Setting Up a Virtual Environment in Django
Last Updated :
03 Apr, 2024
Setting up a virtual environment in Django is essential for isolating your project’s dependencies and ensuring consistent behavior across different environments. A virtual environment allows you to install packages locally without affecting the global Python installation. Here’s how to set up a virtual environment for your Django project.
Setting Up a Virtual Environment in Django
Below, is a step-by-step explanation of how to set up a virtual environment in Django in Python:
Step 1: Installation
We will install the following dependencies and modules before starting our setup:
If you haven’t installed virtualenv yet, you can do so using pip:
pip install virtualenv

install virtualenv
Step 2: Create a New Directory for your Django Project
Navigate to the directory where you want to create your Django project and create a new directory for it
mkdir my_django_project
cd my_django_project
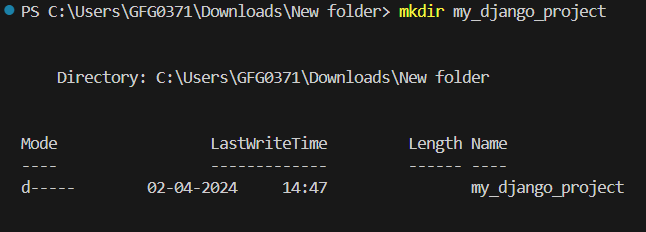
Create new Directory
Step 3: Create a Virtual Environment
Inside your project directory, create a new virtual environment using virtualenv. You can name your virtual environment whatever you like (e.g., ‘venv’, ‘env’, ‘myenv’).
python -m venv env

create virtual environment
Step 4: Activate the Virtual Environment
On Windows, type the following command to activate the virtual environment:
venv\Scripts\activate

Step 5: Install Django in the Virtual Environment
Once the virtual environment is activated, you can install Django and any other dependencies your project requires using pip.
pip install django
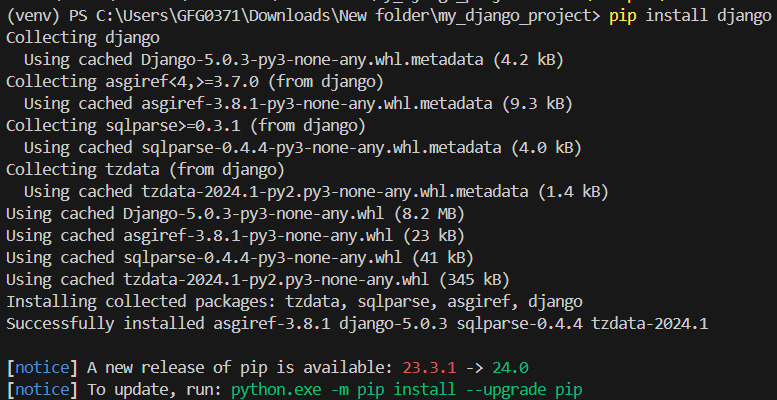
Istall Django
Step 6: Create a New Django Project
Now that your virtual environment is set up and activated, you can create a new Django project using the django-admin command.
django-admin startproject myproject
Replace ‘myproject‘ with the name of your project.
Step 7: Verify your Django Installation
You can verify that Django is installed correctly by running the development server.
cd myproject
python manage.py runserver
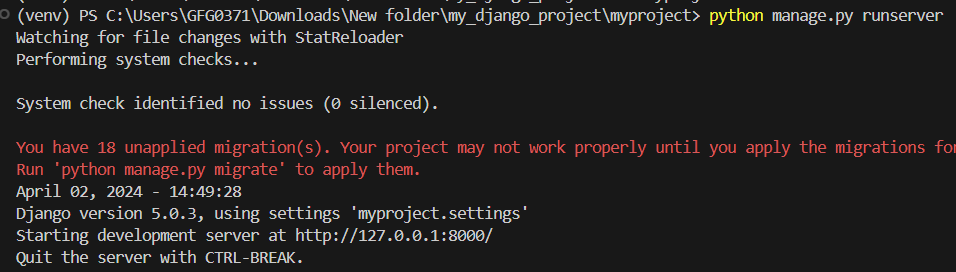
Verify Installation ( Running the Project)
Open your web browser and navigate to http://127.0.0.1:8000/. If you see the Django welcome page, your installation was successful.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...