Print sums of all subsets of a given set
Last Updated :
22 Feb, 2023
Given an array of integers, print sums of all subsets in it. Output sums can be printed in any order.
Examples :
Input : arr[] = {2, 3}
Output: 0 2 3 5
Input : arr[] = {2, 4, 5}
Output : 0 2 4 5 6 7 9 11
Method 1 (Recursive)
We can recursively solve this problem. There are total 2n subsets. For every element, we consider two choices, we include it in a subset and we don’t include it in a subset. Below is recursive solution based on this idea.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void subsetSums(int arr[], int l, int r, int sum = 0)
{
if (l > r) {
cout << sum << " ";
return;
}
subsetSums(arr, l + 1, r, sum + arr[l]);
subsetSums(arr, l + 1, r, sum);
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 5, 4, 3 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
subsetSums(arr, 0, n - 1);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
static void subsetSums(int[] arr, int l, int r, int sum)
{
if (l > r) {
System.out.print(sum + " ");
return;
}
subsetSums(arr, l + 1, r, sum + arr[l]);
subsetSums(arr, l + 1, r, sum);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] arr = { 5, 4, 3 };
int n = arr.length;
subsetSums(arr, 0, n - 1, 0);
}
}
|
Python3
def subsetSums(arr, l, r, sum=0):
if l > r:
print(sum, end=" ")
return
subsetSums(arr, l + 1, r, sum + arr[l])
subsetSums(arr, l + 1, r, sum)
arr = [5, 4, 3]
n = len(arr)
subsetSums(arr, 0, n - 1)
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static void subsetSums(int[] arr, int l, int r, int sum)
{
if (l > r) {
Console.Write(sum + " ");
return;
}
subsetSums(arr, l + 1, r, sum + arr[l]);
subsetSums(arr, l + 1, r, sum);
}
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 5, 4, 3 };
int n = arr.Length;
subsetSums(arr, 0, n - 1, 0);
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function subsetSums($arr, $l,
$r, $sum = 0)
{
if ($l > $r)
{
echo $sum , " ";
return;
}
subsetSums($arr, $l + 1, $r,
$sum + $arr[$l]);
subsetSums($arr, $l + 1, $r, $sum);
}
$arr = array(5, 4, 3);
$n = count($arr);
subsetSums($arr, 0, $n - 1);
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
function subsetSums(arr, l, r, sum)
{
if (l > r)
{
document.write(sum + " ");
return;
}
subsetSums(arr, l + 1, r,
sum + arr[l]);
subsetSums(arr, l + 1, r, sum);
}
let arr = [5, 4, 3];
let n = arr.length;
subsetSums(arr, 0, n - 1, 0);
</script>
|
Output :
12 9 8 5 7 4 3 0
Time complexity : O(2^n)
Auxiliary Space : O(n)
Method 2 (Iterative)
As discussed above, there are total 2n subsets. The idea is to generate a loop from 0 to 2n – 1. For every number, pick all array elements corresponding to 1s in the binary representation of the current number.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void subsetSums(int arr[], int n)
{
long long total = 1 << n;
for (long long i = 0; i < total; i++) {
long long sum = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
if (i & (1 << j))
sum += arr[j];
cout << sum << " ";
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 5, 4, 3 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
subsetSums(arr, n);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static void subsetSums(int arr[], int n)
{
int total = 1 << n;
for (int i = 0; i < total; i++) {
int sum = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
if ((i & (1 << j)) != 0)
sum += arr[j];
System.out.print(sum + " ");
}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr[] = new int[] { 5, 4, 3 };
int n = arr.length;
subsetSums(arr, n);
}
}
|
Python3
def subsetSums(arr, n):
total = 1 << n
for i in range(total):
Sum = 0
for j in range(n):
if ((i & (1 << j)) != 0):
Sum += arr[j]
print(Sum, "", end = "")
arr = [ 5, 4, 3 ]
n = len(arr)
subsetSums(arr, n);
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static void subsetSums(int[] arr, int n)
{
int total = 1 << n;
for (int i = 0; i < total; i++) {
int sum = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
if ((i & (1 << j)) != 0)
sum += arr[j];
Console.Write(sum + " ");
}
}
static void Main() {
int[] arr = { 5, 4, 3 };
int n = arr.Length;
subsetSums(arr, n);
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function subsetSums($arr, $n)
{
$total = 1 << $n;
for ($i = 0; $i < $total; $i++)
{
$sum = 0;
for ($j = 0; $j < $n; $j++)
if ($i & (1 << $j))
$sum += $arr[$j];
echo $sum , " ";
}
}
$arr = array(5, 4, 3);
$n = sizeof($arr);
subsetSums($arr, $n);
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
function subsetSums(arr, n)
{
let total = 1 << n;
for(let i = 0; i < total; i++)
{
let sum = 0;
for(let j = 0; j < n; j++)
if ((i & (1 << j)) != 0)
sum += arr[j];
document.write(sum + " ");
}
}
let arr = [ 5, 4, 3 ];
let n = arr.length;
subsetSums(arr, n);
</script>
|
Output :
0 5 4 9 3 8 7 12
Time Complexity: O(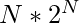 )
)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Thanks to cfh for suggesting above iterative solution in a comment.
Note: We haven’t actually created sub-sets to find their sums rather we have just used recursion to find sum of non-contiguous sub-sets of the given set.
A more Efficient Iterative method:
In this method, while visiting a new element, we take its sum with all previously stored sums. This method stores the sums of all subsets and hence it is valid for smaller inputs.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void subsetSums(int nums[], int n)
{
vector<int> s = {0};
for (int i = 0; i <n; i++) {
const int v = s.size();
for (int t = 0; t < v; t++) {
s.push_back(s[t] + nums[i]);
}
}
for(int i=0;i<s.size();i++)
cout << s[i] << " ";
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 5, 4, 3 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
subsetSums(arr, n);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
public static void subsetSums(int[] nums, int n) {
ArrayList<Integer> s = new ArrayList<Integer>();
s.add(0);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int v = s.size();
for (int t = 0; t < v; t++) {
s.add(s.get(t) + nums[i]);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(s.get(i) + " ");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 5, 4, 3 };
int n = arr.length;
subsetSums(arr, n);
}
}
|
Python3
def subsetSums(nums,n):
s = [0]
for i in range(n):
v = len(s)
for t in range(v):
s.append(s[t] + nums[i])
print(s,end=' ')
arr = [5, 4, 3 ]
n = len(arr)
subsetSums(arr, n)
|
C#
using System;
public class Subsets
{
static void subsetSums(int[] nums, int n)
{
int[] s = new int[1];
s[0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int v = s.Length;
for (int t = 0; t < v; t++)
{
Array.Resize(ref s, s.Length + 1);
s[s.Length - 1] = s[t] + nums[i];
}
}
Console.Write(string.Join(" ", s));
}public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 5, 4, 3 };
int n = arr.Length;
subsetSums(arr, n);
}
}
|
Javascript
function subsetSums(nums, n) {
let s = [0];
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
let v = s.length;
for (let t = 0; t < v; t++) {
s.push(s[t] + nums[i]);
}
}
for (let i=0; i<s.length; i++) {
process.stdout.write(s[i]+" ");
}
}
let arr = [5, 4, 3];
let n = arr.length;
subsetSums(arr, n);
|
Output:
0 5 4 9 3 8 7 12
Time Complexity: O(2^N)
Auxiliary Space: O(N) for storing the ans
Thanks to shivampatidar6116 for suggesting the above iterative solution
The above-mentioned techniques can be used to perform various operations on sub-sets like multiplication, division, XOR, OR, etc, without actually creating and storing the sub-sets and thus making the program memory efficient.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...