Square Root (Sqrt) Decomposition Algorithm Using JavaScript Array
Last Updated :
13 Sep, 2023
In this article, we are going to learn how we can use the Square Root (Sqrt) Decomposition Algorithm using a JavaScript array. The square Root Decomposition Technique is one of the most common query optimization techniques used by competitive programmers. This technique helps us to reduce Time Complexity by a factor of sqrt(N).
Approaches for Square Root (Sqrt) Decomposition Algorithm:
- Brute force
- Efficient approach
Square Root (Sqrt) Decomposition Algorithm Using Brute force
- In this approach, we simply iterate over each element in the range l to r and calculate its corresponding answer.
- Let’s consider these chunks or blocks as an individual array each of which contains sqrt(N) elements and you have computed your desired answer(according to your problem) individually for all the chunks.
- Now, you need to answer certain queries asking you the answer for the elements in the range l to r(l and r are starting and ending indices of the array) in the original n-sized array.
- Simply iterate over each element in the range l to r calculate its sum and return it for an answer.
Example:
Javascript
const MAXN = 20000;
const arr = [];
function query(l, r) {
let sum = 0;
for (let i = l; i <= r; i++) {
sum += arr[i];
}
return sum;
}
function main() {
const input = [10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1];
const n = input.length;
arr.push(...input);
console.log("query(3,8) : ", query(3, 8));
console.log("query(1,6) : ", query(1, 6));
arr[5] = 0;
console.log("query(6,6) : ", query(6, 6));
}
main();
|
Output
query(3,8) : 27
query(1,6) : 39
query(6,6) : 4
Time Complexity: O(N)
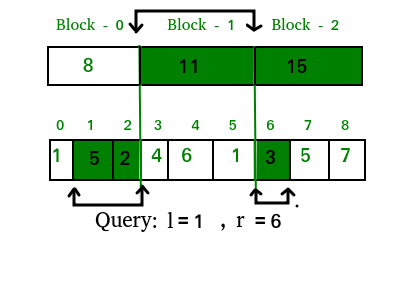
We can deal with these types of queries by summing the data from the completely
overlapped decomposed blocks lying in the query range and then summing elements one
by one from the original array whose corresponding block is not completely overlapped by the query range.
So the answer for the above query in the described image will be: ans = 5 + 2 + 11 + 3 = 21
Efficient approach
- In this approach, we simply find the block in which the given index lies, then subtract its previous value and add the new updated value as per the point update query.
- We have constructed the decomposed array of sqrt(N) blocks and now we need to print the sum of elements in a given range.
- The range may totally cover the continuous sqrt blocks. So we can easily answer the sum of values in this range as the sum of completely overlapped blocks.
Example:
Javascript
let MAXN = 10000;
let SQRSIZE = 100;
let arr = new Array(MAXN);
for (let i = 0; i < MAXN; i++) {
arr[i] = 0;
}
let block = new Array(SQRSIZE);
for (let i = 0; i < SQRSIZE; i++) {
block[i] = 0;
}
let x;
function update(idx, val) {
let blockNumber = idx / x;
block[blockNumber] += val - arr[idx];
arr[idx] = val;
}
function query(l, r) {
let sum = 0;
while (l < r && l % x != 0 && l != 0) {
sum += arr[l];
l++;
}
while (l + x - 1 <= r) {
sum += block[l / x];
l += x;
}
while (l <= r) {
sum += arr[l];
l++;
}
return sum;
}
function preprocess(input, n) {
let x = -1;
x = Math.floor(Math.sqrt(n));
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = input[i];
if (i % x == 0) {
x++;
}
block[x] += arr[i];
}
}
let input = [1, 5, 2, 4, 6, 1, 3, 5, 7, 10];
let n = input.length;
preprocess(input, n);
console.log("query(3,7) : " +
query(3, 7));
console.log("query(4,4) : " +
query(4, 4));
update(6, 0);
console.log("query(5,5) : " +
query(5, 5));
|
Output
query(3,7) : 19
query(4,4) : 6
query(5,5) : 1
Time Complexity: O(sqrt(N))
Auxiliary Space: O(MAXN), since MAXN extra space has been taken, where MAXN is the maximum value of N
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...