid-i+1)])
Algorithm rotate(arr, d, N):
reverse(arr, 1, d) ;
reverse(arr, d + 1, N);
reverse(arr, 1, N);
Illustration:
Follow the illustration below to for better understanding of the algorithm and intuition:
For example take the array arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7} and d = 2.

Array
The rotated array will look like:

Rotated Array
1st Step: Consider the array as a combination of two blocks. One containing the first two elements and the other containing the remaining elements as shown above.
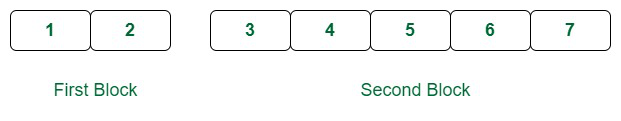
Considered 2 blocks
2nd Step: Now reverse the first d elements. It becomes as shown in the image
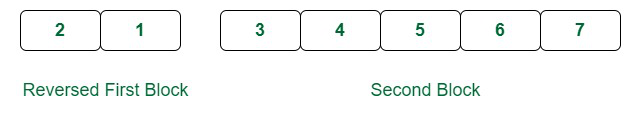
Reverse the first K elements
3rd Step: Now reverse the last (N-d) elements. It become as it is shown in the below image:

Reverse the last (N-K) elements
4th Step: Now the array is the exact reversed form of how it should be if left shifted d times. So reverse the whole array and you will get the required rotated array.

The total array is reversed
See that the array is now the same as the rotated array.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <algorithm> // for reverse function
#include <iostream> // for input/output operations
#include <vector> // for vector container
using namespace std;
void rotateArray(vector<int>& arr, int k)
{
int n = arr.size();
k %= n;
reverse(arr.begin(), arr.end());
reverse(arr.begin(), arr.begin() + k);
reverse(arr.begin() + k, arr.end());
}
int main()
{
vector<int> arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int k = 2;
rotateArray(arr, k);
for (int i : arr) {
cout << i << " ";
}
return 0;
}
|
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void reverseArray(int arr[], int start, int end)
{
while (start < end) {
int temp = arr[start];
arr[start] = arr[end];
arr[end] = temp;
start++;
end--;
}
}
void leftRotate(int arr[], int d, int n)
{
if (d == 0)
return;
d = d % n;
reverseArray(arr, 0, d - 1);
reverseArray(arr, d, n - 1);
reverseArray(arr, 0, n - 1);
}
void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 };
int N = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int d = 2;
leftRotate(arr, d, N);
printArray(arr, N);
return 0;
}
|
C
#include <stdio.h>
void printArray(int arr[], int size);
void reverseArray(int arr[], int start, int end);
void leftRotate(int arr[], int d, int n)
{
if (d == 0)
return;
d = d % n;
reverseArray(arr, 0, d - 1);
reverseArray(arr, d, n - 1);
reverseArray(arr, 0, n - 1);
}
void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
void reverseArray(int arr[], int start, int end)
{
int temp;
while (start < end) {
temp = arr[start];
arr[start] = arr[end];
arr[end] = temp;
start++;
end--;
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int d = 2;
leftRotate(arr, d, n);
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class LeftRotate {
static void leftRotate(int arr[], int d)
{
if (d == 0)
return;
int n = arr.length;
d = d % n;
reverseArray(arr, 0, d - 1);
reverseArray(arr, d, n - 1);
reverseArray(arr, 0, n - 1);
}
static void reverseArray(int arr[], int start, int end)
{
int temp;
while (start < end) {
temp = arr[start];
arr[start] = arr[end];
arr[end] = temp;
start++;
end--;
}
}
static void printArray(int arr[])
{
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 };
int n = arr.length;
int d = 2;
leftRotate(arr, d);
printArray(arr);
}
}
|
Python3
def reverseArray(arr, start, end):
while (start < end):
temp = arr[start]
arr[start] = arr[end]
arr[end] = temp
start += 1
end = end-1
def leftRotate(arr, d):
if d == 0:
return
n = len(arr)
d = d % n
reverseArray(arr, 0, d-1)
reverseArray(arr, d, n-1)
reverseArray(arr, 0, n-1)
def printArray(arr):
for i in range(0, len(arr)):
print (arr[i],end=' ')
arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
n = len(arr)
d = 2
leftRotate(arr, d)
printArray(arr)
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static void leftRotate(int[] arr, int d)
{
if (d == 0)
return;
int n = arr.Length;
d = d % n;
reverseArray(arr, 0, d - 1);
reverseArray(arr, d, n - 1);
reverseArray(arr, 0, n - 1);
}
static void reverseArray(int[] arr, int start,
int end)
{
int temp;
while (start < end) {
temp = arr[start];
arr[start] = arr[end];
arr[end] = temp;
start++;
end--;
}
}
static void printArray(int[] arr)
{
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++)
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
}
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 };
int n = arr.Length;
int d = 2;
leftRotate(arr, d);
printArray(arr);
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function leftRotate(&$arr, $d, $n)
{
if ($d == 0)
return;
$d = ($d % $n);
reverseArray($arr, 0, $d - 1);
reverseArray($arr, $d, $n - 1);
reverseArray($arr, 0, $n - 1);
}
function reverseArray(&$arr,
$start, $end)
{
while ($start < $end)
{
$temp = $arr[$start];
$arr[$start] = $arr[$end];
$arr[$end] = $temp;
$start++;
$end--;
}
}
function printArray($arr, $size)
{
for ($i = 0; $i < $size; $i++)
print $arr[$i]." ";
}
$arr = array(1, 2, 3,
4, 5, 6, 7);
$n = sizeof($arr);
$d = 2;
leftRotate($arr, $d, $n);
printArray($arr, $n);
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
function reverseArray(arr, start, end) {
while (start < end) {
var temp = arr[start];
arr[start] = arr[end];
arr[end] = temp;
start++;
end--;
}
}
function leftRotate(arr, d, n) {
if (d == 0) return;
d = d % n;
reverseArray(arr, 0, d - 1);
reverseArray(arr, d, n - 1);
reverseArray(arr, 0, n - 1);
}
function printArray(arr, size)
{
for (var i = 0; i < size; i++) document.write(arr[i] + " ");
}
var arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7];
var n = arr.length;
var d = 2;
leftRotate(arr, d, n);
printArray(arr, n);
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Another Method :- Using C++ STL reverse
C++
#include <algorithm> // for reverse function
#include <iostream> // for input/output operations
#include <vector> // for vector container
using namespace std;
void rotateArray(vector<int>& arr, int k)
{
int n = arr.size();
k %= n;
reverse(arr.begin(), arr.end());
reverse(arr.begin(), arr.begin() + k);
reverse(arr.begin() + k, arr.end());
}
int main()
{
vector<int> arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int k = 2;
rotateArray(arr, k);
for (int i : arr) {
cout << i << " ";
}
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList<Integer> arr = new ArrayList<>();
arr.add(1);
arr.add(2);
arr.add(3);
arr.add(4);
arr.add(5);
int k = 2;
rotateArray(arr, k);
for (int i : arr) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}
public static void rotateArray(ArrayList<Integer> arr,
int k)
{
int n = arr.size();
k %= n;
Collections.reverse(arr);
for (int i = 0; i < k / 2; i++) {
int temp = arr.get(i);
arr.set(i, arr.get(k - i - 1));
arr.set(k - i - 1, temp);
}
for (int i = k; i < (n + k) / 2; i++) {
int temp = arr.get(i);
arr.set(i, arr.get(n + k - i - 1));
arr.set(n + k - i - 1, temp);
}
}
}
|
Python3
def rotateArray(arr, k):
n = len(arr);
k %= n;
arr[0:n] = arr[0:n][::-1]
arr[0:k] = arr[0:k][::-1]
arr[k:n] = arr[k:n][::-1]
arr = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ];
k = 2;
rotateArray(arr, k);
for i in range(0,len(arr)):
print(arr[i], end= " ");
|
Javascript
function rotateArray(arr, k) {
const n = arr.length;
k %= n;
arr.reverse();
for (let i = 0; i < k / 2; i++) {
const temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[k - i - 1];
arr[k - i - 1] = temp;
}
for (let i = k; i < (n + k) / 2; i++) {
const temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[n + k - i - 1];
arr[n + k - i - 1] = temp;
}
}
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const k = 2;
rotateArray(arr, k);
console.log(arr.join(' '));
|
C#
using System;
using System.Linq;
namespace ArrayRotation {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int k = 2;
RotateArray(ref arr, k);
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(" ", arr));
Console.ReadKey();
}
static void RotateArray(ref int[] arr, int k)
{
int n = arr.Length;
k %= n;
Array.Reverse(arr, 0, n - k);
Array.Reverse(arr, n - k, k);
Array.Reverse(arr);
}
}
}
|
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...