Mutual Recursion with example of Hofstadter Female and Male sequences
Last Updated :
17 Nov, 2022
Mutual recursion is a variation recursion. Two functions are called mutually recursive if the first function makes a recursive call to the second function and the second function, in turn, calls the first one.
In software development, this concept is used in circular dependency which is a relation between two or more modules which either directly or indirectly depend on each other to function properly. Such modules are also known as mutually recursive.
A great example of mutual recursion would be implementing the Hofstadter Sequence.
Hofstadter Sequence
In mathematics, a Hofstadter sequence is a member of a family of related integer sequences defined by non-linear recurrence relations. In this example we are going to focus on Hofstadter Female and Male sequences:
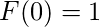 [Tex]M ( 0 ) = 0[/Tex]
[Tex]M ( 0 ) = 0[/Tex] 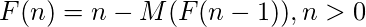
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int hofstadterFemale(int);
int hofstadterMale(int);
int hofstadterFemale(int n)
{
if (n < 0)
return 0;
else
if (n == 0)
return 1;
else
return (n - hofstadterFemale(n - 1));
}
int hofstadterMale(int n)
{
if (n < 0)
return 0;
else
if (n == 0)
return 0;
else
return (n - hofstadterMale(n - 1));
}
int main()
{
int i;
cout << "F: ";
for (i = 0; i < 20; i++)
cout << hofstadterFemale(i) << " ";
cout << "\n";
cout << "M: ";
for (i = 0; i < 20; i++)
cout << hofstadterMale(i)<< " ";
return 0;
}
|
C
#include <stdio.h>
int hofstaderFemale(int);
int hofstaderMale(int);
int hofstaderFemale(int n)
{
if (n < 0)
return;
else
return (n == 0) ? 1 : n - hofstaderFemale(n - 1);
}
int hofstaderMale(int n)
{
if (n < 0)
return;
else
return (n == 0) ? 0 : n - hofstaderMale(n - 1);
}
int main()
{
int i;
printf("F: ");
for (i = 0; i < 20; i++)
printf("%d ", hofstaderFemale(i));
printf("\n");
printf("M: ");
for (i = 0; i < 20; i++)
printf("%d ", hofstaderMale(i));
return 0;
}
|
Java
Python3
C#
PHP
Javascript
Output:
F: 1 0 2 1 3 2 4 3 5 4 6 5 7 6 8 7 9 8 10 9
M: 0 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 7 8 8 9 9 10
Disadvantages of Circular Dependency/Mutual Recursion:
- Circular dependencies can cause a domino effect when a small local change in one module spreads into other modules and has unwanted global effects
- Circular dependencies can also result in infinite recursions or other unexpected failures.
- Circular dependencies may also cause memory leaks by preventing certain very primitive automatic garbage collectors (those that use reference counting) from deallocating unused objects.
References: Wikipedia
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...