Queries for decimal values of subarrays of a binary array
Last Updated :
28 Mar, 2023
Given a binary array arr[], we to find the number represented by the subarray a[l..r]. There are multiple such queries.
Examples:
Input : arr[] = {1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1};
l = 2, r = 4
l = 4, r = 5
Output : 5
3
Subarray 2 to 4 is 101 which is 5 in decimal.
Subarray 4 to 5 is 11 which is 3 in decimal.
Input : arr[] = {1, 1, 1}
l = 0, r = 2
l = 1, r = 2
Output : 7
3
A Simple Solution is to compute decimal value for every given range using simple binary to decimal conversion. Here each query takes O(len) time where len is length of range.
An Efficient Solution is to do per-computations, so that queries can be answered in O(1) time.
The number represented by subarray arr[l..r] is arr[l]*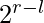 + arr[l+1]*
+ arr[l+1]*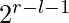 ….. + arr[r]*
….. + arr[r]*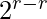
- Make an array pre[] of same size as of given array where pre[i] stores the sum of arr[j]*
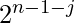 where j includes each value from i to n-1.
where j includes each value from i to n-1. - The number represented by subarray arr[l..r] will be equal to (pre[l] – pre[r+1])/
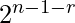 .pre[l] – pre[r+1] is equal to arr[l]*
.pre[l] – pre[r+1] is equal to arr[l]*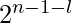 + arr[l+1]*
+ arr[l+1]*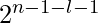 +……arr[r]*
+……arr[r]*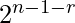 . So if we divide it by
. So if we divide it by 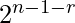 , we get the required answer
, we get the required answer
Flowchart
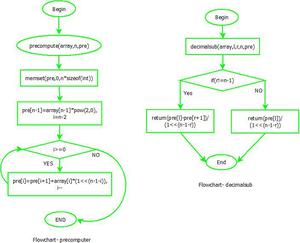
Flowchart
Implementation:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void precompute(int arr[], int n, int pre[])
{
memset(pre, 0, n * sizeof(int));
pre[n - 1] = arr[n - 1] * pow(2, 0);
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--)
pre[i] = pre[i + 1] + arr[i] * (1 << (n - 1 - i));
}
int decimalOfSubarr(int arr[], int l, int r,
int n, int pre[])
{
if (r != n - 1)
return (pre[l] - pre[r + 1]) / (1 << (n - 1 - r));
return pre[l] / (1 << (n - 1 - r));
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int pre[n];
precompute(arr, n, pre);
cout << decimalOfSubarr(arr, 2, 4, n, pre) << endl;
cout << decimalOfSubarr(arr, 4, 5, n, pre) << endl;
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.Arrays;
class GFG {
static void precompute(int arr[], int n, int pre[])
{
Arrays.fill(pre, 0);
pre[n - 1] = arr[n - 1] * (int)(Math.pow(2, 0));
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--)
pre[i] = pre[i + 1] + arr[i] * (1 << (n - 1 - i));
}
static int decimalOfSubarr(int arr[], int l, int r,
int n, int pre[])
{
if (r != n - 1)
return (pre[l] - pre[r + 1]) / (1 << (n - 1 - r));
return pre[l] / (1 << (n - 1 - r));
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1 };
int n = arr.length;
int pre[] = new int[n];
precompute(arr, n, pre);
System.out.println(decimalOfSubarr(arr,
2, 4, n, pre));
System.out.println(decimalOfSubarr(arr,
4, 5, n, pre));
}
}
|
Python3
from math import pow
def precompute(arr, n, pre):
pre[n - 1] = arr[n - 1] * pow(2, 0)
i = n - 2
while(i >= 0):
pre[i] = (pre[i + 1] + arr[i] *
(1 << (n - 1 - i)))
i -= 1
def decimalOfSubarr(arr, l, r, n, pre):
if (r != n - 1):
return ((pre[l] - pre[r + 1]) /
(1 << (n - 1 - r)))
return pre[l] / (1 << (n - 1 - r))
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1]
n = len(arr)
pre = [0 for i in range(n)]
precompute(arr, n, pre)
print(int(decimalOfSubarr(arr, 2, 4, n, pre)))
print(int(decimalOfSubarr(arr, 4, 5, n, pre)))
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static void precompute(int[] arr, int n, int[] pre)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
pre[i] = 0;
pre[n - 1] = arr[n - 1] * (int)(Math.Pow(2, 0));
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--)
pre[i] = pre[i + 1] + arr[i] * (1 << (n - 1 - i));
}
static int decimalOfSubarr(int[] arr, int l, int r,
int n, int[] pre)
{
if (r != n - 1)
return (pre[l] - pre[r + 1]) / (1 << (n - 1 - r));
return pre[l] / (1 << (n - 1 - r));
}
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1 };
int n = arr.Length;
int[] pre = new int[n];
precompute(arr, n, pre);
Console.WriteLine(decimalOfSubarr(arr,
2, 4, n, pre));
Console.WriteLine(decimalOfSubarr(arr,
4, 5, n, pre));
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function precompute(&$arr, $n, &$pre)
{
$pre[$n - 1] = $arr[$n - 1] * pow(2, 0);
for ($i = $n - 2; $i >= 0; $i--)
$pre[$i] = $pre[$i + 1] + $arr[$i] *
(1 << ($n - 1 - $i));
}
function decimalOfSubarr(&$arr, $l, $r, $n, &$pre)
{
if ($r != $n - 1)
return ($pre[$l] - $pre[$r + 1]) /
(1 << ($n - 1 - $r));
return $pre[$l] / (1 << ($n - 1 - $r));
}
$arr = array(1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1 );
$n = sizeof($arr);
$pre = array_fill(0, $n, NULL);
precompute($arr, $n, $pre);
echo decimalOfSubarr($arr, 2, 4, $n, $pre) . "\n";
echo decimalOfSubarr($arr, 4, 5, $n, $pre) . "\n";
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
function precompute(arr, n, pre)
{
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
pre[i] = 0;
pre[n - 1] = arr[n - 1] * (Math.pow(2, 0));
for (let i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--)
pre[i] = pre[i + 1] + arr[i] *
(1 << (n - 1 - i));
}
function decimalOfSubarr(arr, l, r,n, pre)
{
if (r != n - 1)
return (pre[l] - pre[r + 1]) / (1 << (n - 1 - r));
return pre[l] / (1 << (n - 1 - r));
}
let arr = [1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1];
let n = arr.length;
let pre = new Array(n)
precompute(arr, n, pre);
document.write(decimalOfSubarr(arr,2, 4, n, pre)+"<br>");
document.write(decimalOfSubarr(arr, 4, 5, n, pre));
</script>
|
Time complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space: O(n)
Efficient approach :
traverse the array from the given start index to end index, multiplying each binary digit with the corresponding power of 2 and adding the result.
Implementation :
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int decimalOfSubarr(int arr[], int l, int r, int n) {
int ans = 0, p = 1;
for (int i = r; i >= l; i--) {
ans += arr[i] * p;
p *= 2;
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
int arr[] = {1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << decimalOfSubarr(arr, 2, 4, n) << endl;
cout << decimalOfSubarr(arr, 4, 5, n) << endl;
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static int decimalOfSubarr(int[] arr, int l, int r, int n) {
int ans = 0, p = 1;
for (int i = r; i >= l; i--) {
ans += arr[i] * p;
p *= 2;
}
return ans;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1};
int n = arr.length;
System.out.println(decimalOfSubarr(arr, 2, 4, n));
System.out.println(decimalOfSubarr(arr, 4, 5, n));
}
}
|
Python3
def decimalOfSubarr(arr, l, r, n):
ans = 0
p = 1
for i in range(r, l-1, -1):
ans += arr[i] * p
p *= 2
return ans
arr = [1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1]
n = len(arr)
print(decimalOfSubarr(arr, 2, 4, n))
print(decimalOfSubarr(arr, 4, 5, n))
|
Javascript
function decimalOfSubarr(arr, l, r, n) {
let ans = 0
let p = 1
for (let i = r; i >= l; i--) {
ans += arr[i] * p
p *= 2
}
return ans
}
let arr = [1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1]
let n = arr.length
console.log(decimalOfSubarr(arr, 2, 4, n))
console.log(decimalOfSubarr(arr, 4, 5, n))
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static int decimalOfSubarr(int[] arr, int l, int r,
int n)
{
int ans = 0, p = 1;
for (int i = r; i >= l; i--) {
ans += arr[i] * p;
p *= 2;
}
return ans;
}
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1 };
int n = arr.Length;
Console.WriteLine(decimalOfSubarr(arr,
2, 4, n));
Console.WriteLine(decimalOfSubarr(arr,
4, 5, n));
}
}
|
Time complexity: O(r-l+1), which is equivalent to the length of the subarray
Auxiliary Space: O(1), as we are not using any additional data structures.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...