SQL SELECT Query
Last Updated :
06 May, 2024
The SQL SELECT Statement retrieves data from a database.
SELECT Statement in SQL
The SELECT statement in SQL is used to fetch or retrieve data from a database. It allows users to access the data and retrieve specific data based on specific conditions.
We can fetch either the entire table or according to some specified rules. The data returned is stored in a result table. This result table is also called the result set. With the SELECT clause of a SELECT command statement, we specify the columns that we want to be displayed in the query result and, optionally, which column headings we prefer to see above the result table.
The SELECT clause is the first clause and is one of the last clauses of the select statement that the database server evaluates. The reason for this is that before we can determine what to include in the final result set, we need to know all of the possible columns that could be included in the final result set.
Syntax
The syntax for the SELECT statement is:
SELECT column1,column2…. FROM table_name ;
SELECT Statement Example
Let’s look at some examples of the SQL SELECT statement, to understand it better.
Let’s create a table which will be used in examples:
CREATE TABLE:
CREATE TABLE Customer(
CustomerID INT PRIMARY KEY,
CustomerName VARCHAR(50),
LastName VARCHAR(50),
Country VARCHAR(50),
Age int(2),
Phone int(10)
);
-- Insert some sample data into the Customers table
INSERT INTO Customer (CustomerID, CustomerName, LastName, Country, Age, Phone)
VALUES (1, 'Shubham', 'Thakur', 'India','23','xxxxxxxxxx'),
(2, 'Aman ', 'Chopra', 'Australia','21','xxxxxxxxxx'),
(3, 'Naveen', 'Tulasi', 'Sri lanka','24','xxxxxxxxxx'),
(4, 'Aditya', 'Arpan', 'Austria','21','xxxxxxxxxx'),
(5, 'Nishant. Salchichas S.A.', 'Jain', 'Spain','22','xxxxxxxxxx');
Output:
Retrieve Data using SELECT Query
In this example, we will fetch CustomerName, LastName from the table Customer:
Query:
SELECT CustomerName, LastName FROM Customer;
Output:
Fetch All Table using SELECT Statement
In this example, we will fetch all the fields from the table Customer:
Query:
SELECT * FROM Customer;
Output:
SELECT Statement with WHERE Clause
Suppose we want to see table values with specific conditions then WHERE Clause is used with select statement.
Query:
SELECT CustomerName FROM Customer where Age = '21';
Output:
SQL SELECT Statement with GROUP BY Clause
In this example, we will use SELECT statement with GROUP BY Clause
Query:
SELECT COUNT (item), Customer_id FROM Orders GROUP BY order_id;
Output:
SELECT Statement with HAVING Clause
Consider the following database for HAVING Clause:
Query:
SELECT Department, sum(Salary) as Salary
FROM employee
GROUP BY department
HAVING SUM(Salary) >= 50000;
Output:

SELECT Statement with ORDER BY clause in SQL
In this example, we will use SELECT Statement with ORDER BY clause
Query:
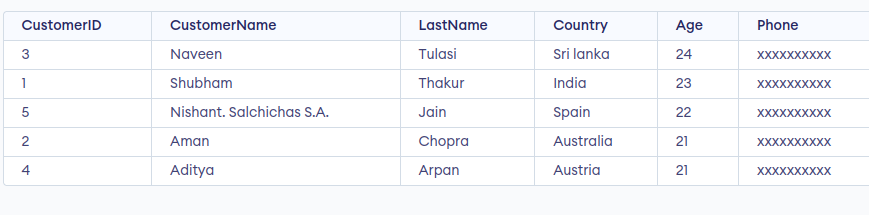
SELECT * FROM Customer ORDER BY Age DESC;
Output:
Important Points with SQL SELECT Statement
- It is used to access records from one or more database tables and views.
- The SELECT statement retrieves selected data based on specified conditions.
- The result of a SELECT statement is stored in a result set or result table.
- The SELECT statement can be used to access specific columns or all columns from a table.
- It can be combined with clauses like WHERE, GROUP BY, HAVING, and ORDER BY for more refined data retrieval.
- The SELECT statement is versatile and allows users to fetch data based on various criteria efficiently.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...