Overview of Wireless Metropolitan Area Network (WMAN)
Last Updated :
04 Aug, 2022
WMAN : Wireless Metropolitan Area Network (WMAN) is a type of Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) and the only thing is that the connectivity is wireless. It spans multiple locations within a geographic area and it serves the range greater than 100 meters. It is one type of wireless networking which has a coverage area approximately the size of a city. Generally it spans or covers an area which is larger than the Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) but smaller than Wireless Wide Area Network (WWAN). WMAN connections can be Point to Point or Point to Multipoint networks. It is a newer type networking technology which supplements to some wired technologies like Gigabit Ethernet, Resilient Packet Ring (RPR), SONET over IP etc.
A WMAN is mostly governed by a single entity such as an Internet Service Provider (ISP), government entity, or any other large corporation. The user has to take the authorized access from the providers to use WMAN as the access is restricted only to the authorized users/subscribers.
The below figure illustrates a WMAN
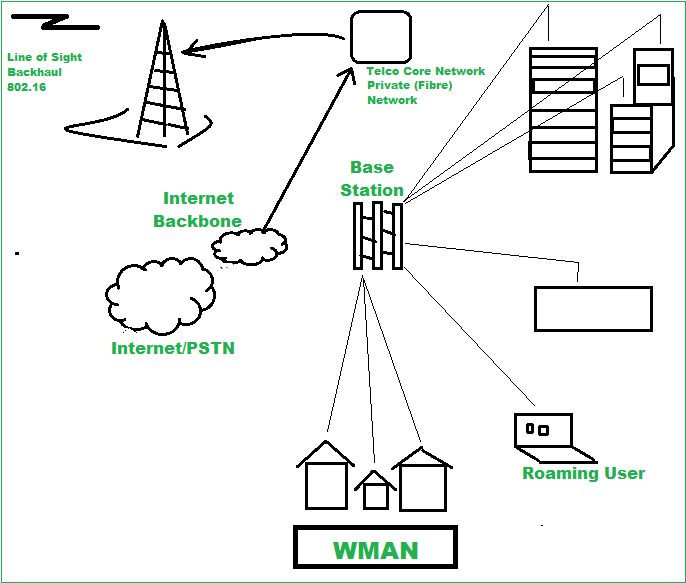
Types of WMAN :
There are two fundamental types of wireless MAN i.e.
1. Back haul –
It is an enterprise type of network , cellular-tower connection. It can also use WiFi hotspot. In this type of network fixed wireless is used which saves large amount of money per year. Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) can also be used in Back haul, but Wireless connection is faster and less cost than normal fiber optics connection.
2. Last mile –
It is used for temporary networks means where network requirement is for a temporary period. Like some large construction buildings/sites where conventional network service ( like DSL broadband and cable modem) is disrupted.
Characteristics of WMAN :
- Connection can be Point to Point or Point to Multipoint networks.
- Service to multiple nodes from one access point.
- Covers a larger area within a radius up to 50 km.
- Stable connections to the terminals.
WMAN Technology :
- Wireless Interoperable Metropolitan Area Exchange (WiMAX) –
WiMAX is mostly used Wireless Metropolitan Area Network (WMAN) technology based on the IEEE 802.16 set of standards. It provides Multiple Physical Layer(PHY) and Media Access Control (MAC) options. It acts as an alternate wireless version of Ethernet and deployed in a variety of spectrum bands: 2.3GHz, 2.5GHz, 3.5GHz, and 5.8GHz.
- Local Multipoint Distributed Service (LMDS) –
It is a broadband microwave wireless transmission technology which provides reliable digital two-way voice, data and Internet services. It is a wireless point to multipoint communication system that’s why called as Local Multipoint Distribution System where Local refers to signal range limit, Multipoint refers to broadcast access, Distributed refers to transmission of wide range of data, Service refers to relationship between operators and users. It generally uses low powered, high frequency i.e. 25 to 31 GHz over a short distance.
- Multi-Channel Multipoint Distributed Service (MMDS) –
MMDS was previously known as Wireless Cable or Broadband Radio Service (BRS). It is a wireless telecommunication technology which operates in the ultra-high-frequency (UHF) portion of the radio spectrum between 2.5GHz and 2.7GHz and is used for telecommunications technology and general-purpose broadband networking.
Benefits of WMAN :
- Covers multiple locations within a metropolitan area.
- Does not require high cost for infrastructure in placing fiber or copper cabling and leasing lines.
- Works as backups for wired networks.
- Easy to use, extend, exchange.
Examples of WMAN :
- WiMAX
- WiBro
- Networking between buildings that are under construction.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...