Merge two sorted arrays
Last Updated :
03 Oct, 2023
Given two sorted arrays, the task is to merge them in a sorted manner.
Examples:
Input: arr1[] = { 1, 3, 4, 5}, arr2[] = {2, 4, 6, 8}
Output: arr3[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 8}
Input: arr1[] = { 5, 8, 9}, arr2[] = {4, 7, 8}
Output: arr3[] = {4, 5, 7, 8, 8, 9}
Naive Approach:
It is the brute force method to do the same. Take all the elements of arr1 and arr2 in arr3. Then simply sort the arr3.
The implementation of above approach is:
C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void mergeArrays(int arr1[], int arr2[], int n1,
int n2, int arr3[])
{
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
while(i < n1){
arr3[k++] = arr1[i++];
}
while(j < n2){
arr3[k++] = arr2[j++];
}
sort(arr3, arr3+n1+n2);
}
int main()
{
int arr1[] = {1, 3, 5, 7};
int n1 = sizeof(arr1) / sizeof(arr1[0]);
int arr2[] = {2, 4, 6, 8};
int n2 = sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(arr2[0]);
int arr3[n1+n2];
mergeArrays(arr1, arr2, n1, n2, arr3);
cout << "Array after merging" <<endl;
for (int i=0; i < n1+n2; i++)
cout << arr3[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr1[] = {1, 3, 5, 7};
int n1 = arr1.length;
int arr2[] = {2, 4, 6, 8};
int n2 = arr2.length;
int arr3[] = new int[n1 + n2];
mergeArrays(arr1, arr2, n1, n2, arr3);
System.out.println("Array after merging");
for (int i=0; i < n1+n2; i++)
System.out.print(arr3[i] + " ");
}
public static void mergeArrays(int[] arr1, int[] arr2, int n1, int n2, int[] arr3){
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int k = 0;
while(i < n1){
arr3[k++] = arr1[i++];
}
while(j < n2){
arr3[k++] = arr2[j++];
}
Arrays.sort(arr3);
}
}
|
Python3
def mergeArrays(arr1, arr2, n1, n2, arr3):
i = 0
j = 0
k = 0
while(i < n1):
arr3[k] = arr1[i]
k += 1
i += 1
while(j < n2):
arr3[k] = arr2[j]
k += 1
j += 1
arr3.sort()
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr1 = [1, 3, 5, 7]
n1 = len(arr1)
arr2 = [2, 4, 6, 8]
n2 = len(arr2)
arr3 = [0 for i in range(n1+n2)]
mergeArrays(arr1, arr2, n1, n2, arr3)
print("Array after merging")
for i in range(n1 + n2):
print(arr3[i], end=" ")
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG
{
public static void mergeArrays(int[] arr1, int[] arr2, int n1, int n2, int[] arr3) {
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int k = 0;
while (i < n1) {
arr3[k++] = arr1[i++];
}
while (j < n2) {
arr3[k++] = arr2[j++];
}
Array.Sort(arr3);
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int []arr1 = new int[] {1, 3, 5, 7};
int n1 = arr1.Length;
int []arr2 = new int[] {2, 4, 6, 8};
int n2 = arr2.Length;
int []arr3 = new int[n1 + n2];
mergeArrays(arr1, arr2, n1, n2, arr3);
Console.WriteLine("Array after merging");
for (int i = 0; i < n1 + n2; i++)
Console.Write(arr3[i] + " ");
}
}
|
Javascript
function mergeArrays(arr1, arr2, n1, n2, arr3) {
var i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
while (i < n1) {
arr3[k++] = arr1[i++];
}
while (j < n2) {
arr3[k++] = arr2[j++];
}
arr3.sort();
}
var arr1 = [1, 3, 5, 7];
var n1 = arr1.length;
var arr2 = [2, 4, 6, 8];
var n2 = arr2.length;
var arr3 = new Array(n1 + n2);
mergeArrays(arr1, arr2, n1, n2, arr3);
console.log("Array after merging");
for (var i = 0; i < n1 + n2; i++)
process.stdout.write(arr3[i] + " ");
|
Output
Array after merging
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Time Complexity : O((m+n) log(m+n)) , the whole size of arr3 is m+n
Auxiliary Space: O(m+n), where m is the size of arr1 and n is the size of arr2.
Method 2 (O(n1 * n2) Time and O(n1+n2) Extra Space)
- Create an array arr3[] of size n1 + n2.
- Copy all n1 elements of arr1[] to arr3[]
- Traverse arr2[] and one by one insert elements (like insertion sort) of arr3[] to arr1[]. This step take O(n1 * n2) time.
We have discussed implementation of above method in Merge two sorted arrays with O(1) extra space
Method 3 (O(n1 + n2) Time and O(n1 + n2) Extra Space)
The idea is to use Merge function of Merge sort.
- Create an array arr3[] of size n1 + n2.
- Simultaneously traverse arr1[] and arr2[].
- Pick smaller of current elements in arr1[] and arr2[], copy this smaller element to next position in arr3[] and move ahead in arr3[] and the array whose element is picked.
- If there are remaining elements in arr1[] or arr2[], copy them also in arr3[].
Below is the illustration of the above approach:
Take two sorted arrays Array1 and Array2 and an Empty Array3 . Take three pointers ‘i’, ‘j’, and ‘k’ for comparisons, here ‘i’ pointer points towards 0th index of Array1, similarly ‘j’ and ‘k’ pointer point towards 0th index of Array2 and Array3
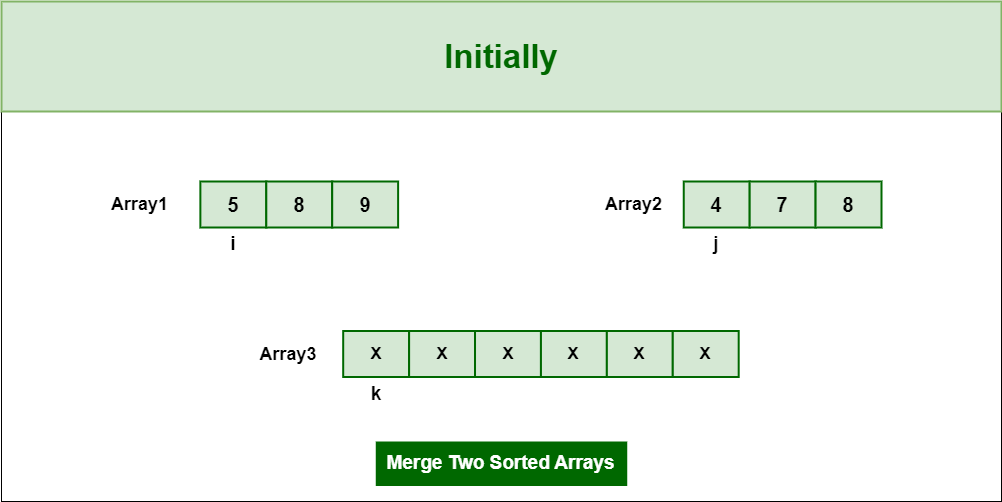
Initial Arrays
Step 1: Pick Smaller element which is 4 and insert in into Array3 and update the pointer ‘j ‘and ‘k’ after comparing ‘i’ and ‘j’.
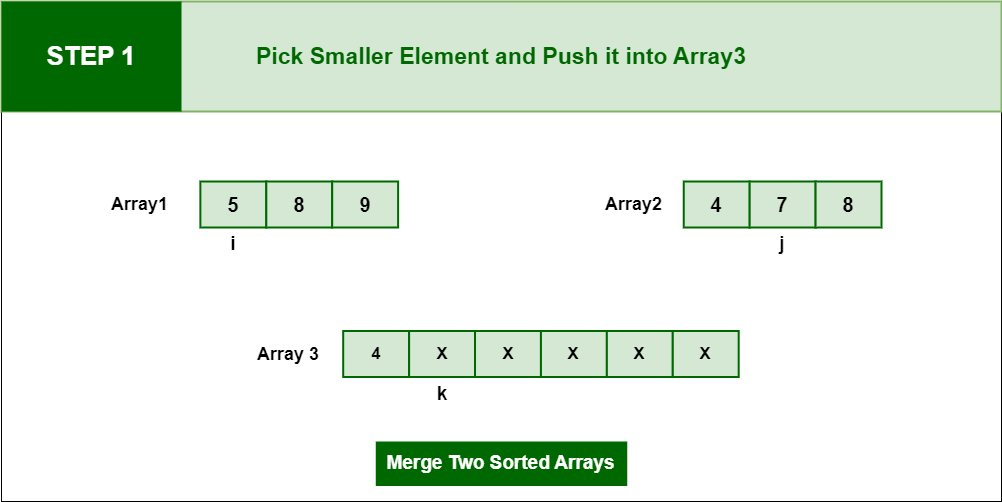
Pick Smaller element which is 4
Step 2: Pick next smaller element which is 5 and insert in into Array3 and update the pointer ‘i’ and ‘k’ after comparing ‘i’ and ‘j’.
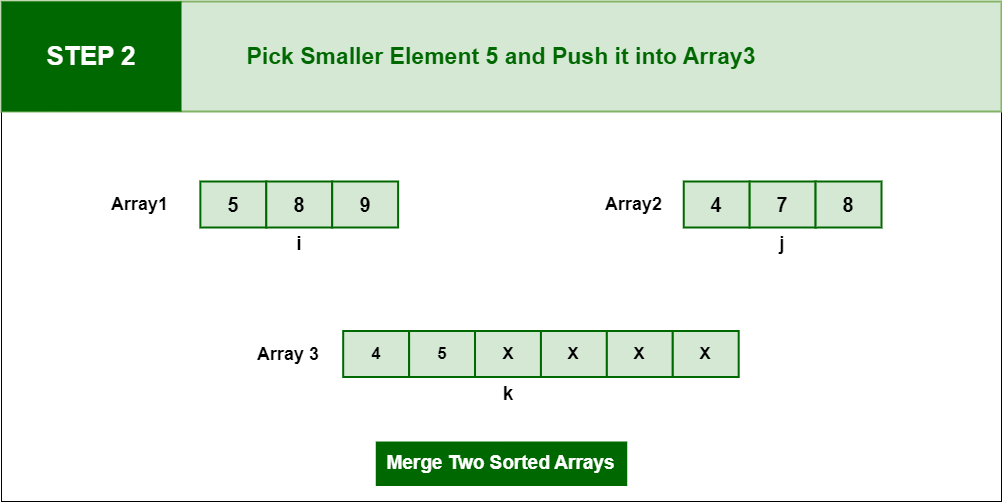
Pick next smaller element which is 5
Step 3: Pick next smaller element which is 7 and insert in into Array3 and update the pointer ‘j’ and ‘k ‘after comparing ‘i’ and ‘j’.
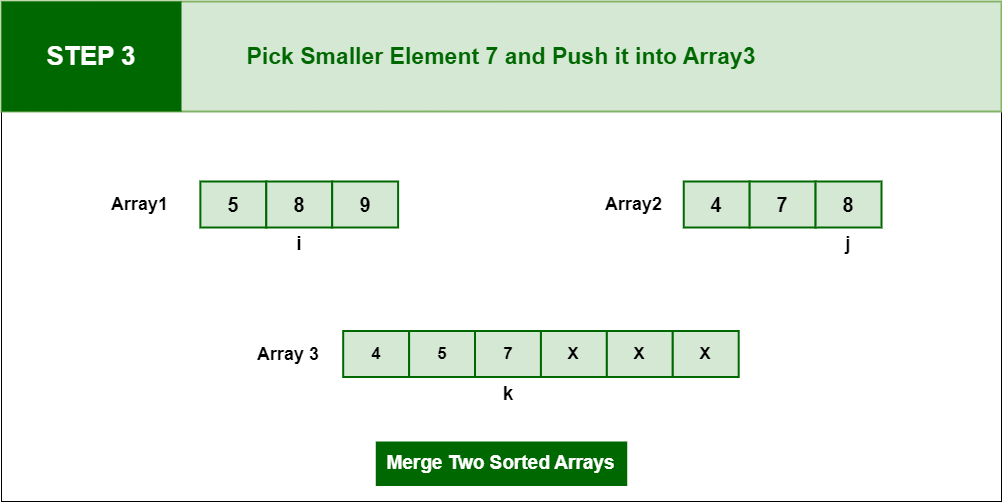
Pick next smaller element which is 7
Step 4: when ‘j’ pointer meets the length of Array2 then first while loop breaks and second while loop copies all elements from arr1 to arr3.
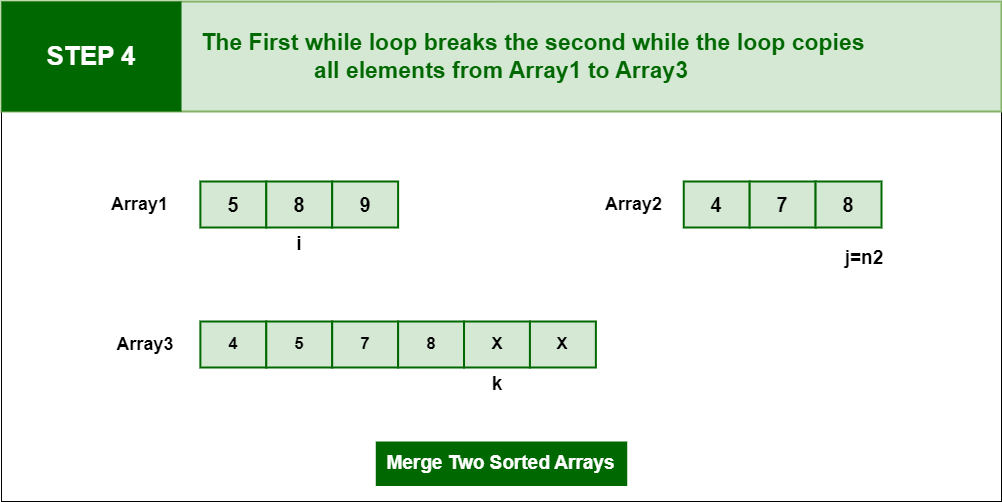
second while loop copies all elements from arr1 to arr3.
Step 5: Pick adjacent element from Array1 and insert in into Array3 and update the pointer i and k
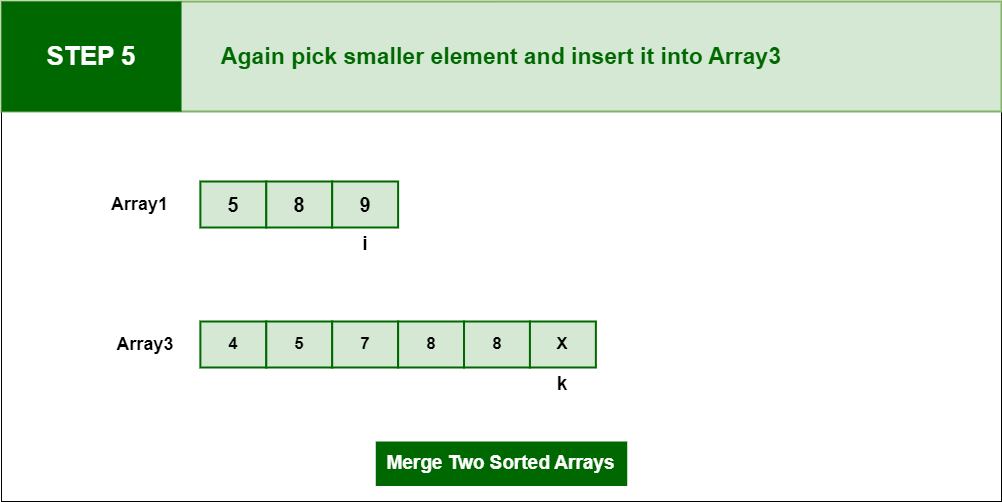
Pick adjacent element from Array1 and insert in into Array3
Step 6: Pick remaining element from Array1 and insert in into Array3, when i pointer meets the length of Array1 that means k = n1+n2 and at last we have merge sorted Array3
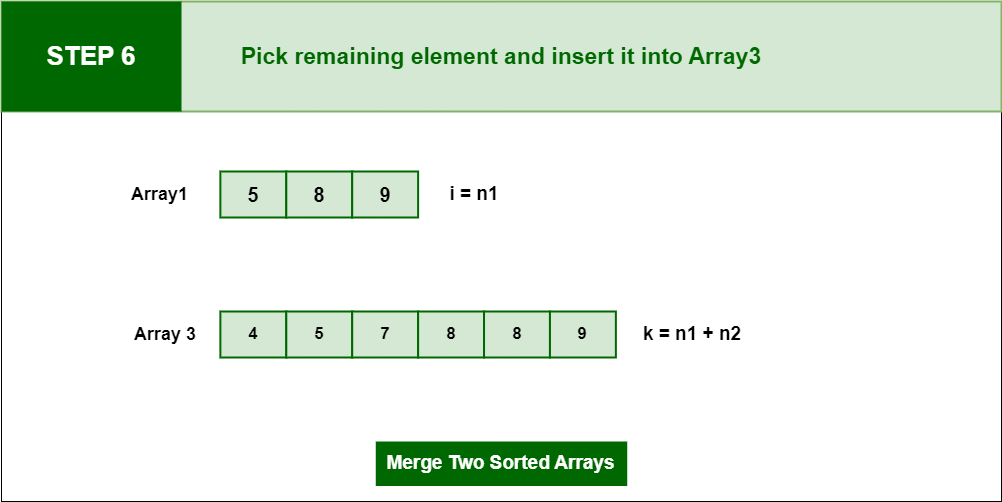
ick remaining element from Array1 and insert in into Array3,
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void mergeArrays(int arr1[], int arr2[], int n1,
int n2, int arr3[])
{
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
while (i<n1 && j <n2)
{
if (arr1[i] < arr2[j])
arr3[k++] = arr1[i++];
else
arr3[k++] = arr2[j++];
}
while (i < n1)
arr3[k++] = arr1[i++];
while (j < n2)
arr3[k++] = arr2[j++];
}
int main()
{
int arr1[] = {1, 3, 5, 7};
int n1 = sizeof(arr1) / sizeof(arr1[0]);
int arr2[] = {2, 4, 6, 8};
int n2 = sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(arr2[0]);
int arr3[n1+n2];
mergeArrays(arr1, arr2, n1, n2, arr3);
cout << "Array after merging" <<endl;
for (int i=0; i < n1+n2; i++)
cout << arr3[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
class MergeTwoSorted
{
public static void mergeArrays(int[] arr1, int[] arr2, int n1,
int n2, int[] arr3)
{
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
while (i<n1 && j <n2)
{
if (arr1[i] < arr2[j])
arr3[k++] = arr1[i++];
else
arr3[k++] = arr2[j++];
}
while (i < n1)
arr3[k++] = arr1[i++];
while (j < n2)
arr3[k++] = arr2[j++];
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int[] arr1 = {1, 3, 5, 7};
int n1 = arr1.length;
int[] arr2 = {2, 4, 6, 8};
int n2 = arr2.length;
int[] arr3 = new int[n1+n2];
mergeArrays(arr1, arr2, n1, n2, arr3);
System.out.println("Array after merging");
for (int i=0; i < n1+n2; i++)
System.out.print(arr3[i] + " ");
}
}
|
Python 3
def mergeArrays(arr1, arr2, n1, n2):
arr3 = [None] * (n1 + n2)
i = 0
j = 0
k = 0
while i < n1 and j < n2:
if arr1[i] < arr2[j]:
arr3[k] = arr1[i]
k = k + 1
i = i + 1
else:
arr3[k] = arr2[j]
k = k + 1
j = j + 1
while i < n1:
arr3[k] = arr1[i];
k = k + 1
i = i + 1
while j < n2:
arr3[k] = arr2[j];
k = k + 1
j = j + 1
print("Array after merging")
for i in range(n1 + n2):
print(str(arr3[i]), end = " ")
arr1 = [1, 3, 5, 7]
n1 = len(arr1)
arr2 = [2, 4, 6, 8]
n2 = len(arr2)
mergeArrays(arr1, arr2, n1, n2);
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
public static void mergeArrays(int[] arr1, int[] arr2,
int n1, int n2, int[] arr3)
{
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
while (i < n1 && j < n2)
{
if (arr1[i] < arr2[j])
arr3[k++] = arr1[i++];
else
arr3[k++] = arr2[j++];
}
while (i < n1)
arr3[k++] = arr1[i++];
while (j < n2)
arr3[k++] = arr2[j++];
}
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr1 = {1, 3, 5, 7};
int n1 = arr1.Length;
int[] arr2 = {2, 4, 6, 8};
int n2 = arr2.Length;
int[] arr3 = new int[n1+n2];
mergeArrays(arr1, arr2, n1, n2, arr3);
Console.Write("Array after merging\n");
for (int i = 0; i < n1 + n2; i++)
Console.Write(arr3[i] + " ");
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function mergeArrays(arr1, arr2 , n1 , n2, arr3) {
var i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
while (i < n1 && j < n2) {
if (arr1[i] < arr2[j])
arr3[k++] = arr1[i++];
else
arr3[k++] = arr2[j++];
}
while (i < n1)
arr3[k++] = arr1[i++];
while (j < n2)
arr3[k++] = arr2[j++];
}
var arr1 = [ 1, 3, 5, 7 ];
var n1 = arr1.length;
var arr2 = [ 2, 4, 6, 8 ];
var n2 = arr2.length;
var arr3 = Array(n1 + n2).fill(0);
mergeArrays(arr1, arr2, n1, n2, arr3);
document.write("Array after merging<br/>");
for (i = 0; i < n1 + n2; i++)
document.write(arr3[i] + " ");
</script>
|
PHP
<?php
function mergeArrays(&$arr1, &$arr2,
$n1, $n2, &$arr3)
{
$i = 0;
$j = 0;
$k = 0;
while ($i < $n1 && $j < $n2)
{
if ($arr1[$i] < $arr2[$j])
$arr3[$k++] = $arr1[$i++];
else
$arr3[$k++] = $arr2[$j++];
}
while ($i < $n1)
$arr3[$k++] = $arr1[$i++];
while ($j < $n2)
$arr3[$k++] = $arr2[$j++];
}
$arr1 = array(1, 3, 5, 7);
$n1 = sizeof($arr1);
$arr2 = array(2, 4, 6, 8);
$n2 = sizeof($arr2);
$arr3[$n1 + $n2] = array();
mergeArrays($arr1, $arr2, $n1,
$n2, $arr3);
echo "Array after merging \n" ;
for ($i = 0; $i < $n1 + $n2; $i++)
echo $arr3[$i] . " ";
?>
|
Output
Array after merging
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Time Complexity : O(n1 + n2)
Auxiliary Space : O(n1 + n2)
Method 4: Using Maps (O(nlog(n) + mlog(m)) Time and O(N) Extra Space)
- Insert elements of both arrays in a map as keys.
- Print the keys of the map.
Below is the implementation of above approach.
CPP
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void mergeArrays(int a[], int b[], int n, int m)
{
map<int, int> mp;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)mp[a[i]]++;
for(int i = 0;i < m;i++)mp[b[i]]++;
for(auto j: mp)
{
for(int i=0; i<j.second;i++)cout<<j.first<<" ";
}
}
int main()
{
int a[] = {1, 3, 5, 7}, b[] = {2, 4, 6, 8};
int size = sizeof(a)/sizeof(int);
int size1 = sizeof(b)/sizeof(int);
mergeArrays(a, b, size, size1);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static void mergeArrays(int a[], int b[], int n, int m)
{
Map<Integer,Boolean> mp = new TreeMap<Integer,Boolean>();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
mp.put(a[i], true);
}
for(int i = 0;i < m;i++)
{
mp.put(b[i], true);
}
for (Map.Entry<Integer,Boolean> me : mp.entrySet())
{
System.out.print(me.getKey() + " ");
}
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int a[] = {1, 3, 5, 7}, b[] = {2, 4, 6, 8};
int size = a.length;
int size1 = b.length;
mergeArrays(a, b, size, size1);
}
}
|
Python3
import bisect
def mergeArrays(a, b, n, m):
mp=[]
for i in range(n):
bisect.insort(mp, a[i])
for i in range(m):
bisect.insort(mp, b[i])
for i in mp:
print(i,end=' ')
arr1 = [1, 3, 5, 7]
arr2 = [2, 4, 6, 8]
size = len(arr1)
size1 = len(arr2)
mergeArrays(arr1, arr2, size, size1)
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG {
static void mergeArrays(int []a, int []b, int n, int m)
{
SortedDictionary<int, Boolean> mp = new SortedDictionary<int, Boolean>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
mp.Add(a[i], true);
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
mp.Add(b[i], true);
}
foreach (KeyValuePair<int, Boolean> me in mp) {
Console.Write(me.Key + " ");
}
}
public static void Main(String[] args) {
int []a = { 1, 3, 5, 7 };
int []b = { 2, 4, 6, 8 };
int size = a.Length;
int size1 = b.Length;
mergeArrays(a, b, size, size1);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function mergeArrays(a , b , n , m)
{
var mp = new Map();
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
mp.set(a[i], true);
}
for (i = 0; i < m; i++) {
mp.set(b[i], true);
}
var a = [];
for ( me of mp.keys()) {
a.push(me);
}
a.sort();
for ( me of a) {
document.write(me + " ");
}
}
var a = [ 1, 3, 5, 7 ], b = [ 2, 4, 6, 8 ];
var size = a.length;
var size1 = b.length;
mergeArrays(a, b, size, size1);
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O( nlog(n) + mlog(m) )
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
Brocade,Goldman-Sachs,Juniper,Linkedin,Microsoft,Quikr,Snapdeal,Synopsys,Zoho
Related Articles :
Merge two sorted arrays with O(1) extra space
Merge k sorted arrays | Set 1
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...