Print Nodes after level K from given node in Graph in ascending order
Last Updated :
20 Apr, 2023
Given an undirected graph, a source node src, and an integer K, the task is to print all nodes after level K from the source node in ascending order
(nodes are from 1 to N ).
Examples:
Input: { (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (2, 10), (2, 4), (3, 8), (3, 9), (4, 11), (5, 6), (5, 7), (8, 12), (10, 13) }, K = 1, src = 1
Output: 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
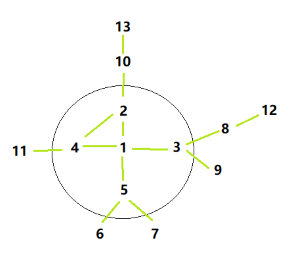
under level 1 – 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
Input 2: {, (1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (4, 5), (5, 6), (6, 7), (7, 8), (8, 9) }, K = 2, src = 4
Output: 1 7 8 9
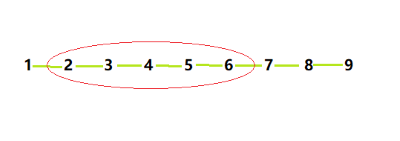
under level 2 : 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
Approach: This can be solved with the following idea:
Using BFS, while moving across the neighboring element of src and maintaining levels in order to keep a count that we have crossed K. Once, K is crossed push the nodes data into a vector which will be returned as output.
Steps involved in the implementation of the above approach:
- Make an adjacency list from the input.
- Take a vector ans to store all nodes after level K.
- Take a queue for BFS traversal.
- When we iterate the queue for more than K times it means that now nodes present in the queue lie after level K.
- Take a visited array to check whether the particular node is previously visited or not.
- Take a top element of the queue and rest on that node and add every neighbor node of that particular node into the queue.
- At last sort the ans array and print all elements.
Below is the code for the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
vector<int> afterLevelK(int src, int k, vector<int> adj[],
int n)
{
vector<int> vis(n + 1, 0);
queue<int> q;
vector<int> ans;
q.push(src);
vis[src] = 1;
while (!q.empty()) {
int n = q.size();
while (n--) {
int top = q.front();
q.pop();
if (k < 0) {
ans.push_back(top);
}
for (auto x : adj[top]) {
if (!vis[x]) {
q.push(x);
vis[x] = 1;
}
}
}
k--;
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int n = 9;
vector<pair<int, int> > links
= { { 1, 2 }, { 2, 3 }, { 3, 4 }, { 4, 5 },
{ 5, 6 }, { 6, 7 }, { 7, 8 }, { 8, 9 } };
vector<int> adj[n + 1];
for (auto it : links) {
int u = it.first;
int v = it.second;
adj[u].push_back(v);
adj[v].push_back(u);
}
int src = 4;
int k = 2;
vector<int> ans = afterLevelK(src, k, adj, n);
sort(ans.begin(), ans.end());
for (auto it : ans) {
cout << it << " ";
}
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static List<Integer>
afterLevelK(int src, int k, ArrayList<Integer>[] adj,
int n)
{
boolean[] vis = new boolean[n + 1];
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
q.offer(src);
vis[src] = true;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int len = q.size();
while (len-- > 0) {
int top = q.poll();
if (k < 0) {
ans.add(top);
}
for (int x : adj[top]) {
if (vis[x] == false) {
q.add(x);
vis[x] = true;
}
}
}
k--;
}
return ans;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 9;
int[][] links
= { { 1, 2 }, { 2, 3 }, { 3, 4 }, { 4, 5 },
{ 5, 6 }, { 6, 7 }, { 7, 8 }, { 8, 9 } };
ArrayList<Integer>[] adj = new ArrayList[n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
adj[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (int[] link : links) {
int u = link[0];
int v = link[1];
adj[u].add(v);
adj[v].add(u);
}
int src = 4;
int k = 2;
List<Integer> ans = afterLevelK(src, k, adj, n);
Collections.sort(ans);
for (int it : ans) {
System.out.print(it + " ");
}
}
}
|
Python3
from collections import deque
def after_level_k(src, k, adj, n):
vis = [False] * (n + 1)
q = deque()
ans = []
q.append(src)
vis[src] = True
while q:
n = len(q)
while n > 0:
top = q.popleft()
if k < 0:
ans.append(top)
for x in adj[top]:
if not vis[x]:
q.append(x)
vis[x] = True
n -= 1
k -= 1
return ans
if __name__ == "__main__":
n = 9
links = [(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (4, 5), (5, 6), (6, 7), (7, 8), (8, 9)]
adj = [[] for _ in range(n+1)]
for u, v in links:
adj[u].append(v)
adj[v].append(u)
src = 4
k = 2
ans = after_level_k(src, k, adj, n)
ans.sort()
for it in ans:
print(it, end=" ")
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
class Program {
static List<int> AfterLevelK(int src, int k,
List<int>[] adj, int n)
{
bool[] vis = new bool[n + 1];
Queue<int> q = new Queue<int>();
List<int> ans = new List<int>();
q.Enqueue(src);
vis[src] = true;
while (q.Count > 0) {
int count = q.Count;
while (count-- > 0) {
int top = q.Dequeue();
if (k < 0) {
ans.Add(top);
}
foreach(int x in adj[top])
{
if (!vis[x]) {
q.Enqueue(x);
vis[x] = true;
}
}
}
k--;
}
return ans;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int n = 9;
Tuple<int, int>[] links = new Tuple<int, int>[] {
Tuple.Create(1, 2), Tuple.Create(2, 3),
Tuple.Create(3, 4), Tuple.Create(4, 5),
Tuple.Create(5, 6), Tuple.Create(6, 7),
Tuple.Create(7, 8), Tuple.Create(8, 9)
};
List<int>[] adj = new List<int>[ n + 1 ];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
adj[i] = new List<int>();
}
foreach(Tuple<int, int> it in links)
{
int u = it.Item1;
int v = it.Item2;
adj[u].Add(v);
adj[v].Add(u);
}
int src = 4;
int k = 2;
List<int> ans = AfterLevelK(src, k, adj, n);
ans.Sort();
foreach(int it in ans) { Console.Write(it + " "); }
}
}
|
Javascript
function afterLevelK(src, k, adj, n) {
const vis = new Array(n + 1).fill(0);
const q = [];
const ans = [];
q.push(src);
vis[src] = 1;
while (q.length !== 0) {
const levelSize = q.length;
for (let i = 0; i < levelSize; i++) {
const top = q.shift();
if (k < 0) {
ans.push(top);
}
for (let j = 0; j < adj[top].length; j++) {
const neighbour = adj[top][j];
if (!vis[neighbour]) {
q.push(neighbour);
vis[neighbour] = 1;
}
}
}
k--;
}
return ans;
}
(function main() {
const n = 9;
const links = [
[1, 2],
[2, 3],
[3, 4],
[4, 5],
[5, 6],
[6, 7],
[7, 8],
[8, 9]
];
const adj = new Array(n + 1).fill().map(() => []);
for (const [u, v] of links) {
adj[u].push(v);
adj[v].push(u);
}
const src = 4;
const k = 2;
const ans = afterLevelK(src, k, adj, n);
ans.sort((a, b) => a - b);
console.log(ans.join(' '));
})();
|
Time Complexity: O (V+E)
Auxiliary Space: O (V)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...