Querying Multiple Tables in SQL
Last Updated :
21 Apr, 2021
Here, we are going to see how to query multiple tables in SQL. For example, here, we will first create a database named “geeks” then we will create 2 tables “department” and “employee” in that database. After, that we will execute our query on the tables.
Creating a Database :
Use the below SQL statement to create a database called geeks:
CREATE DATABASE geeks;
Using Database :
USE geeks;
The department Table Definition:
We have the following department table in our geeks database :
Create Table department(
ID int,
SALARY int,
NAME Varchar(20),
DEPT_ID Varchar(255));
Output:

You can use the below statement to query the description of the created table:
EXEC SP_COLUMNS department;

Adding Data to department Table:
The date data type uses the format ‘YYYY-MM-DD‘. Use the below statement to add data to the department table:
INSERT INTO department VALUES (1,'Neha','F','1994-06-03');
INSERT INTO department VALUES (2,'Harsh','M','1996-03-12');
INSERT INTO department VALUES (3,'Harsh','M','1995-05-01');
INSERT INTO department VALUES (4,'Rupali','F',1996-11-11');
INSERT INTO department VALUES (5,'Rohan','M','1992-03-08');
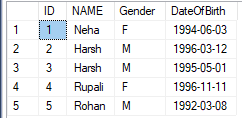
To verify the contents of the table use the below statement:
SELECT * FROM department;
The employee Table Definition:
Now create another table called employee:
CREATE TABLE employee(
ID int,
Email Varchar(255),
City Varchar(20) );
Adding Data to employee Table:
Add values into the table “employee“:
INSERT INTO employee VALUES (1, "ANURAG@xyz.com", "Noida");
INSERT INTO employee VALUES (2, "HARSH@xyz.com", "Jaipur");
INSERT INTO employee VALUES (3, "SUMIT@xyz.com", "Noida");
INSERT INTO employee VALUES (4, "RUHI@xyz.com", "Jaipur");
INSERT INTO employee VALUES (5, "KAE@xyz.com", "Noida");
To verify the contents of the table use the below statement:
SELECT * FROM employee;

Querying Multiple Tables in SQL:
Method 1:
The most common way to query multiple tables is with a simple SELECT expression. To integrate results from different tables, use the FROM clause to name more than one table. Here’s how it works in practice:
Syntax:
SELECT table1name.column1name, table2name.column2name FROM table1name, table2name
WHERE table1name.column1name = table2name.column1name;
Example:
SELECT department.ID, department.NAME, employee.Email, employee.City FROM department, employee
WHERE department.ID = employee.ID;
Output:

Method 2: Using JOINS
SQL Joins can also be used for the same purpose using the below syntax:
Syntax:
SELECT table1.column1,table1.column2,table2.column1,....
FROM table1
JOIN table2
ON table1.matching_column = table2.matching_column;
Example:
SELECT department.ID, department.NAME, employee.Email, employee.City
FROM department JOIN employee ON department.ID = employee.ID;
Output:

Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...