SQL CASE Statement
Last Updated :
30 Apr, 2024
SQL CASE statement is a control statement that allows for the execution of different actions based on specified conditions. It evaluates a list of conditions and returns a value based on the first true condition.
For example, we can use the CASE statement for categorizing the employees based on their salary range and displaying the corresponding job title. In this article, we will explore the CASE-Switch Statement in SQL. The CASE statement is SQL’s way of handling if/else logic.
CASE Statement in SQL
The CASE Statement in SQL allows to conditionally assign values based on different conditions. It goes through the given conditions and returns the value when any condition is met.
Once a condition is met, the CASE statement will return the result and not read the rest of the conditions. If no conditions are true, then it will return the value in the clause.
Note: If no condition is true and ELSE part is missing, CASE statement will return Null
Syntax
CASE case_value
WHEN condition THEN result1
WHEN condition THEN result2
…
Else result
END CASE;
SQL CASE Statement Example
Let’s look at some examples of the CASE statement in SQL to understand it better.
Demo SQL Database
We will be using this sample SQL table for our examples on SQL CASE statement:
| CustomerID | CustomerName | LastName | Country | Age | Phone |
|---|
| 1 | Shubham | Thakur | India | 23 | xxxxxxxxxx |
| 2 | Aman | Chopra | Australia | 21 | xxxxxxxxxx |
| 3 | Naveen | Tulasi | Sri Lanka | 24 | xxxxxxxxxx |
| 4 | Aditya | Arpan | Austria | 21 | xxxxxxxxxx |
| 5 | Nishant. Salchichas S.A. | Jain | Spain | 22 | xxxxxxxxxx |
You can create the same Database in your system, by writing the following MySQL query:
MySQL
CREATE TABLE Customer(
CustomerID INT PRIMARY KEY,
CustomerName VARCHAR(50),
LastName VARCHAR(50),
Country VARCHAR(50),
Age int(2),
Phone int(10)
);
-- Insert some sample data into the Customers table
INSERT INTO Customer (CustomerID, CustomerName, LastName, Country, Age, Phone)
VALUES (1, 'Shubham', 'Thakur', 'India','23','xxxxxxxxxx'),
(2, 'Aman ', 'Chopra', 'Australia','21','xxxxxxxxxx'),
(3, 'Naveen', 'Tulasi', 'Sri lanka','24','xxxxxxxxxx'),
(4, 'Aditya', 'Arpan', 'Austria','21','xxxxxxxxxx'),
(5, 'Nishant. Salchichas S.A.', 'Jain', 'Spain','22','xxxxxxxxxx');
Adding Multiple Conditions to a CASE statement Example
We can add multiple conditions in the CASE statement by using multiple WHEN clauses.
Query:
SELECT CustomerName, Age,
CASE
WHEN Age> 22 THEN 'The Age is greater than 22'
WHEN Age = 21 THEN 'The Age is 21'
ELSE 'The Age is over 30'
END AS QuantityText
FROM Customer;
Output:
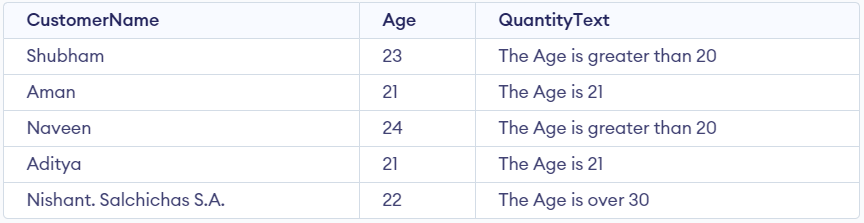
Output
Using CASE Statement With ORDER BY Clause Example
Let’s take the Customer Table which contains CustomerID, CustomerName, LastName, Country, Age, and Phone. We can check the data of the Customer table by using the ORDER BY clause with the CASE statement.
Query:
SELECT CustomerName, Country
FROM Customer
ORDER BY
(CASE
WHEN Country IS 'India' THEN Country
ELSE Age
END);
Output:

output
Important Points About CASE Statement
- The SQL CASE statement is a conditional expression that allows for the execution of different queries based on specified conditions.
- There should always be a SELECT in the CASE statement.
- END ELSE is an optional component but WHEN THEN these cases must be included in the CASE statement.
- We can make any conditional statement using any conditional operator (like WHERE ) between WHEN and THEN. This includes stringing together multiple conditional statements using AND and OR.
- We can include multiple WHEN statements and an ELSE statement to counter with unaddressed conditions.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...