A fraction is a number in the form of a/b where a and b are whole numbers and b ≠ 0. There are different types of fractions in mathematics based on the numerators and denominators of any given fraction. There are primarily three types of fractions namely Proper Fractions, Improper Fractions, and Mixed Fractions. However, there are other types of fractions as well such as like and unlike fractions, unit fractions, and equivalent fractions. Hence in total, there are 7 kinds of fractions namely, Proper Fractions, Improper Fractions, Mixed Fractions, Like Fractions, Unlike Fraction, Unit Fractions, and Equivalent Fractions.
In this article, we will learn what are the different types of fractions in maths, examples of types of Fractions, and solve problems based on them.
What are Types of Fractions in Maths?
Fractions are divided into different types depending on the numbers above and below the fraction line. Two parts make a fraction: the upper number is called the numerator, and the lower number is known as the denominator. The numerator shows the quantity of parts being considered, while the denominator indicates the total number of parts in the whole.
The 7 types of fractions are:
Proper Fraction
When the number on top of a fraction (numerator) is smaller than the number at the bottom (denominator), then the fraction is called a Proper Fraction. Take a delicious pizza which Lily wants to share with her friends. The pizza gets sliced into 8 equal parts. Lily takes 2 of those slices for herself while sharing the rest with her friends. Now Lily’s portion is represented as 2/8. This is still a proper fraction because 2 remains smaller than 8.
Let’s take another instance of a a bag full colorful marbles that needs to be shared with a cousin. Four marbles are taken, and your cousin is given 7 marbles. Your portion becomes 4/11, which is, once again, a proper fraction since 4 continues to be smaller than 11. Proper fractions show that a part of a larger quantity is being possessed, similar to having a smaller piece of the whole.
Example of Proper Fraction includes 2/3, 4/5, 6/19, 7/9, 13/45 etc.
Improper Fraction
An improper fraction is a fraction where the numerator, is greater than the denominator. It means the fraction is equal to or more than a whole. For example, on selling a product, a shopkeeper makes a profit of 120% which is equal to 120/100 = 6/5.
Most of the mathematician also consider that in case in a fraction, if numerator is equal to the denominator, they are also considered as Improper Fraction.
Improper Fraction Example includes 19/13, 129/20, 45/6, 17/8 etc. In these examples, we can see the numerators are greater than denominators, hence these are examples of Improper Fraction.
Mixed Fraction
A mixed fraction is a number that shows a whole part and a smaller part together. Suppose from a pizza you have eaten 2 out of 8 slices, you can say you’ve eaten “2 and 1/4” slices. This is a mixed fraction i.e.  . The “2” represents the whole slices you ate, and the “1/4” shows the extra part of another slice you ate. So, you’ve had a bit more than 2 slices.
. The “2” represents the whole slices you ate, and the “1/4” shows the extra part of another slice you ate. So, you’ve had a bit more than 2 slices.
Like Fractions
Like fractions are fractions that have the same denominators. This means the bottom number (denominator) in these fractions is the same. For instance, 2/5, 3/5, and 4/5 are like fractions. It is simple to add or subtract these type of fractions because there is no need to change the denominator as it is same ‘5’ in all fractions. For example, while adding 2/5, 3/5, and 4/5, it gives (2+3+4)/5 = 9/5.
Unlike Fractions
Unlike fractions are fractions with different denominators. In other words, the bottom numbers (denominators) of these fractions are not the same. For instance, 1/4, 1/3, and 1/6 are unlike fractions. To add or subtract unlike fractions, it is required to find the least common multiple or LCM of the denominators, which is the smallest number that all the denominators can divide into. Then, adjust the fractions to have the same denominator by multiplying both the numerator and denominator by the same number and then add or subtract them. For example, to add 1/4 and 1/3, you find the LCM of 4 and 3, which is 12. Then, make both fractions have a denominator of 12, resulting in 3/12 and 4/12. Finally, add them to get 7/12.
Equivalent Fractions
Equivalent fractions are different fractions that represent the same portion of the whole. They may look different, but they have the same value. For example, 2/3 and 4/6 are equivalent because when simplified, they both represent the same amount. Another example is 3/8 and 6/16; they are equivalent because they also represent the same portion of something. Equivalent fractions can be found by simplifying fractions to their simplest form, which means dividing both the numerator and denominator by the greatest common factor (GCF). When two or more fractions simplify to the same result, they are equivalent.
Unit Fractions
A unit fraction is a type of fraction where the numerator is 1, and the denominator can be any whole number other than 0. In other words, a unit fraction is always written as 1 over something, such as 1/2, 1/3, 1/4, and so on.
Unit fractions represent one part of a whole, and which are called unit because they refer to a single, indivisible unit or piece. For example, 1/2 represents one-half of something, 1/3 represents one-third, and 1/4 represents one-fourth. They are essential in understanding parts and fractions of objects or quantities.
Types of Fractions Chart
The following chart shows all the types of fractions along with examples

Improper Fraction and Mixed Fraction Conversion
Since, in improper fraction numerator is greater than denominator, hence we can convert it into a combination of a whole number and proper fraction. And the mixed fraction so obtained can also be converted into improper fraction.
Improper Fraction to Mixed Fraction
By following solving the improper fraction using division method it can be transformed into a mixed fraction. Divide the numerator by denominator, then the remainder comes from this division will become the numerator, the number of times denominator divides the numerator becomes the whole number and the denominator stays unchanged.
Let’s take an example of improper fraction 7/3, to convert this fraction into mixed follow the below steps:
Step 1: Divide the numerator 7 by the denominator 3
Step 2: This division will give 2 as the quotient and 1 as the remainder.
Step 3: express the fraction into mixed fraction as 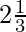 .
.

Improper fraction into Mixed fraction
Mixed Fraction to Improper Fraction
A combination of a whole number and a proper fraction is called as mixed fraction. To change a mixed fraction into an improper fraction, it is required to multiply the whole number part by the denominator and then add the numerator. The outcome becomes the new numerator, while the denominator stays unchanged.
For example, Let’s convert the mixed fraction 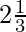 to an improper fraction.
to an improper fraction.
Step 1: Multiply the whole number 2 by the denominator 3 , which will become 6.
Step 2: Add the numerator 1 to the result obtained from step 1 ; 1+6=7
Step 3: The result of step 2 is the new numerator and the denominator stays unchanged. Therefore the improper fractions is 7/3

Mixed fraction into Improper fraction.
Examples of Types of Fractions
Fractions represent parts of a whole and can be classified into various types based on their characteristics. Here are examples of different types of fractions:
- Proper Fractions: These are fractions where the numerator is smaller than the denominator, representing values less than 1.
- Examples: 1/2, 3/4, 5/8.
- Improper Fractions: These fractions have numerators that are equal to or greater than the denominators, representing values equal to or greater than 1.
- Examples: 5/3, 7/4, 11/6
- Mixed Fractions: Mixed fractions consist of a whole number and a proper fraction.
- Examples:
 , 2 \dfrac{3}{4}, 3 \dfrac{2}{5}.
, 2 \dfrac{3}{4}, 3 \dfrac{2}{5}.
- Unlike Fractions: Unlike fractions have different denominators.
- Examples: 1/3 and 2/5, 2/7 and 3/4, 3/8 and 5/6.
- Like Fractions: Like fractions have the same denominators.
- Examples: 2/5 and 3/5, 4/7 and 5/7, 1/3 and 2/3.
- Equivalent Fractions: Equivalent fractions represent the same portion of a whole but have different numerators and denominators.
- Examples: 1/2 and 2/4, 3/5 and 6/10, 2/3 and 4/6.
- Unit Fractions: Unit fractions have a numerator of 1.
- Examples: 1/2, 1/3, 1/4.
Types of Fractions Solved Questions
Question 1: Add 2/5 and 3/5.
Solution:
Both fractions have the same denominator (5)
∴ Add their numerators together
= 2/5 + 3/5
= (2 + 3)/5
= 5/5
= 1
Question 2: Subtract 1/3 from 2/3.
Solution:
Both fractions have the same denominator (3)
∴ Subtract their numerators
= 2/3 – 1/3
= (2 – 1)/3
= 1/3
Question 3: Find an equivalent fraction for 4/7.
Solution:
Multiply both the numerator and denominator by the same number 2
= 4×2/7×2
= 8/14
Question 4: Convert  into an improper fraction.
into an improper fraction.
Solution:
Multiply the whole number (2) by the denominator (4) and then add the numerator (1)
∴ 2(1/4) as an improper fraction is (2 × 4 + 1)/4 = 9/4
Question 5: Add 1/6 and 1/8.
Solution:
Find least common multiple (LCM) of 6 and 8, which is 24.
Adjust both fractions to have a common denominator:
1/6 becomes 4/24 on multiplying both denominator and numerator by 4
1/8 becomes 3/24 on multiplying both denominator and numerator by 3
Add,
= 4/24 + 3/24
= 7/24
Practice Questions on Types of Fractions
Q1. A recipe calls for 2/3 cup of flour, but you only have 1/4 cup. How much more flour do you need to complete the recipe?
Q2. You have 3/8 of a candy bar, and your friend has 2/8 of the same candy bar. How much candy do you both have together?
Q3. You have 3/8 of a candy bar, and your friend has 2/8 of the same candy bar. How much candy do you both have together?
Q4. A school bus is filled with 48 students. 3/8 of them are in the first-grade class. How many students are not in the first grade?
Q5. You want to share 5/6 of a chocolate bar equally with your two friends. How much will each person get?
Q6. Find the first 5 Equivalent Fractions of 2/3.
Q7. Convert 19/8 in Mixed Fractions.
Types of Fractions – FAQs
What are Different Types of Fractions with Examples?
The different types of fractions are proper fractions, improper fractions, mixed fractions, like fractions, unlike fractions, unit fractions and equivalent fraction. Some examples of different types of fractions are proper fractions (e.g., 1/2), improper fractions (e.g., 5/4), mixed numbers (e.g., 2 1/3), and more.
What is Fraction in Maths?
Fraction in maths is a number which is represented as a/b where a nd b are whole numbers and b is not equal to zero.
What are Proper and Improper Fractions?
Proper Fractions are the fractions in which numerator is less than denominator and improper fractions are the fractions in which numerator is greater than denominator.
What is Mixed Fraction?
A mixed fraction is a fraction that consists of a whole number and a proper fraction.
What are Like and Unlike Fractions?
Like Fractions are the fractions whose denominators are same while unlike fractions are those whose denominators are not same.
How do I Add fractions with different Denominators?
To add fractions with different denominators, find a common denominator and adjust the fractions accordingly before adding.
How do I convert a Mixed fraction into an Improper fraction?
Multiply the whole number by the denominator, then add the numerator over the denominator.
How do I compare Fractions to determine which is Larger or Smaller?
To compare fractions, find a common denominator and then compare the numerators.
What is Decimal Equivalent of a Fraction?
A decimal equivalent of a fraction is a decimal number that represents the same value as the fraction. For example, 1/2 is equivalent to 0.5 as a decimal.
What is Percent Equivalent of a Fraction?
A percent equivalent of a fraction is a percentage that represents the same value as the fraction. For example, 1/4 is equivalent to 25% as a percent.
What is Reciprocal of a Fraction?
The reciprocal of a fraction is the fraction obtained by flipping it, where the numerator becomes the denominator and vice versa. For example, the reciprocal of 3/4 is 4/3.
What is a Vulgar Fraction?
A vulgar fraction is another term for a common fraction, which is a fraction that represents a part of a whole, expressed as one integer divided by another. For example, 3/4 is a vulgar fraction.
List 7 Types of Fractions.
The 7 types of fractions are:
- Proper fractions
- Improper fractions
- Mixed fractions
- Unlike fractions
- Like fractions
- Equivalent fractions
- Unit fractions
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...