Sum of cost of all paths to reach a given cell in a Matrix
Last Updated :
03 May, 2021
Given a matrix grid[][] and two integers M and N, the task is to find the sum of cost of all possible paths from the (0, 0) to (M, N) by moving a cell down or right. Cost of each path is defined as the sum of values of the cells visited in the path.
Examples:
Input: M = 1, N = 1, grid[][] = {{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}, {7, 8, 9}}
Output: 18
Explanation:
There are only 2 ways to reach (1, 1)
Path 1: (0, 0) => (0, 1) => (1, 1)
Path cost = 1 + 2 + 5 = 8
Path 2: (0, 0) => (1, 0) => (1, 1)
Path cost = 1 + 4 + 5 = 10
Total Path Sum = 8 + 10 = 18
Input: M = 2, N = 2, grid = { {1, 1, 1}, {1, 1, 1}, {1, 1, 1} }
Output: 30
Explanation:
Sum of path cost of all path is 30.
Approach: The idea is to find the contribution of each cell of the matrix for reaching (M, N), that is, the contribution of the every i and j, where 0 <= i <= M and 0 <= j <= N.
Below is the illustration of the contribution of each cell to all paths from (0, 0) to (M, N) through the respective cells:
Number of ways to reach (M, N) from (0, 0) = 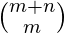
Number of ways to reach (M, N) from (0, 0) via (i, j) = 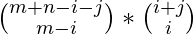
Therefore, Contribution of each grid (i, j) is = ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com grid[i][j] * \binom{m+n-i-j}{m-i} * \binom{i+j}{i}](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-010913adcdf5e09bf69b8691d400b292_l3.png)
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int Col = 3;
int fact(int n);
int nCr(int n, int r)
{
return fact(n) / (fact(r)
* fact(n - r));
}
int fact(int n)
{
int res = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
res = res * i;
return res;
}
int sumPathCost(int grid[][Col],
int m, int n)
{
int sum = 0, count;
for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) {
count
= nCr(i + j, i)
* nCr(m + n - i - j, m - i);
sum += count * grid[i][j];
}
}
return sum;
}
int main()
{
int m = 2;
int n = 2;
int grid[][Col] = { { 1, 2, 3 },
{ 4, 5, 6 },
{ 7, 8, 9 } };
cout << sumPathCost(grid, m, n);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static int Col = 3;
static int nCr(int n, int r)
{
return fact(n) / (fact(r) *
fact(n - r));
}
static int fact(int n)
{
int res = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
res = res * i;
return res;
}
static int sumPathCost(int grid[][],
int m, int n)
{
int sum = 0, count;
for(int i = 0; i <= m; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j <= n; j++)
{
count = nCr(i + j, i) *
nCr(m + n - i - j, m - i);
sum += count * grid[i][j];
}
}
return sum;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int m = 2;
int n = 2;
int grid[][] = { { 1, 2, 3 },
{ 4, 5, 6 },
{ 7, 8, 9 } };
System.out.println(sumPathCost(grid, m, n));
}
}
|
Python3
Col = 3;
def nCr(n, r):
return fact(n) / (fact(r) *
fact(n - r));
def fact(n):
res = 1;
for i in range(2, n + 1):
res = res * i;
return res;
def sumPathCost(grid, m, n):
sum = 0;
count = 0;
for i in range(0, m + 1):
for j in range(0, n + 1):
count = (nCr(i + j, i) *
nCr(m + n - i - j, m - i));
sum += count * grid[i][j];
return sum;
if __name__ == '__main__':
m = 2;
n = 2;
grid = [ [ 1, 2, 3 ],
[ 4, 5, 6 ],
[ 7, 8, 9 ] ];
print(int(sumPathCost(grid, m, n)));
|
C#
using System;
class GFG{
static int nCr(int n, int r)
{
return fact(n) / (fact(r) *
fact(n - r));
}
static int fact(int n)
{
int res = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
res = res * i;
return res;
}
static int sumPathCost(int [,]grid,
int m, int n)
{
int sum = 0, count;
for(int i = 0; i <= m; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j <= n; j++)
{
count = nCr(i + j, i) *
nCr(m + n - i - j, m - i);
sum += count * grid[i, j];
}
}
return sum;
}
public static void Main()
{
int m = 2;
int n = 2;
int [, ]grid = { { 1, 2, 3 },
{ 4, 5, 6 },
{ 7, 8, 9 } };
Console.Write(sumPathCost(grid, m, n));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
var Col = 3;
function nCr(n, r)
{
return fact(n) / (fact(r)
* fact(n - r));
}
function fact(n)
{
var res = 1;
for (var i = 2; i <= n; i++)
res = res * i;
return res;
}
function sumPathCost(grid, m, n)
{
var sum = 0, count;
for (var i = 0; i <= m; i++) {
for (var j = 0; j <= n; j++) {
count
= nCr(i + j, i)
* nCr(m + n - i - j, m - i);
sum += count * grid[i][j];
}
}
return sum;
}
var m = 2;
var n = 2;
var grid = [ [ 1, 2, 3 ],
[ 4, 5, 6 ],
[ 7, 8, 9 ] ];
document.write( sumPathCost(grid, m, n));
</script>
|
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...