Types of Array Processor
Last Updated :
03 May, 2024
Array Processor performs computations on large array of data. These are two types of Array Processors: Attached Array Processor, and SIMD Array Processor. These are explained as following below.
1. Attached Array Processor :
To improve the performance of the host computer in numerical computational tasks auxiliary processor is attached to it.
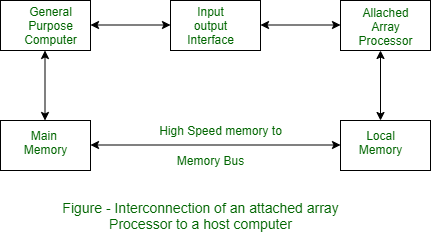
Attached array processor has two interfaces:
- Input output interface to a common processor.
- Interface with a local memory.
Here local memory interconnects main memory. Host computer is general purpose computer. Attached processor is back end machine driven by the host computer.
The array processor is connected through an I/O controller to the computer & the computer treats it as an external interface.
Working:
Let us assume that we are executing vast number of instructions, in that case it is not possible to execute all instructions with the help of host computer. Sometimes it may take days of weeks to execute these vast number of introductions. So in order to enhance the speed and performance of the host computer as shown in above diagram.
I/o interface is used to connect and resolve the difference between host and attached process. Attached array processor is normally used to enhance the performance of the host computer . Array processor mean bunch/group of process used together to perform any computation.
2. SIMD array processor :
This is computer with multiple process unit operating in parallel Both types of array processors, manipulate vectors but their internal organization is different.
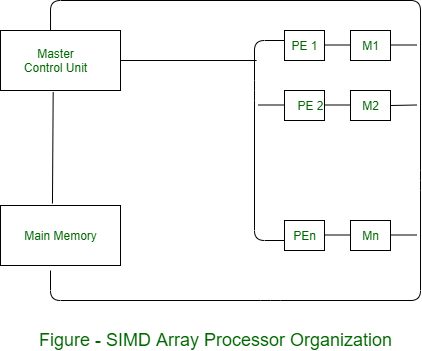
SIMD is a computer with multiple processing units operating in parallel.
The processing units are synchronized to perform the same operation under the control of a common control unit. Thus providing a single instruction stream, multiple data stream (SIMD) organization. As shown in figure, SIMD contains a set of identical processing elements (PES) each having a local memory M.
Working:
Here array processor is in built into the computer unlike in attached array processor where array processor is attached externally to the host computer. Initially mark control unit decodes the instruction and generate the control signals and passes it into all the processor elements(PE’s) or ALU upon receiving the control signals from master control unit, all the processing elements come to throw that operations need to perform. The data perform the operations will be accessed from main memory into the local memory of respective PE’s. SIMD array processor is normally used to compute vector data. All PE’s execute same instruction simultaneously on different data.
for ex: Ci= Ai + Bi
Here the vector instruction Ci= Ai+ Bi need to be executed is addition operation, the master control unit generate control signal and passes it onto all processing elements and data.
parallelly on same instruction on with different data, that’s why it is called as Single instruction multiple data streams(SIMD) array processor.
Each PE includes –
- ALU
- Floating point arithmetic unit
- Working registers
Master control unit controls the operation in the PEs. The function of master control unit is to decode the instruction and determine how the instruction to be executed. If the instruction is scalar or program control instruction then it is directly executed within the master control unit.
Main memory is used for storage of the program while each PE uses operands stored in its local memory.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...