What are Stand-Alone Procedures?
Last Updated :
21 Mar, 2024
Stand-Alone procedures are fundamental components in modern database systems. They make things organized, fast, and safe. Learning about these procedures helps people managing databases to create good ones. Using simple procedures right means data work flows smoothly.
In this article, we will see about stand-alone procedures. It will cover what they are, everyday terms, and why they are important in managing databases. By using simple explanations and examples, you’ll learn how these procedures help to organize database tasks and better the system’s performance.
What are Stand-Alone Procedures?
Stand-Alone Procedures make operations more effective in the Database Management Systems (DBMS). These procedures are self-contained with related to certain tasks or functionalities, functioning independently within the DBMS environment hence enabling modularity and flexibility in managing database operations. This increases effectiveness in databases. Though these examples are basic, extra safety checks should be added to keep data safe and accurate.
Primary Terminologies Related to Stand-Alone Procedures
- DBMS (Database Management System): It’s a software. It is useful for creating, organizing, and using databases. It lets users save, get, and manage data easily.
- Procedure: It is a certain step to do a task. When working with DBMS, we use procedures to perform pre-defined operations on the database.
- Stand-Alone Procedure: It is a DBMS procedure that stands alone, that doesn’t require any additional database entities or transactions. These procedures aren’t associated with any table or schema, meaning you can call them into action whenever you want.
Why Stand-Alone Procedures are Important?
- Modularity: Each process or procedure performs a specific function in the database. It’s simple and neat, and you can use it again without difficulty.
- Efficiency: Putting tasks that repeat or use a lot of resources into stand-alone procedures can improve a DBMS’s speed and capacity. It’s like getting a faster, stronger engine for your database.
- Better Security: Stand-alone procedures are like security for your data. They make sure only the right sensitive operations, keeping operations safe inside procedures.
How to Create an Independent Procedure?
- Design the Procedure: Choose a name, decide on input parameters, and determine its functions.
- Build the Procedure’s Logic: write the procedure’s inside workings. This includes altering and handling data effectively.
- Compile the Procedure: In the DBMS environment, compile the code for the procedure. This checks if its syntax and meanings are correct.
- Run the Procedure: After successful compiling, the independent procedure is all set. Commands or application integration can trigger it.
Example
Let’s first create a simple table named Customers in a SQL database, and then I’ll provide two examples of procedures that interact with this table.
CREATE TABLE Customer (
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(100),
adress VARCHAR(255)
);
Example 1: Inserting a record using procedure:
Now, let’s create aprocedures for inserting a new customer into the Customer table.
CREATE PROCEDURE insert_customer
@id INT,
@name VARCHAR(100),
@address VARCHAR(255)
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
INSERT INTO Customer (id, name, adress)
VALUES (@id, @name, @address);
SELECT 'Customer inserted successfully.' AS StatusMessage;
END;
Here’s how we work with the Customer table. We add new customers. You give us these details, and we do the job. Then, it let you know success or failure of the operation.
Output

create and insrt customer
now lets run that procedure, to check it.
EXEC [dbo].[insert_customer]
@id = 1,
@name = N'abul',
@address = N'lucknow';
Output

Run Insert Procedure
Example 2 – Verifying a Customer Record Using Procedure:
Now, let’s create aprocedures for verifing a customer from the Customer table.
CREATE PROCEDURE verify_customer
@id INT,
@name VARCHAR(100),
@address VARCHAR(255)
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
DECLARE @verification_status VARCHAR(50);
IF EXISTS (SELECT 1 FROM Customer WHERE id = @id)
BEGIN
IF EXISTS (SELECT 1 FROM Customer WHERE id = @id AND name = @name AND adress = @address)
BEGIN
SET @verification_status = 'Verified';
END
ELSE
BEGIN
SET @verification_status = 'Identity Mismatch';
END
END
ELSE
BEGIN
SET @verification_status = 'Customer Not Found';
END
SELECT @verification_status AS VerificationStatus;
END;
Output
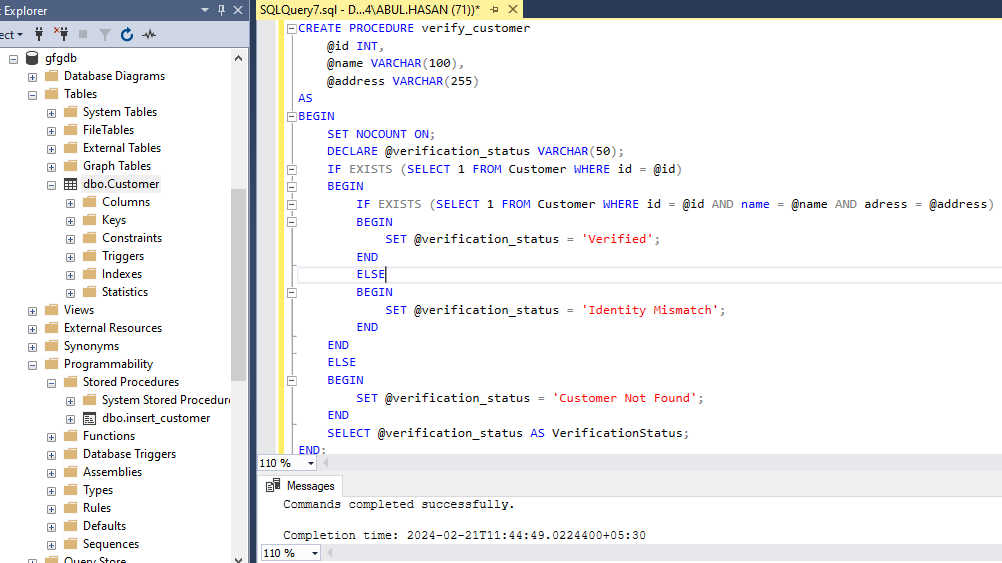
create procedure to verify
lets execute the procedure and verify a customer.
EXEC [dbo].[verify_customer]
@id = 1,
@name = N'abul',
@address = N'lucknow';
EXEC [dbo].[verify_customer]
@id = 1,
@name = N'abdul',
@address = N'lucknow';
EXEC [dbo].[verify_customer]
@id = 2,
@name = N'abul',
@address = N'lucknow';

verifying customer
Frequently Asked Questions on Stand-Alone Procedures – FAQs
What is stand-alone procedures in a DBMS?
A stand-alone procedure is a set of DBMS commands. It’s independent, doesn’t related on other database items or actions.
Is there a difference between a stand-alone procedure and functions or stored procedures in a DBMS?
Functions or procedures are related to certain tables. where Stand-alone procedures, aren’t related to anything. You can use them whenever you want, no specific database items needed.
Why would we use stand-alone procedures in DBMS?
Using stand-alone procedures gives some key benefits. It enhances modularity and performance. It boosts security. Finally, it helps reusing code and making maintenance easier in database systems.
Can stand-alone procedures be invoked from external applications?
Stand-alone procedures can be invoked from both external applications and within the DBMS environment, depending on the system’s configuration and access permissions.
How are stand-alone procedures created in a DBMS?
A DBMS Stand-alone procedures created by procedural programming language. Oracle uses PL/SQL. For Microsoft SQL Server, we use Transact-SQL.
Can stand-alone procedures be modified or updated after they are created?
We can change procedures as needed by altering their code in the DBMS. But, always be careful. Changes shouldn’t break current functionalities.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...