Operational Acceptance Testing (OAT)
Last Updated :
09 Nov, 2023
Operational Acceptance Testing (OAT)
is a type of
software testing
that is performed to conduct operational pre-release of a software, system or application to check the quality of it. Operational Acceptance Testing is a very usual software testing whose type is non-functional and it is mainly used in software development and software maintenance projects. Operational Acceptance Testing mainly focuses on the operational readiness of the software and to become part of the production environment. Functional testing in operational acceptance testing is limited to the tests required to verify the non-functional aspects of the system. Operational Acceptance Testing is also known as Operational Readiness Testing (ORT) or Operations Readiness and Assurance Testing (ORAT).
Objective of Operational Acceptance Testing:
The objective of Operational Acceptance Testing is:
- To determine resiliency of the software.
- To determine recovering ability of the software.
- To determine integrity of the software.
- To determine software can be deployed on a network on ITIL standards.
- To determine supportability of the software.
Operational Acceptance Testing Steps:
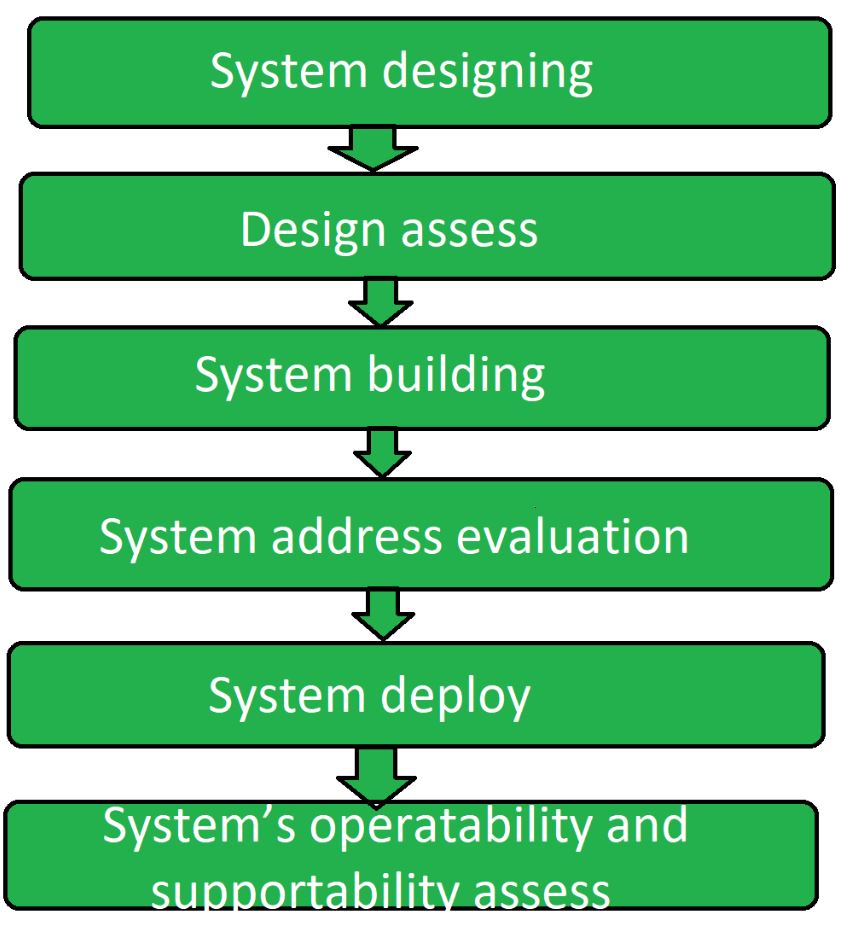
- System designing: First step is designing the system as per the user requirements. The system is designed in such a way that it fulfills the end user requirements.
- Design assess: After the designing of the system, its designing is analyzed. It is analyzed that whether the system is according to user requirements and whether it will operate the way it is designed.
- System building: After the design of system is prepared and analysis is done, system construction phase starts. It is the main phase of operational acceptance testing.
- System address evaluation: Once the system building is finished, after that system address is evaluated and it is checked whether is according to user requirement.
- System deploy: After building and address evaluation of software, it is established according to perform the specific task for the purpose of which it is constructed.
- System’s operability and supportability assess: Now in the last phase the operability and supportability of the software system or application is tested. This leads to the end of whole procedure.
Types of Operational Acceptance Testing:
- Load Testing: It evaluates a system’s or application’s performance in its operational setting under normal load levels. Its purpose is to assess the system’s capacity to respond quickly, process large amounts of data and use its resources efficiently under different conditions of simultaneous user activity.
- Performance Testing: It includes load testing, stress testing and other performance-related evaluations to see if the system operates properly under typical operating conditions.
- Installation Testing: This type of testing makes sure that the system can be properly setup and installed in a production environment. It also makes sure that everything is installed correctly and that the installation process goes quickly.
- Backup and Restore Testing: This type of testing assesses the system’s capacity to generate backups, carry out planned backups and restore data or the entire system in the event of calamities or failures.
- Security Testing: It focuses on assessing the security measures in place in the system and making sure that they comply to data protection regulations, security policies and access controls.
- Recovery Testing: It assesses how resistant the system is to major occurrences, including data breaches or catastrophic events and confirms the efficiency of disaster recovery protocols.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...