What is Discharge Lamp?
Last Updated :
27 Feb, 2024
Artificial light lamps using electrical discharge as a means of artificial illumination constitute an important break-through. Discharge lamps are dependable, economic and long lasting forms of lighting equipment. The operation of these lamps is based upon the movement of an electric current through a vaporous gas in a closed chamber to cause the atoms or molecules therein to flash.
For instance, the fluorescent lamp is composed of mercury vapor plus phosphor coatings encapsulated in a glass tube. When the electric current passes through, it produces ultraviolet radiation which in turn causes an electron excitation of a phosphor. Another type utilizing gas-discharge lighting for high efficiency, predominantly found outdoors or in factories and workshops is the HID (high-intensity discharge) lamp which comes across a range of different types–from metal halide to high pressure sodium lamps.
What is Discharge Lamp?
Working Principles Discharge lamps operate by generating an arc or discharge in a gas-binding chamber. The lamp consists of electrodes, a sealed envelope and electric ballast to square the ups-and-downs in electrical current. The method relies on the fact that when electric current flows through gas or vapor, its electrodes ionize atoms in the substance and release photons to generate visible light. The application requires knowledge of the characteristics imparted by this mechanism, which vary according to lamp type and are used in different ways. For example HID or fluorescent lamps can be found almost anywhere from factories, big stores and public utilities buildings all housing multitudes of publicly lit up LG world products to flashing neon signs on green grocers shops fronts; while Discharge lamps ’ mechanism of action provides them with innate advantages in terms of efficiency and durability, which explain their current essential status for modern lighting.
In principle, the construction of a discharge lamp consists of several parts. Each was an essential participant in light generation.
- Envelope or Tube: The discharge lamp is enclosed within a sealed container made of glass or quartz and usually tubular in form. Held within this enclosure is the gas that will be discharged.
- Electrodes: This method places two electrodes inside the envelope at either end. They are electrodes, connected with conductive material which become the two points over which electric arc passes.
- Gas or Vapor: Inside the envelope is injected a special gas, vapor or air mixture. They are used to produce a gas that affects the nature of light emitted. Take the fluorescent lamp for instance. Mercury vapor is common in it as well.
- Phosphor Coating (for some lamps): As for fluorescent lamps, the outer surface of its interior wall can be phosphor coated. During the process of reproduction, this coating absorbs some ultraviolet light emitted by the slate and turns it into visible regularity.

Discharge Lamp
Working of Discharge Lamp
The working of Discharge Lamp is shown below that how it works and under what conditions :
- Initiation: It is an electrical circuit, and the electrodes are hooked up to it. There’s a voltage across them; this powers up one of those lamps. The tube contains either a gas or vapor that, under the action of this voltage, becomes conductive.
- Arc Formation: When the gas turns conductive, an electric arc is established across both electrodes. When this arc, by heating the gas itself to extreme temperatures and ionizing it (separating individual cells of matter), causes its atoms or molecules to yield photons.
- Light Emission: Atoms or molecules excited by electrons release photons to return to the original low energy state creating excitement. These emitted photons take the form of visible light, while lamps which have been coated with phosphor compounds also use ultraviolet radiation. This is then combined together with the original waves from the lamp to produce even more useful visible light. This ensures solid operation and stops immoderate current that might damage the lamp.
- Regulation (Ballast): They are generally put together with a ballast, which controls the amount of electrical current traveling through it.
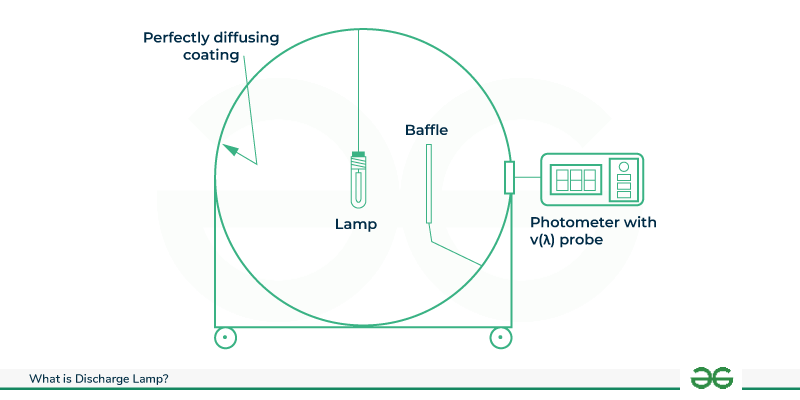
Working of Discharge Lamp
The running precept of a discharge lamp involves the controlled release of light thru the electric discharge manner in a fuel-filled enclosure, supplying an green and dependable supply of synthetic illumination.
Types of Discharge Lamp
The types of Discharge Lamp are discussed below:
- Fluorescent Lamp
- High-Intensity Discharge (HID) Lamps
- Neon Lamp
Fluorescent Lamp
Fluorescent lamps use a aggregate of argon and mercury vapor. When the lamp is energized, the mercury vapor produces ultraviolet (UV) light. This UV light then interacts with the phosphor coating inside the tube, inflicting it to emit seen light.
Features of Fluorescent Lamp
- Energy Efficiency: Fluorescent lamps are widely known for their superior energy efficiency relative to conventional incandescent bulbs. T8 tubes, which are more energy saving than in candescent and with better light and less heat.
- Long Lifespan: Their life is longer, usually eight to ten times that of an incandescent bulb. A fluorescent light has a long life. In particular, T8 tubes can last 20-30, 0 hours.
- Color Temperature Options: Since fluorescent lamps come in many coloration temperatures, users can select between warm and cool lighting. Difference in color temperatures Besides showing different colors of light, T8 tubes offer users more selection options.
- Instant Start or Rapid Start: There are immediate and rapid start talents depending on design, so fluorescent lamps can achieve short illumination.
- Dimmability: Some fluorescent lamps are also dimmable, offering the flexibility of adjusting their mild-toned output to fulfill peculiar tastes as well needs.
- Design and Structure: T8: The fluorescent-type linear lamp, made of tubular glass tube with phosphor hot coated.
- Instant Start or Rapid Start: Instant start T8s Easy to operate Our rapid-start versions are full of flexibility.
Circuit Diagram of Fluorescent Lamp
The fundamental circuit for a fluorescent lamp includes a ballast to adjust the modern-day. The ballast is connected in series with the lamp.

Circuit diagram of Fluorescent Lamp
Advantages of Fluorescent Lamp
- Energy Efficiency: Fluorescent lamps are more energy efficient than incandescent bulbs, and convert a greater portion of power into visible light.
- Long Lifespan: They have a longer life cycle, and thus fewer replacements over the years.
- Color Options: With a whole lot of color temperatures, fluorescent lamps allow flexibility in special lighting fixtures choices and packages.
- Instant and Rapid Start: Even fluorescent lamps, based on their type are available in immediate-start or fast-start alternatives for rapid illumination.
Disadvantages of Fluorescent Lamp
- Mercury Content: Fluorescent lamps contain a tiny bit of mercury, so they bring environmental problems and must be disposed properly.
- Flicker Issues: There are certain types of fluorescent lamps where the flickering can cause pain or complications for some human beings.
- Ballast Dependency: Ballasts are what fluorescent lamps rely upon, and failure of the ballast can result in flickering or even total loss.
- Dimming Challenges: Differences in dimming capabilities can also be an obstacle for traditional fluorescent lamps, compared to the other light technologies.
- Color Shift Over Time: As fluorescent lamps age, the shade may change slightly and mild is compromised throughout their lifetime.
High-Intensity Discharge (HID) Lamps
HID lamps encompass steel halide, high-pressure sodium, and mercury vapor lamps. They perform by using passing an electric powered current through a gas or a aggregate of gases and steel salts, generating extreme mild appropriate for outside and business programs.
Features of HID Lamps
- High Luminous Efficacy: HID lamps generate a large quantity of light per watt, and for this reason have high luminous efficacy.
- Longer Lifespan: Compared to incandescent bulbs, these lamps have a longer lifetimes. They are suitable for packages where frequent replacement is impractical.
- Wide Range of Applications: HID lamps are used in many devices: street lighting fixtures, sports arenas and business centers.
- Color Rendering: Metal halide HID lamps have good color rendering so they are suitable for those environments in which accurate color replication is important.
- High Output and Brightness: Humanizing the sentence: As they produce extreme, concentrated light output HID lamps are well suited to high-ceiling spaces and outdoor lighting fixtures.
Circuit Diagram of HID Lamps
HID lamps require a ballast as properly, and the circuit is more complicated than that of fluorescent lamps. The ballast is designed to offer the vital voltage and current regulation.
.png)
HID Lamps Circuit Diagram
Advantages of HID Lamps
- High Luminous Efficiency: HID lamps with metal halide produce a large quantity of light per unit electrical energy, and so are green.
- Applications in Large Spaces: Can be particularly applicable for use outside and in large inside areas where high-intensity lighting fixtures is demanded, such as sports arenas or commercial facilities.
- Good Color Rendering: Suitable colour rendering is also important on packages, and metal halide lamps are frequently used for this.
- Longer Lifespan: Another way to reduce upkeep costs is through the replacement of incandescent bulbs with HID lamps, which have a longer lifecycle.
- Versatility: For flexibility in lighting systems, HID lamps come in a variety of types made for various applications.
Disadvantages of HID Lamps
- Warm-Up Time: However, some HID lamps have a heat-up time before they get to full brightness. In certain applications this can be an undesirable trait.
- Complex Ballast Requirements: HID lamps, with the addition of extra complicated ballast structures add to both cost and preservation complexity.
- UV Emission: Because high-intensity discharge lamps, especially metal halide ones already emit ultraviolet (UV) radiation, UV blocking substances are added in some packages.
Neon Lamp
Neon lamps include neon gasoline, and whilst a high voltage is carried out throughout the electrodes, the gasoline emits mild. Neon lamps are recognized for their colourful glow and are frequently used for ornamental purposes.
Features of Neon Lamp
- Decorative Lighting: Because of their precise and colorful colors, neon lamps are widely used for decorative lighting fixtures, such as neon signs.
- Low Operating Temperature: Compared with other forms of discharge lamps, neon lamps work at extremely low temperatures. This enhances security in some applications.
- Custom Shapes and Sizes: They can be bent into myriad shapes and sizes, making it possible for creatively designed lighting fixtures.
- Low Power Consumption: Surprisingly low power intake: Neon lamps are also an energy-efficient option for ornamental schemes.
- Stable Light Output: For decorative or signage purposes, neon lamps are invaluable because when once lit they produce steady mild output. take, making them an strength-efficient desire for sure ornamental packages.
Circuit Diagram of Neon Lamp
The circuit for a neon lamp commonly includes a resistor to restrict the current and a transformer or high-voltage energy supply to generate the desired voltage.

Neon Lamp
Advantages of Neon Lamp
- Decorative Applications: Neon lamps are also widely used to create such visually attractive signage and art.
- Customizable Shapes: Tubes made of neon can be bent into numerous styles and sizes, offering many creative options.
- Low Power Consumption: Because of their high energy-efficiency, neon lamps are suitable for applications where low consumption figures play an important role.
- Stable Light Output: Once lit, neon lamps form a stable and continuous light source. Their stability has made them ideal for decorative as well as signage work.
- Decorative Applications: Both colorful and unique, the hues emitted by neon lamps provide another aesthetic element to their applications.
Disadvantages of Neon Lamp
- Fragile: These neon tubes are fragile and must be treated with care both when being installed or maintained to prevent breakage.
- Limited Color Range: Compared to other lighting technologies, neon lamps have a more restricted color range.
- Heat Dissipation : In some applications, neon lamps give off heat. Heat dissipation must be considered in these cases.
- Specialized Handling: Such things as the installation and maintenance of neon lamps require special knowledge or skills.
- Lifespan : A neon lamp’s lifespan is decent, but over the course of time problems may arise with gas leakage or worn electrodes.
Applications of Neon Lamp
- Commercial and Office Spaces: For commercial and office settings, they are widely rented for light-fluorescent or even working fluorescents.
- Street and Outdoor Lighting: Because high-depth discharge lamps, together with metal halide and excessive pressure sodium, cover huge areas efficiently it is broadly used for street lighting fixtures as well as outdoors programs.
- Retail and Signage: These neon lamps become frequently used in shops and other retail environments for creating special display items, enhancing the visibility of displays or attracting attention.
- Industrial Warehouses and Facilities: These high-intensity discharge lamps are especially suited to the demands of business, filling huge warehouses and centers flooded with light.
- Residential Lighting: Supplying high efficiency and stable illumination, fluorescent lamps are generally used in standard lighting fixtures for homes.
Characteristics of Discharge Lamp
- Gas or Vapor Excitation: Discharge lamps operate by means of passing an electric powered modern thru a fuel, vapor, or aggregate of gases, main to the excitation of atoms or molecules.
- Emission of Light: The excited atoms or molecules emit photons, ensuing in the production of visible light as they go back to a decrease power state.
- Enclosed Glass or Quartz Envelope: Discharge lamps are housed in sealed glass or quartz envelopes, which shield the gasoline or vapor and facilitate the electrical discharge manner.
- Electrodes for Electric Arc: Electrodes inside the lamp create the electrical arc or discharge vital for stimulating the fuel and initiating the light-emitting technique.
- Ballast Regulation: Many discharge lamps require a ballast in the electric circuit to alter the modern, making sure stable operation and stopping damage to the lamp.
- Energy Efficiency: Discharge lamps are usually more strength-efficient than conventional incandescent bulbs, changing a better percent of electrical input into seen light.
- Versatility in Applications: Discharge lamps discover programs throughout a wide range of settings, which includes residential, commercial, industrial, and decorative programs, showcasing their versatility in meeting diverse lighting fixtures wishes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, discharge lamps constitute a numerous and quintessential category of artificial lighting fixtures solutions, each tailored to satisfy precise illumination requirements. Fluorescent lamps, exemplified by means of the T8 Fluorescent Tube, are broadly embraced for their energy efficiency, long lifespan, and adaptability to diverse settings, from residential houses to business spaces. High-Intensity Discharge (HID) lamps, substantially the Metal Halide Lamp, excel in outdoor and commercial programs, supplying high luminous efficacy and desirable shade rendering. Neon lamps, exemplified by means of the Neon Sign Tube, make a contribution vibrancy and creativity to ornamental lighting fixtures, signage, and inventive installations.
As generation maintains to advance, the lighting fixtures panorama evolves, with LEDs rising as formidable competitors to discharge lamps. Nevertheless, discharge lamps stay applicable and widely utilized, contributing to the varied tapestry of lights answers throughout residential, commercial, and creative domain names. The choice amongst those lamps in the end hinges on unique lighting wishes, environmental concerns, and the favored visible effect.
FAQs on Discharge Lamp
1. Are all discharge lamps the identical, or do they serve distinct functions?
No, discharge lamps range in types and serve specific purposes. Fluorescent lamps are commonly used for well known lights, even as high-intensity discharge (HID) lamps, like steel halide, are favored for out of doors and commercial packages. Neon lamps, then again, are often employed for decorative and signage functions.
2. What are the environmental considerations associated with discharge lamps?
Discharge lamps, mainly fluorescent lamps, incorporate small quantities of mercury, posing environmental issues if not well disposed of. It is important to follow right recycling and disposal tactics to reduce environmental impact. Additionally, some excessive-depth discharge lamps may also incorporate substances that require careful dealing with at some stage in disposal.
3. How do discharge lamps evaluate to LED lighting fixtures in terms of efficiency and lifespan?
While discharge lamps, along with fluorescents and HIDs, are recognized for their performance and longevity, LED lighting fixtures has emerged as a more electricity-green and longer-lasting alternative. LEDs generally have a higher luminous efficacy and longer lifespan, making them a popular preference for diverse lighting packages. However, the selection between discharge lamps and LEDs depends on specific lights desires and alternatives.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...