A light where an electric discharge happens all through a metallic vapor is known as a vapor lamp. These lights are accessible in two types sodium vapor lamps and mercury vapor lamps which emit various shades of light like thick blue and yellow respectively. These lights are highly efficient and provide concentrated illumination, making them ideal for open spaces and for lighting up large distances.
A vapor lamp typically includes a double tube where vapor is enclosed within the tube while the outside tube is empty with air, so it retains risky hazardous UV radiation.
In this article, we will be going through Sodium Vapor Lamps, We will start our Article with What is a Sodium Vapor Lamp? and Its Working, Then we will go through the Types of Sodium Vapor Lamp which are High- Pressure Sodium Vapor Lamps and Low-Pressure Sodium Vapor Lamp with their working, At last we will conclude our Article with Advantages, Disadvantages, Application and Some FAQs on Sodium Vapor Lamps.
What is Sodium Vapor Lamp?
A gas-discharge lamp that uses sodium (Na) in an exciting condition to produce light at a 589 nm wavelength is known as a sodium vapor lamp. Philips introduced the first commercially available sodium lamps in 1932 in Holland.

Sodium-Vapor-Lamps
The sodium vapor lamp working principle is, that it works on the principle of disintegrated sodium metal by making an electric arc. Different gases and materials are used in activating the lamp and also controlling its color. These lamps are utilized in streetlamps and modern purposes. The sodium vapor lamp is shown in the above figure.
Sodium Vapor Lamp Circuit
The sodium vapor lamp circuit diagram is shown in below. Here, the type of lamp uses in this circuit is a low-power sodium vapor lamp (LPSVL). The construction of this light is like a mercury vapor lamp. In this lamp configuration, two electrodes, E1 and E2, along with a capacitor (C), a choke (L), and a small step-down transformer (T) are connected in series with the lamp. The choke (L) is an inductor is Connected in series with a low-power sodium vapor lamp. It stabilizes the discharge in the same way that overload protection does. The transformer utilized in the above circuit is a step down transformer for reducing the voltage supply and settling the circular segment. The vapor lamp, choke, and transformer are all connected in series to heat the cathode electrode “E1” inside a G1 glass tube that contains sodium and a small amount of argon or neon gases. This G1 glass tube is set in a G2 evacuated external tube.
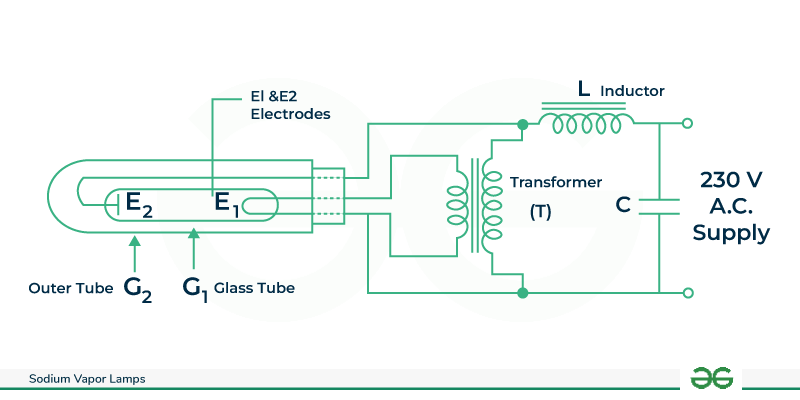
Sodium-Vapor-Lamp-Circuit
Sodium vapor is extremely active chemically, so the glass lamp is planned firmly to Withstand the hot sodium vapor action. By keeping the discharge tube’s exact temperature at 300 degrees Celsius, so we can achieve maximum efficiency and operating conditions and reduce the heat loss from the tube.
Working of Sodium Vapor Lamp
When the sodium vapor lamp is turned ON, it releases neon gas inside , which produces adequate intensity to dissipate the Na (sodium). A small transformer is utilized to warm the cathode fiber inside the release tube while the anode terminal is associated straight to the 230V AC supply all through a choke. In light of both the transformer and gag, the power factor (P.F) of the above circuit will turn exceptionally low, so a capacitor is used for correction purposes.

Sodium-Vapor-Lamp-Working
At the point when the vapor lamp is not in operation, Na (sodium) is deposit on the sidewalls of the tube. When the fume light is associated with the power supply, neon gas is released which produces red-orange variety light. Neon gas emission results in the transformation of heat into solid sodium vapor. After fifteen minutes, it begins creating total yellow light.
These sodium fume lights are accessible in 50 Watt, 100 Watt, 200 Watt, 500 Watt. This lamp only works with AC power.
Sodium Vapor Lamp Types
There are two kinds of sodium vapor lamp accessible in the market are as follows:
- LPS fume light (Low-Pressure Sodium Vapor Lamp)
- HPS vapor Lamp (High- Pressure Sodium Vapor Lamp).
Low-Pressure Sodium Vapor Lamp
Low-Pressure Sodium Vapor Lamp In 1920, Arthur H. Compton at Westinghouse developed the first low-pressure sodium vapor lamp (LPSV). The primary created sodium light is a LPS light or low-pressure sodium light. The distinctive color of this lamp, which is a monochromatic yellow, makes it easy to identify it. It was utilized in Europe since it didn’t used in different industrial areas due to its poor efficiency in producing light.

Low-Pressure-Sodium-Vapor-Lamp
Working of Low-Pressure Sodium Vapor Lamp
LPS Lamp is an extremely proficient light Worldwide because of its few Advantages. The light produced by this lamp is at a wavelength most responsive to the human eye, making it highly visible. In reality, an incandescent lamp emits light across a wide range of frequencies, from infrared (IR) to ultraviolet (UV). The low-pressure sodium lamp is also known as a SOX lamp.
The LPS fume light is for the most part utilized for open air lighting in Europe. At the point when the light starts, it initially makes a red shine due to the neon gas, however neon gas lights just at less temperature. The sodium begins to vaporize at a higher temperature, transforming into a pure, monochromatic yellow light.
High- Pressure Sodium Vapor Lamp
The principal HPSV light was developed and Introduced into the market in Schenectady, New York and Nela Park, Ohio in the year 1964. The HPSV light is the most often utilized in road lighting. The improvement of the LPS light is the HPS light but it has less proficiency with respect to LPS. The HPS light utilizes a restricted arc tube supported by a frame within a bulb.

High-Pressure-Sodium-Vapor-Lamp
Working of High- Pressure Sodium Vapor Lamp
The circular segment tube is designed with aluminum oxide ceramic since it Withstands the acidic impacts of soluble bases like Na (sodium). The curve tube uses high tension for higher proficiency. In this cylinder, xenon, sodium, and mercury are typically utilized.
The most common method to activate the light is through a pulse start. An ignitor inside the ballast sends a high-voltage signal through the arc tube, activating an arc with the xenon gas. As a result, the light turns blue, similar to xenon lights.
After that, the mercury (Hg) is heated by the arc, and its vapor gives the lamp a bluish color. The light gets heat and the sodium is the last material to Vaporize. White light is produced when sodium (Na) vapor meets an arc at temperatures above 240 degrees Celsius. The mercury helps to enhance and refine the yellow hue of the sodium light, contributing to its ideal shade.
Components of Sodium Vapor Lamp
The components of sodium vapor lamp are discussed below in detail:

Components-of-Sodium-Vapor-Lamp
- Outer Bulb : The outer bulb is the first part, usually made of borosilicate glass. The inner components of the sodium vapor lamp are shielded from the elements and provided with thermal insulation by this bulb. The bulb’s external structure also helps to maintain the necessary operating temperature for optimal performance and efficiency.
- Ballast: To manage the current that is passing through the sodium vapor lamp, a ballast is very importantly employed. The ballast controls the flow of electrical energy ensuring and guarantees that the lamp works safely and efficiently. It keeps excessive current from current to and contacting the light, prolonging its lifespan and maintaining stable illumination.
- Sodium and Mercury: A sodium vapor lamp’s primary illuminating agents are sodium and mercury. The arc tube contains exceptionally little measures of these components in their vapor forms. At the point when the lamp is ignited, an electric discharge through the arc tube, making the sodium and mercury fumes become ionized and emit light.
- Electrodes: To light and support the electric release inside the curve tube, two anodes are significantly fundamental. These electrodes, which are made of a refractory metal like tungsten, are coated in a material that makes it easy to start them up and keeps them running smoothly. The terminals give the fundamentally electrical associations with the light to work in an extremely legitimate manner.
- Neon Gas (Ne): A limited quantity of neon gas is used to initiate the discharge in the light.
- Arc Tube: Contained inside the outer bulb is the core of the sodium vapor light – the arc tube. A small, cylindrical design made of an extremely top notch transparent material, such as, aluminum oxide is the arc tube. A mixture of noble gases, typically argon, and a small amount of neon can be found inside the arc tube, which serves as a very useful starting aid.
- Sodium (Na) Metal: The light contains a modest quantity of metallic sodium, which is a key component for producing the yellow-orange light when it is vaporized and excited by an electric discharge.
Comparison Between Sodium Vapor Lamp and Mercury Vapor Lamp
|
Sodium Vapor Lamp
|
Mercury Vapor Lamp
|
|
Sodium vapor lamp efficiency is around 100 lumens/watt.
|
It produces between 35 and 65 lumens per watt of light.
|
|
Sodium vapor lamp is a gas discharge lamp.
|
Mercury vapor is likewise a gas discharge lamp
|
|
This lamp uses sodium in an energized condition to emit light.
|
This light purposes an electric arc segment with vaporized mercury to radiate light
|
|
The light in this lamp is from the process of a atomic emission.
|
The light in this lamp is from the process of fluorescence emission.
|
|
It is used for street and other lighting.
|
It is used to provide like streets, sports arenas, gyms, shops, and banks.
|
|
Its life expectancy is around 18,000 hours.
|
Its life expectancy is around 24,000 hours.
|
|
Sodium vapor lamp wavelength is 589 nm
|
Mercury vapor lamp wavelength is 254 nm
|
Advantages of Sodium Vapor Lamp
The advantages of sodium vapor lamp incorporate the following.
- Sodium vapor lamp efficiency is high.
- It has a longer lifespan
- It can be easily disposed of.
- The operating temperature is low.
- It has a more Energy-efficient.
- It provide very effective in foggy and rainy seasons.
- Produced heat is low.
- It goes from less grades to high grades.
- Its variety temperature is warm consistently.
- These are ideal for a different of uses.
Disadvantages of Sodium Vapor Lamp
The disadvantages of sodium vapor lights incorporate the following.
- Color temperature
- Glare control requires ballast and controlling elements.
- It isn’t applicable in color identification areas.
- It is more dangerous due to it can produce fire in contact with air.
- It needs an additional transformer
- The power factor is poor.
- For indoor lighting, the yellow tone isn’t appropriate.
- For sufficient light output, it needs long tubes.
- It needs 5 to 10 minutes to provide complete light.
Applications of Sodium Vapor Lamp
The applications of sodium vapor lamps incorporate the following.
- These lights are extensively utilized for air terminals, Goods yards, lighting of roads, shipping yards and so on
- At times, these lamps are used for advertisement purposes.
- The most commonly used rating of lights are 250 watts or more.
- HPS lights are broadly used to give lighting in industries
- These lights are utilized for outside region lighting like streets, security regions, parking garages, and so on.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sodium vapor lamps have shown to be a huge progression in lighting innovation, especially in outside and road lighting applications. These lights, known for their distinctive warm glow, are highly efficient and offer significant benefits. The utilization of sodium vapor lamps, Specially high-pressure sodium (HPS) lamps, has become inescapable because of their energy proficiency and long functional life. Their illumination enhances visibility and color rendering, making them suitable for various applications where color accuracy isn’t crucial.
Sodium vapor lamps offer significant advantages in terms of lumen output per watt, contributing to energy conservation and cost-effectiveness. Their extended lifespan also reduces maintenance requirements and associated costs. However, it’s essential to acknowledge potential drawbacks, such as the distinctive yellow-orange hue that could impact color perception. Additionally, in certain scenarios, there may be limitations in warm-up time and restrike time following a power outage.
FAQs on Sodium Vapor Lamps
What is A sodium vapor lamp?
A sodium vapor lamp is a sort of gas release light that involves sodium in different structures to deliver light. It is ordinarily utilized for open air lighting.
Are sodium vapor lamp reasonable for all applications?
While sodium vapor lamp enjoy benefits, they may not be great for circumstances requiring exact variety insight because of their trademark warm variety. In such situations, LED technology is frequently preferred.
What are the sorts of sodium vapor lamp?
There are two fundamental types: Low-pressure Sodium (LPS) lamps and High-Pressure Sodium (HPS) lamps. LPS lights radiate a monochromatic yellow light, while HPS lights transmit a more extensive range with a trademark warm variety.
What are the benefits of sodium vapor lamp?
Sodium vapor lamp are energy-effective, have a long life expectancy, and give great lumen yield per watt. They are appropriate for outside lighting because of their perceivability upgrading properties.
How operate sodium vapor lamps?
Sodium vapor lamp work by passing an electric current through a tube containing sodium gas. This interaction creates light as the gas becomes ionized.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...