What is Network Attached Storage?
Last Updated :
26 Feb, 2024
In today’s data-driven world, the need for efficient and reliable storage solutions has become paramount for organizations of all sizes. Network-attached storage (NAS) is a cost-effective versatile solution for storing and managing data across networks, allowing centralized storage for multiple users and devices
NAS devices are special devices or storage servers that are connected to a network, enabling users to access and store data through a local area network (LAN) or wide area network (WAN) Unlike traditional storage solutions which are attached directly to a personal computer, a NAS provides a centralized storage repository that can be accessed by multiple users at the same time
What is Network Attached Storage(NAS)?
Network-attached storage (NAS) is a file-based storage architecture that makes stored data more accessible to networked devices means multiple users or client devices retrieve data from a single storage system. As the multiple clients or users connected through a Local Area Network access the data from a centralized disk capacity by Ethernet that’s why it is referred to as Network Attached Storage. Network Attached Storage(NAS) gives all the connected devices of the network a single access point for storage which is called NAS Storage Server.
The below image illustrates the Architecture of NAS:
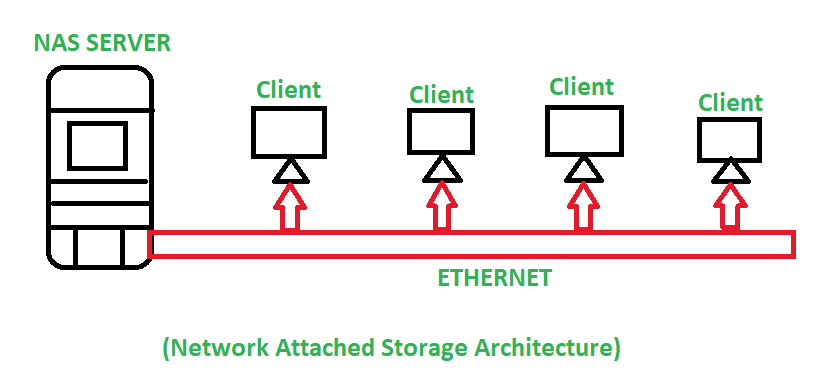
This is a simple Network Attached Storage Architecture which shows that there exists a central storage system i.e., NAS Server, and multiple clients/Users are connected to that NAS server and access data from that. NAS contains unstructured data, such as audio, video, websites, text files, etc.
- NAS Hardware: A NAS box, NAS unit, NAS server, or NAS head is an example of network appliance hardware (NAS) and is essentially just a server with CPUs, Random Access Memory (RAM), and storage devices.. These are the basic hardware system that builds the NAS hardware structure.
- NAS Software: Storage software is installed in the dedicated hardware of the NAS hardware system. NAS software is deployed on a lightweight Operating System.
- NAS Protocol: Data transfer protocols are there for sending and receiving data that are accessed by switches. Internet Protocol(IP) and Transfer Control Protocol(TCP) is the most fundamental data transfer protocol that is there through most clients/users transfer data. Network File Systems (NFS), and Server Message Blocks (SMB) are the format in which the files transfer in the protocols.
What is Network Attached Storage Used for?
- For storing and exchanging files
- For data backup and catastrophe recovery, create active data archives.
- Provide a virtual desktop environment.
- Test and create server-side and web apps.
- Stream torrents and media files
- Save any pictures and movies that you need to access frequently.
- Establish a printing repository within the company.
Components of NAS
- Processor: Every NAS has a processor at its core, which monitor the memory and central processing unit (CPU).
- Interface of a network: USB and Wi-Fi connectivity are two examples of direct computer connections that small Network Storage Devices (NAS) intended for desktop or single-user use may support.
- Physical storage: It usually takes the form of disc drives, is a requirement for every NAS. The drives, which frequently accommodate a variety of various storage devices, may be conventional magnetic HDDs, SSDs, or other non-volatile memory devices.
- Operating System: The OS arranges and controls the NAS hardware and makes storage accessible to clients, such as users and other apps, much like it does on a traditional computer.
Key Considerations in Selecting NAS
- Storage Capacity: Determine the amount of storage area you need each now and inside the future. Consider elements including the size of your existing records, anticipated information boom, and any particular requirements for storing multimedia documents, backups, or large datasets.
- Scalability: Choose a NAS that offers scalability to deal with future needs. Look for devices that support enlargement alternatives.
- Performance: Assess the performance requirements of your NAS, together with data transfer speeds, read/write s, and help for RAID configurations.
- Data Redundancy and Protection: Ensure that the NAS device offers sturdy facts safety capabilities, which includes RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) ranges for facts redundancy, snapshots for factor-in-time recovery, and built-in backup and replication abilties to guard against records loss.
- Data Accessibility and Sharing: Evaluate the NAS tool’s abilities for information accessibility and sharing across more than one devices and structures.
Future of Network Attached Storage
- Started supporting virtualization technology.
- Support to Gigabit Ethernet (GigE) for faster data transfer.
- scalable Storage capacity.
- Providing service from small to the large business sector.
Advantages of NAS
- Performance – Provides better performance in serving files.
- High-end data features – Provides storage management and security.
- Scale-up – Supports a scalable storage system.
- Accessibility – Every client/user in the network can easily access to NAS.
- Easy setup – NAS architecture is easy to set up.
Disadvantages of NAS
- Complexity: A SAN can increase workload management by adding new layers of complexity to already-existing systems.
- Cost: For new users, the expense of setting up and maintaining a SAN may be prohibitive.
- Management: SANs can be difficult to oversee and may need to be managed by a specialised professional.
Difference Between NAS and SAN
|
NAS
|
SAN
|
|
Network Attached Storage is shortened to NAS.
|
SAN stands for Storage Area Network.
|
|
It is a physical device that uses an Ethernet to connect a LAN
|
To connect the various data storage devices, it makes use of the fibre channel
|
|
Homes are the usual places it is used.
|
It’s applied in business and formal settings
|
|
It is simple to handle.
|
Additional administration is required for management
|
|
Compared to Storage Area Networks, Network Attached Storage is less complicated
|
Compared to network attached storage, storage area networks are more complicated
|
|
It is less expensive .
|
The price is higher than that of network attached storage
|
|
It leverages the high-speed fibre channel network instead of relying on the local area network.
|
The TCP/IP network is necessary and depends on the local area network
|
Frequently Asked Question on NAS – FAQs
What are the benefits of NAS?
- Performance – Provides better performance in serving files.
- High-end data features – Provides storage management and security.
- Scale-up – Supports a scalable storage system.
What is the role of a NAS administrator?
The storage environment must be maintained by the storage administrator, who does this by creating data storage plans, building and deploying storage systems and backups, spotting problems.
Can NAS devices used for remote access?
Setting up port forwarding on your network router is a common way to make NAS devices remotely accessible (to someone who is not on the network).
What is the security measure in NAS?
Make sure you’re adhering to fundamental security guidelines, such as creating secure passwords, routinely updating software and firmware, and refraining from opening dubious email attachments, as your NAS is only as safe as your router and local network.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...