We are given two sorted arrays. We need to merge these two arrays such that the initial numbers (after complete sorting) are in the first array and the remaining numbers are in the second array
Examples:
Input: ar1[] = {10}, ar2[] = {2, 3}
Output: ar1[] = {2}, ar2[] = {3, 10}
Input: ar1[] = {1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20}, ar2[] = {2, 3, 8, 13}
Output: ar1[] = {1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 9}, ar2[] = {10, 13, 15, 20}
Note: This task is simple and O(m+n) if we are allowed to use extra space. But it becomes really complicated when extra space is not allowed and doesn’t look possible in less than O(m*n) worst-case time. Though further optimizations are possible
Efficient Approach: To solve the problem follow the below idea:
The idea is to begin from the last element of ar2[] and search for it in ar1[]. If there is a greater element in ar1[], then we move the last element of ar1[] to ar2[]. To keep ar1[] and ar2[] sorted, we need to place the last element of ar2[] at the correct place in ar1[]. We can use the Insertion Sort for this
Follow the below steps to solve the problem:
- Iterate through every element of ar2[] starting from the last element
- Do the following for every element ar2[i]
- Store last element of ar1[]: last = ar1[m-1]
- Loop from the second last element of ar1[] while element ar1[j] is greater than ar2[i].
- ar1[j+1] = ar1[j] Move element one position ahead, then j–
- If last element of ar1[] is greater than ar2[i], then ar1[j+1] = ar2[i] and ar2[i] = last
- Print the arrays
Note: In the above loop, elements in ar1[] and ar2[] are always kept sorted.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// C++ program to merge two sorted arrays with O(1) extra
// space.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Merge ar1[] and ar2[] with O(1) extra space
void merge(int ar1[], int ar2[], int m, int n)
{
// Iterate through all elements
// of ar2[] starting from the last element
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
// Find the smallest element greater than ar2[i].
// Move all elements one position ahead till the
// smallest greater element is not found */
int j, last = ar1[m - 1];
for (j = m - 2; j >= 0 && ar1[j] > ar2[i]; j--)
ar1[j + 1] = ar1[j];
// If there was a greater element
if (last > ar2[i]) {
ar1[j + 1] = ar2[i];
ar2[i] = last;
}
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int ar1[] = { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
int ar2[] = { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
int m = sizeof(ar1) / sizeof(ar1[0]);
int n = sizeof(ar2) / sizeof(ar2[0]);
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
cout << "After Merging \nFirst Array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
cout << ar1[i] << " ";
cout << "\nSecond Array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << ar2[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
// C program to merge two sorted arrays with O(1) extra
// space.
#include <stdio.h>
// Merge ar1[] and ar2[] with O(1) extra space
void merge(int ar1[], int ar2[], int m, int n)
{
// Iterate through all elements
// of ar2[] starting from the last element
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
// Find the smallest element greater than ar2[i].
// Move all elements one position ahead till the
// smallest greater element is not found */
int j, last = ar1[m - 1];
for (j = m - 2; j >= 0 && ar1[j] > ar2[i]; j--)
ar1[j + 1] = ar1[j];
// If there was a greater element
if (last > ar2[i]) {
ar1[j + 1] = ar2[i];
ar2[i] = last;
}
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int ar1[] = { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
int ar2[] = { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
int m = sizeof(ar1) / sizeof(ar1[0]);
int n = sizeof(ar2) / sizeof(ar2[0]);
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
printf("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
printf("%d ", ar1[i]);
printf("\nSecond Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", ar2[i]);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Aditya Kumar (adityakumar129)
// Java program to merge two
// sorted arrays with O(1) extra space.
import java.util.Arrays;
class Test {
static int arr1[] = new int[] { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
static int arr2[] = new int[] { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
static void merge(int m, int n)
{
// Iterate through all elements of ar2[] starting
// from the last element
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
/* Find the smallest element greater than
ar2[i]. Move all elements one position ahead
till the smallest greater element is not
found */
int j, last = arr1[m - 1];
for (j = m - 2; j >= 0 && arr1[j] > arr2[i];
j--)
arr1[j + 1] = arr1[j];
// If there was a greater element
if (last > arr2[i]) {
arr1[j + 1] = arr2[i];
arr2[i] = last;
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
merge(arr1.length, arr2.length);
System.out.print("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr1));
System.out.print("Second Array: ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr2));
}
}
# Python program to merge
# two sorted arrays
# with O(1) extra space.
# Merge ar1[] and ar2[]
# with O(1) extra space
def merge(ar1, ar2, m, n):
# Iterate through all
# elements of ar2[] starting from
# the last element
for i in range(n-1, -1, -1):
# Find the smallest element
# greater than ar2[i]. Move all
# elements one position ahead
# till the smallest greater
# element is not found
last = ar1[m-1]
j = m-2
while(j >= 0 and ar1[j] > ar2[i]):
ar1[j+1] = ar1[j]
j -= 1
# If there was a greater element
if (last > ar2[i]):
ar1[j+1] = ar2[i]
ar2[i] = last
# Driver code
ar1 = [1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20]
ar2 = [2, 3, 8, 13]
m = len(ar1)
n = len(ar2)
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n)
print("After Merging \nFirst Array:", end="")
for i in range(m):
print(ar1[i], " ", end="")
print("\nSecond Array: ", end="")
for i in range(n):
print(ar2[i], " ", end="")
# This code is contributed
# by Anant Agarwal.
// C# program to merge two
// sorted arrays with O(1) extra space.
using System;
// Java program to merge two
// sorted arrays with O(1) extra space.
public class Test {
static int[] arr1 = new int[] { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
static int[] arr2 = new int[] { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
static void merge(int m, int n)
{
// Iterate through all elements of ar2[] starting
// from the last element
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
/* Find the smallest element greater than
ar2[i]. Move all elements one position ahead
till the smallest greater element is not found
*/
int j, last = arr1[m - 1];
for (j = m - 2; j >= 0 && arr1[j] > arr2[i];
j--)
arr1[j + 1] = arr1[j];
// If there was a greater element
if (last > arr2[i]) {
arr1[j + 1] = arr2[i];
arr2[i] = last;
}
}
}
// Driver method to test the above function
public static void Main()
{
merge(arr1.Length, arr2.Length);
Console.Write("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < arr1.Length; i++) {
Console.Write(arr1[i] + " ");
}
Console.Write("\nSecond Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < arr2.Length; i++) {
Console.Write(arr2[i] + " ");
}
}
}
/*This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar*/
<script>
// Javascript program to merge two
// sorted arrays with O(1) extra space.
let arr1=[1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20];
let arr2=[2, 3, 8, 13];
function merge(m,n)
{
// Iterate through all elements of ar2[] starting from
// the last element
for (let i=n-1; i>=0; i--)
{
/* Find the smallest element greater than ar2[i]. Move all
elements one position ahead till the smallest greater
element is not found */
let j, last = arr1[m-1];
for (j=m-2; j >= 0 && arr1[j] > arr2[i]; j--)
arr1[j+1] = arr1[j];
// If there was a greater element
if (last > arr2[i])
{
arr1[j+1] = arr2[i];
arr2[i] = last;
}
}
}
// Driver method to test the above function
merge(arr1.length,arr2.length);
document.write("After Merging <br>First Array: ");
for(let i=0;i<arr1.length;i++)
{
document.write(arr1[i]+" ");
}
document.write("<br>Second Array: ");
for(let i=0;i<arr2.length;i++)
{
document.write(arr2[i]+" ");
}
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
</script>
<?php
// PHP program to merge two sorted arrays with O(1) extra space.
// Merge ar1[] and ar2[] with O(1) extra space
function merge(&$ar1, &$ar2, $m, $n)
{
// Iterate through all elements of ar2[] starting from
// the last element
for ($i = $n-1; $i >= 0; $i--)
{
/* Find the smallest element greater than ar2[i]. Move all
elements one position ahead till the smallest greater
element is not found */
$last = $ar1[$m-1];
for ($j = $m-2; $j >= 0 && $ar1[$j] > $ar2[$i]; $j--)
$ar1[$j+1] = $ar1[$j];
// If there was a greater element
if ($last > $ar2[$i])
{
$ar1[$j+1] = $ar2[$i];
$ar2[$i] = $last;
}
}
}
// Driver program
$ar1 = array(1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20);
$ar2 = array(2, 3, 8, 13);
$m = 6;
$n = 4;
merge($ar1, $ar2, $m, $n);
echo "After Merging \nFirst Array: ";
for ($i=0; $i<$m; $i++)
echo $ar1[$i] . " ";
echo "\nSecond Array: ";
for ($i=0; $i<$n; $i++)
echo $ar2[$i] ." ";
return 0;
?>
OutputAfter Merging
First Array: 1 2 3 5 8 9
Second Array: 10 13 15 20
Time Complexity: O(M * N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Below is the illustration of the above approach:
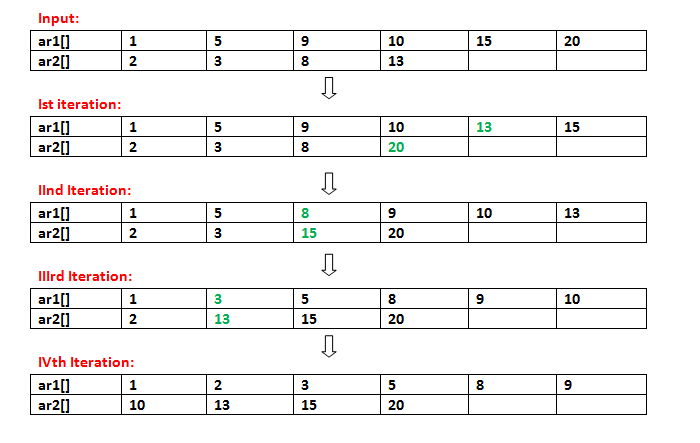
Initial Arrays:
ar1[] = {1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20};
ar2[] = {2, 3, 8, 13};
=> After First Iteration:
ar1[] = {1, 5, 9, 10, 13, 15};
ar2[] = {2, 3, 8, 20};
20 is moved from ar1[] to ar2[]
13 from ar2[] is inserted in ar1[]
=> After Second Iteration:
ar1[] = {1, 5, 8, 9, 10, 13};
ar2[] = {2, 3, 15, 20};
15 is moved from ar1[] to ar2[]
8 from ar2[] is inserted in ar1[]
=> After Third Iteration:
ar1[] = {1, 3, 5, 8, 9, 10};
ar2[] = {2, 13, 15, 20};
13 is moved from ar1[] to ar2[]
3 from ar2[] is inserted in ar1[]
=> After Fourth Iteration:
ar1[] = {1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 9};
ar2[] = {10, 13, 15, 20};
10 is moved from ar1[] to ar2[]
2 from ar2[] is inserted in ar1[]
Efficient Approach: To solve the problem follow the below idea:
The solution can be further optimized by observing that while traversing the two sorted arrays parallelly, if we encounter the jth second array element being smaller than ith first array element, then the jth element is to be included and replace some kth element in the first array. This observation helps us with the following algorithm
Follow the below steps to solve the problem:
- Initialize i,j,k as 0,0,n-1 where n is the size of arr1
- Iterate through every element of arr1 and arr2 using two pointers i and j respectively
- if arr1[i] is less than arr2[j], then increment i
- else swap the arr2[j] and arr1[k]and increment j and decrement k
- Sort both arr1 and arr2
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// CPP program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to merge two arrays
void merge(int arr1[], int arr2[], int n, int m)
{
int i = 0, j = 0, k = n - 1;
// Until i less than equal to k
// or j is less than m
while (i <= k && j < m) {
if (arr1[i] < arr2[j])
i++;
else {
swap(arr2[j++], arr1[k--]);
}
}
// Sort first array
sort(arr1, arr1 + n);
// Sort second array
sort(arr2, arr2 + m);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int ar1[] = { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
int ar2[] = { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
int m = sizeof(ar1) / sizeof(ar1[0]);
int n = sizeof(ar2) / sizeof(ar2[0]);
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
cout << "After Merging \nFirst Array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
cout << ar1[i] << " ";
cout << "\nSecond Array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << ar2[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
class GFG {
static int arr1[] = new int[] { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
static int arr2[] = new int[] { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
// Function to merge two arrays
static void merge(int m, int n)
{
int i = 0, j = 0, k = m - 1;
while (i <= k && j < n) {
if (arr1[i] < arr2[j])
i++;
else {
int temp = arr2[j];
arr2[j] = arr1[k];
arr1[k] = temp;
j++;
k--;
}
}
Arrays.sort(arr1);
Arrays.sort(arr2);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
merge(arr1.length, arr2.length);
System.out.print("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr1));
System.out.print("Second Array: ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr2));
}
}
# Python program for the above approach
arr1 = [1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20]
arr2 = [2, 3, 8, 13]
# Function to merge two arrays
def merge(n, m):
i = 0
j = 0
k = n - 1
while (i <= k and j < m):
if (arr1[i] < arr2[j]):
i += 1
else:
temp = arr2[j]
arr2[j] = arr1[k]
arr1[k] = temp
j += 1
k -= 1
arr1.sort()
arr2.sort()
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
merge(len(arr1), len(arr2))
print("After Merging \nFirst Array: ", ','.join(str(x) for x in arr1))
print("Second Array: ", ','.join(str(x) for x in arr2))
# This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
public class GFG {
static int[] arr1 = { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
static int[] arr2 = { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
// Function to merge two arrays
static void merge(int m, int n)
{
int i = 0, j = 0, k = n - 1;
while (i <= k && j < m) {
if (arr1[i] < arr2[j])
i++;
else {
int temp = arr2[j];
arr2[j] = arr1[k];
arr1[k] = temp;
j++;
k--;
}
}
Array.Sort(arr1);
Array.Sort(arr2);
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
merge(arr1.Length, arr2.Length);
Console.Write("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
foreach(int i in arr1) { Console.Write(i + " "); }
Console.Write("\nSecond Array: ");
foreach(int i in arr2) { Console.Write(i + " "); }
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
<script>
// javascript program for the above approach
var arr1 = [ 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 ];
var arr2 = [ 2, 3, 8, 13 ];
// Function to merge two arrays
function merge(m , n) {
var i = 0, j = 0, k = n - 1;
while (i <= k && j < m) {
if (arr1[i] < arr2[j])
i++;
else {
var temp = arr2[j];
arr2[j] = arr1[k];
arr1[k] = temp;
j++;
k--;
}
}
arr1.sort((a,b)=>a-b);
arr2.sort((a,b)=>a-b);
}
merge(arr1.length, arr2.length);
document.write("After Merging <br/>First Array:<br/> ");
for(var a of arr1)
document.write(a+" ");
document.write("<br/>Second Array: <br/> ");
for(var a of arr2)
document.write(a+" ");
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
</script>
OutputAfter Merging
First Array: 1 2 3 5 8 9
Second Array: 10 13 15 20
Time Complexity: O((N+M) * log(N+M))
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Efficient Approach: To solve the problem follow the below idea:
We can compare the last element of array one with first element of array two and if the last element is greater than first element the swap the elements and sort the second array as the elements of first array should be less than or equal to elements in second array. Repeating this process while this condition holds true will give us two sorted arrays
Follow the below steps to solve the problem:
- Initialize i with 0
- Iterate while loop until the last element of array 1 is greater than the first element of array 2
- if arr1[i] greater than first element of arr2
- swap arr1[i] with arr2[0]
- sort arr2
- Incrementing i by 1
- Print the arrays
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void merge(int arr1[], int arr2[], int n, int m)
{
int i = 0;
// while loop till last element of array 1(sorted) is
// greater than first element of array 2(sorted)
while (arr1[n - 1] > arr2[0]) {
if (arr1[i] > arr2[0]) {
// swap arr1[i] with first element
// of arr2 and sorting the updated
// arr2(arr1 is already sorted)
swap(arr1[i], arr2[0]);
sort(arr2, arr2 + m);
}
i++;
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int ar1[] = { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
int ar2[] = { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
int m = sizeof(ar1) / sizeof(ar1[0]);
int n = sizeof(ar2) / sizeof(ar2[0]);
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
cout << "After Merging \nFirst Array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
cout << ar1[i] << " ";
cout << "\nSecond Array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << ar2[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
// Java program for the above approach
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
class GFG {
static int arr1[] = new int[] { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
static int arr2[] = new int[] { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
static void merge(int n, int m)
{
int i = 0;
int temp = 0;
// While loop till last element
// of array 1(sorted)
// is greater than first element
// of array 2(sorted)
while (arr1[n - 1] > arr2[0]) {
if (arr1[i] > arr2[0]) {
// Swap arr1[i] with first element
// of arr2 and sorting the updated
// arr2(arr1 is already sorted)
// swap(arr1[i],arr2[0]);
temp = arr1[i];
arr1[i] = arr2[0];
arr2[0] = temp;
Arrays.sort(arr2);
}
i++;
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
merge(arr1.length, arr2.length);
System.out.print("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr1));
System.out.print("Second Array: ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr2));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Aakash Tiwari(nighteagle)
# Python3 program for the above approach
arr1 = [1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20]
arr2 = [2, 3, 8, 13]
def merge(n, m):
i = 0
temp = 0
# While loop till last element
# of array 1(sorted)
# is greater than first element
# of array 2(sorted)
while (arr1[n - 1] > arr2[0]):
if (arr1[i] > arr2[0]):
# Swap arr1[i] with first element
# of arr2 and sorting the updated
# arr2(arr1 is already sorted)
# swap(arr1[i],arr2[0]);
temp = arr1[i]
arr1[i] = arr2[0]
arr2[0] = temp
arr2.sort()
i += 1
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
merge(len(arr1), len(arr2))
print("After Merging \nFirst Array: ", arr1)
print("Second Array: ", arr2)
# This code contributed by gauravrajput1
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
public class GFG {
static int[] arr1 = new int[] { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
static int[] arr2 = new int[] { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
static void merge(int n, int m)
{
int i = 0;
int temp = 0;
// While loop till last element
// of array 1(sorted)
// is greater than first element
// of array 2(sorted)
while (arr1[n - 1] > arr2[0]) {
if (arr1[i] > arr2[0]) {
// Swap arr1[i] with first element
// of arr2 and sorting the updated
// arr2(arr1 is already sorted)
// swap(arr1[i],arr2[0]);
temp = arr1[i];
arr1[i] = arr2[0];
arr2[0] = temp;
Array.Sort(arr2);
}
i++;
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
merge(arr1.Length, arr2.Length);
Console.Write("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
foreach(int i in arr1) Console.Write(i + " ");
Console.Write("\nSecond Array: ");
foreach(int i in arr2) Console.Write(i + " ");
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
<script>
var arr1 = [1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 ];
var arr2 =[2, 3, 8, 13 ];
function merge(n , m) {
var i = 0;
var temp = 0;
// While loop till last element
// of array 1(sorted)
// is greater than first element
// of array 2(sorted)
while (arr1[n - 1] > arr2[0]) {
if (arr1[i] > arr2[0]) {
// Swap arr1[i] with first element
// of arr2 and sorting the updated
// arr2(arr1 is already sorted)
// swap(arr1[i],arr2[0]);
temp = arr1[i];
arr1[i] = arr2[0];
arr2[0] = temp;
arr2.sort((a,b)=>a-b);
}
i++;
}
}
// Driver code
merge(arr1.length, arr2.length);
document.write("After Merging <br\>First Array: ");
document.write(arr1.toString());
document.write("<br\>Second Array: ");
document.write(arr2.toString());
// This code is contributed by umadevi9616
</script>
OutputAfter Merging
First Array: 1 2 3 5 8 9
Second Array: 10 13 15 20
Time Complexity: O(M * (N * logN))
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Approach: Follow the below steps to solve the problem
Note: Let the length of the shorter array be ‘M’ and the larger array be ‘N’
- Select the shorter array and find the index at which the partition should be done.
- Partition the shorter array at its median (l1)
- Select the first N-l1 elements from the second array

- Compare the border elements i.e.
- if l1 < r2 and l2 < r2 we have found the index
- else if l1 > r2 we have to search in the left subarray
- else we have to search in the right subarray
Note: This step will store all the smallest elements in the shorter array
- Swap all the elements right to the index(i) of the shorter array with the first N-i elements of the larger array
- Sort both arrays
Note: if length(arr1) > length(arr2) all the smallest elements are stored in arr2 so we have to move all the elements in arr1 since we have to print arr1 first.
- Rotate the larger array (arr1) M times counter-clockwise
- Swap the first M elements of both arrays
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void swap(int& a, int& b)
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
void rotate(int a[], int n, int idx)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < idx / 2; i++)
swap(a[i], a[idx - 1 - i]);
for (i = idx; i < (n + idx) / 2; i++)
swap(a[i], a[n - 1 - (i - idx)]);
for (i = 0; i < n / 2; i++)
swap(a[i], a[n - 1 - i]);
}
void sol(int a1[], int a2[], int n, int m)
{
int l = 0, h = n - 1, idx = 0;
//---------------------------------------------------------
while (l <= h) {
// select the median of the remaining subarray
int c1 = (l + h) / 2;
// select the first elements from the larger array
// equal to the size of remaining portion to the
// right of the smaller array
int c2 = n - c1 - 1;
int l1 = a1[c1];
int l2 = a2[c2 - 1];
int r1 = c1 == n - 1 ? INT_MAX : a1[c1 + 1];
int r2 = c2 == m ? INT_MAX : a2[c2];
// compare the border elements and check for the
// target index
if (l1 > r2) {
h = c1 - 1;
if (h == -1)
idx = 0;
}
else if (l2 > r1) {
l = c1 + 1;
if (l == n - 1)
idx = n;
}
else {
idx = c1 + 1;
break;
}
}
for (int i = idx; i < n; i++)
swap(a1[i], a2[i - idx]);
sort(a1, a1 + n);
sort(a2, a2 + m);
}
void merge(int arr1[], int arr2[], int n, int m)
{
// code here
if (n > m) {
sol(arr2, arr1, m, n);
rotate(arr1, n, n - m);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
swap(arr2[i], arr1[i]);
}
else {
sol(arr1, arr2, n, m);
}
}
int main()
{
int ar1[] = { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
int ar2[] = { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
int m = sizeof(ar1) / sizeof(ar1[0]);
int n = sizeof(ar2) / sizeof(ar2[0]);
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
cout << "After Merging \nFirst Array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
cout << ar1[i] << " ";
cout << "\nSecond Array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << ar2[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static void swap(int a, int b)
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
static void rotate(int a[], int n, int idx)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < idx / 2; i++)
swap(a[i], a[idx - 1 - i]);
for (i = idx; i < (n + idx) / 2; i++)
swap(a[i], a[n - 1 - (i - idx)]);
for (i = 0; i < n / 2; i++)
swap(a[i], a[n - 1 - i]);
}
static void sol(int a1[], int a2[], int n, int m)
{
int l = 0, h = n - 1, idx = 0;
//---------------------------------------------------------
while (l <= h) {
// select the median of the remaining subarray
int c1 = (int)(l + h) / 2;
// select the first elements from the larger
// array equal to the size of remaining portion
// to the right of the smaller array
int c2 = n - c1 - 1;
int l1 = a1[c1];
int l2 = a2[c2 - 1];
int r1 = (c1 == n - 1) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE
: a1[c1 + 1];
int r2 = (c2 == m) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : a2[c2];
// compare the border elements and check for the
// target index
if (l1 > r2) {
h = c1 - 1;
if (h == -1)
idx = 0;
}
else if (l2 > r1) {
l = c1 + 1;
if (l == n - 1)
idx = n;
}
else {
idx = c1 + 1;
break;
}
}
for (int i = idx; i < n; i++)
swap(a1[i], a2[i - idx]);
Arrays.sort(a1);
Arrays.sort(a2);
}
static void merge(int arr1[], int arr2[], int n, int m)
{
// code here
if (n > m) {
sol(arr2, arr1, m, n);
rotate(arr1, n, n - m);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
swap(arr2[i], arr1[i]);
}
else {
sol(arr1, arr2, n, m);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int ar1[] = {1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 9};
int ar2[] = {10, 13, 15, 20};
int m = ar1.length;
int n = ar2.length;
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
System.out.print("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
System.out.print(ar1[i] + " ");
System.out.print("\nSecond Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(ar2[i] + " ");
}
}
// This code is contributed by sanjoy_62.
# Python program to merge
# two sorted arrays
# with O(1) extra space.
# Merge ar1[] and ar2[]
# with O(1) extra space
def rotate(a, n, idx):
for i in range((int)(idx/2)):
a[i], a[idx-1-i] = a[idx-1-i], a[i]
for i in range(idx, (int)((n+idx)/2)):
a[i], a[n-1-(i-idx)] = a[n-1-(i-idx)], a[i]
for i in range((int)(n/2)):
a[i], a[n-1-i] = a[n-1-i], a[i]
def sol(a1, a2, n, m):
l = 0
h = n-1
idx = 0
while (l <= h):
c1 = (int)((l+h)/2)
c2 = n-c1-1
l1 = a1[c1]
l2 = a2[c2-1]
r1 = sys.maxint if c1 == n-1 else a1[c1+1]
r2 = sys.maxint if c2 == m else a2[c2]
if l1 > r2:
h = c1-1
if h == -1:
idx = 0
elif l2 > r1:
l = c1+1
if l == n-1:
idx = n
else:
idx = c1+1
break
for i in range(idx, n):
a1[i], a2[i-idx] = a2[i-idx], a1[i]
a1.sort()
a2.sort()
def merge(a1, a2, n, m):
if n > m:
sol(a2, a1, m, n)
rotate(a1, n, n-m)
for i in range(m):
a1[i], a2[i] = a2[i], a1[i]
else:
sol(a1, a2, n, m)
# Driver program
ar1 = [1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20]
ar2 = [2, 3, 8, 13]
m = len(ar1)
n = len(ar2)
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n)
print("After Merging \nFirst Array:", end="")
for i in range(m):
print(ar1[i], " ", end="")
print("\nSecond Array: ", end="")
for i in range(n):
print(ar2[i], " ", end="")
# This code is contributed
# by Aditya Anand.
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG {
static void swap(int a, int b)
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
static void rotate(int[] a, int n, int idx)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < idx / 2; i++)
swap(a[i], a[idx - 1 - i]);
for (i = idx; i < (n + idx) / 2; i++)
swap(a[i], a[n - 1 - (i - idx)]);
for (i = 0; i < n / 2; i++)
swap(a[i], a[n - 1 - i]);
}
static void sol(int[] a1, int[] a2, int n, int m)
{
int l = 0, h = n - 1, idx = 0;
// ---------------------------------------------------------
while (l <= h) {
// select the median of the remaining subarray
int c1 = (int)(l + h) / 2;
// select the first elements from the larger
// array equal to the size of remaining portion
// to the right of the smaller array
int c2 = n - c1 - 1;
int l1 = a1[c1];
int l2 = a2[c2 - 1];
int r1
= (c1 == n - 1) ? int.MaxValue : a1[c1 + 1];
int r2 = (c2 == m) ? int.MaxValue : a2[c2];
// compare the border elements and check for the
// target index
if (l1 > r2) {
h = c1 - 1;
if (h == -1)
idx = 0;
}
else if (l2 > r1) {
l = c1 + 1;
if (l == n - 1)
idx = n;
}
else {
idx = c1 + 1;
break;
}
}
for (int i = idx; i < n; i++)
swap(a1[i], a2[i - idx]);
Array.Sort(a1);
Array.Sort(a2);
}
static void merge(int[] arr1, int[] arr2, int n, int m)
{
// code here
if (n > m) {
sol(arr2, arr1, m, n);
rotate(arr1, n, n - m);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
swap(arr2[i], arr1[i]);
}
else {
sol(arr1, arr2, n, m);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int[] ar1 = {1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 9};
int[] ar2 = {10, 13, 15, 20};
int m = ar1.Length;
int n = ar2.Length;
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
Console.Write("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
Console.Write(ar1[i] + " ");
Console.Write("\nSecond Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
Console.Write(ar2[i] + " ");
}
}
// This code contributed by gauravrajput1
<script>
// javascript program for the above approach
function swap(a , b) {
var temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
function rotate(a , n , idx) {
var i;
for (i = 0; i < idx / 2; i++)
{
var temp =a[i]
a[i]= a[idx - 1 - i];
a[idx - 1 - i] = temp;
}
for (i = idx; i < (n + idx) / 2; i++)
{
var temp =a[i]
a[i]= a[n - 1 - (i - idx)];
a[n - 1 - (i - idx)] = temp;
}
for (i = 0; i < n / 2; i++)
{
var temp =a[i]
a[i]= a[n - 1 - i];
a[n - 1 - i] = temp;
}
}
function sol(a1 , a2 , n , m) {
var l = 0, h = n - 1, idx = 0;
// ---------------------------------------------------------
while (l <= h)
{
// select the median of the remaining subarray
var c1 = parseInt( (l + h) / 2);
// select the first elements from the larger array
// equal to the size of remaining portion to the
// right of the smaller array
var c2 = n - c1 - 1;
var l1 = a1[c1];
var l2 = a2[c2 - 1];
var r1 = (c1 == n - 1) ? Number.MAX_VALUE : a1[c1 + 1];
var r2 = (c2 == m) ? Number.MAX_VALUE : a2[c2];
// compare the border elements and check for the
// target index
if (l1 > r2) {
h = c1 - 1;
if (h == -1)
idx = 0;
} else if (l2 > r1) {
l = c1 + 1;
if (l == n - 1)
idx = n;
} else {
idx = c1 + 1;
break;
}
}
for (i = idx; i < n; i++)
{
var temp =a1[i]
a1[i]= a2[i - idx];
a2[i - idx] = temp;
}
a1.sort((a,b)=>a-b);
a2.sort((a,b)=>a-b);
}
function merge(arr1 , arr2 , n , m) {
// code here
if (n > m) {
sol(arr2, arr1, m, n);
rotate(arr1, n, n - m);
for (i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
var temp =arr2[i]
arr2[i]= arr1[i];
arr1[i] = temp;
}
} else {
sol(arr1, arr2, n, m);
}
}
// Driver Code
var ar1 = [ 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 ];
var ar2 = [ 2, 3, 8, 13 ];
var m = ar1.length;
var n = ar2.length;
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
document.write("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
for (i = 0; i < m; i++)
document.write(ar1[i] + " ");
document.write("\nSecond Array: ");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
document.write(ar2[i] + " ");
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
</script>
OutputAfter Merging
First Array: 1 2 3 5 8 9
Second Array: 10 13 15 20
Time Complexity: O(max(N * logN, M * logM))
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Merge two sorted arrays with O(1) extra space using Insertion Sort with Simultaneous Merge:
To solve the problem follow the below idea:
We can use the insertion sort in the third approach above to reduce the time complexity as the array is already sorted, so we can place swapped element in its correct position by just performing a single traversal on the second array
Follow the below steps to solve the problem
- Sort list 1 by always comparing with the head/first of list 2 and swap if required
- After each head/first swap, perform insertion of the swapped element into the correct position in list 2 which will eventually sort list 2 at the end
- For every swapped item from list 1, perform insertion sort in list 2 to find its correct position so that when list 1 is sorted, list 2 is also sorted
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void merge(int arr1[], int arr2[], int n, int m)
{
// two pointer to iterate
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
while (i < n && j < m) {
// if arr1[i] <= arr2[j] then both array is already
// sorted
if (arr1[i] <= arr2[j]) {
i++;
}
else if (arr1[i] > arr2[j]) {
// if arr1[i]>arr2[j] then first we swap both
// element so that arr1[i] become smaller means
// arr1[] become sorted then we check that
// arr2[j] is smaller than all other element in
// right side of arr2[j] if arr2[] is not sorted
// then we linearly do sorting
// means while adjacent element are less than
// new arr2[j] we do sorting like by changing
// position of element by shifting one position
// toward left
swap(arr1[i], arr2[j]);
i++;
if (j < m - 1 && arr2[j + 1] < arr2[j]) {
int temp = arr2[j];
int tempj = j + 1;
while (arr2[tempj] < temp && tempj < m) {
arr2[tempj - 1] = arr2[tempj];
tempj++;
}
arr2[tempj - 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int ar1[] = { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
int ar2[] = { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
int m = sizeof(ar1) / sizeof(ar1[0]);
int n = sizeof(ar2) / sizeof(ar2[0]);
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
cout << "After Merging \nFirst Array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
cout << ar1[i] << " ";
cout << "\nSecond Array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << ar2[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static void merge(int arr1[], int arr2[], int n, int m)
{
// two pointer to iterate
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
while (i < n && j < m) {
// if arr1[i] <= arr2[j] then both array is
// already sorted
if (arr1[i] <= arr2[j]) {
i++;
}
else if (arr1[i] > arr2[j]) {
// if arr1[i]>arr2[j] then first we swap
// both element so that arr1[i] become
// smaller means arr1[] become sorted then
// we check that arr2[j] is smaller than all
// other element in right side of arr2[j] if
// arr2[] is not sorted then we linearly do
// sorting means while adjacent element are
// less than new arr2[j] we do sorting like
// by changing position of element by
// shifting one position toward left
int t = arr1[i];
arr1[i] = arr2[j];
arr2[j] = t;
i++;
if (j < m - 1 && arr2[j + 1] < arr2[j]) {
int temp = arr2[j];
int tempj = j + 1;
while (tempj < m && arr2[tempj] < temp
&& tempj < m) {
arr2[tempj - 1] = arr2[tempj];
tempj++;
}
arr2[tempj - 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int ar1[] = { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
int ar2[] = { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
int m = ar1.length;
int n = ar2.length;
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
System.out.print("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
System.out.print(ar1[i] + " ");
System.out.print("\nSecond Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(ar2[i] + " ");
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
# code contributed by mahee96
# "Insertion sort of list 2 with swaps from list 1"
#
# swap elements to get list 1 correctly, meanwhile
# place the swapped item in correct position of list 2
# eventually list 2 is also sorted
# Time = O(m*n) or O(n*m)
# AUX = O(1)
def merge(arr1, arr2):
x = arr1
y = arr2
end = len(arr1)
i = 0
while(i < end): # O(m) or O(n)
if(x[i] > y[0]):
swap(x, y, i, 0)
insert(y, 0) # O(n) or O(m) number of shifts
i += 1
# O(n):
def insert(y, i):
orig = y[i]
i += 1
while (i < len(y) and y[i] < orig):
y[i-1] = y[i]
i += 1
y[i-1] = orig
def swap(x, y, i, j):
temp = x[i]
x[i] = y[j]
y[j] = temp
def test():
c1 = [2, 3, 8, 13]
c2 = [1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20]
c1, c2 = c2, c1
merge(c1, c2)
print(c1, c2)
test()
using System;
public class GFG {
static void merge(int[] arr1, int[] arr2, int n, int m)
{
// two pointer to iterate
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
while (i < n && j < m) {
// if arr1[i] <= arr2[j] then both array is
// already sorted
if (arr1[i] <= arr2[j]) {
i++;
}
else if (arr1[i] > arr2[j]) {
// if arr1[i]>arr2[j] then first we swap
// both element so that arr1[i] become
// smaller means arr1[] become sorted then
// we check that arr2[j] is smaller than all
// other element in right side of arr2[j] if
// arr2[] is not sorted then we linearly do
// sorting means while adjacent element are
// less than new arr2[j] we do sorting like
// by changing position of element by
// shifting one position toward left
int t = arr1[i];
arr1[i] = arr2[j];
arr2[j] = t;
i++;
if (j < m - 1 && arr2[j + 1] < arr2[j]) {
int temp = arr2[j];
int tempj = j + 1;
while (tempj < m && arr2[tempj] < temp
&& tempj < m) {
arr2[tempj - 1] = arr2[tempj];
tempj++;
}
arr2[tempj - 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int[] ar1 = { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
int[] ar2 = { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
int m = ar1.Length;
int n = ar2.Length;
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
Console.Write("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
Console.Write(ar1[i] + " ");
Console.Write("\nSecond Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
Console.Write(ar2[i] + " ");
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
<script>
function merge(arr1 , arr2 , n , m) {
// two pointer to iterate
var i = 0;
var j = 0;
while (i < n && j < m) {
// if arr1[i] <= arr2[j] then both array is already
// sorted
if (arr1[i] <= arr2[j]) {
i++;
} else if (arr1[i] > arr2[j]) {
// if arr1[i]>arr2[j] then first we swap both
// element so that arr1[i] become smaller means
// arr1 become sorted then we check that
// arr2[j] is smaller than all other element in
// right side of arr2[j] if arr2 is not sorted
// then we linearly do sorting
// means while adjacent element are less than
// new arr2[j] we do sorting like by changing
// position of element by shifting one position
// toward left
var t = arr1[i];
arr1[i] = arr2[j];
arr2[j] = t;
i++;
if (j < m - 1 && arr2[j + 1] < arr2[j]) {
var temp = arr2[j];
var tempj = j + 1;
while (tempj < m && arr2[tempj] < temp && tempj < m) {
arr2[tempj - 1] = arr2[tempj];
tempj++;
}
arr2[tempj - 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
var ar1 = [ 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 ];
var ar2 = [ 2, 3, 8, 13 ];
var m = ar1.length;
var n = ar2.length;
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
document.write("After Merging <br/>First Array: <br/>");
for (i = 0; i < m; i++)
document.write(ar1[i] + " ");
document.write("<br/>Second Array: <br/>");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
document.write(ar2[i] + " ");
// This code contributed by gauravrajput1
</script>
OutputAfter Merging
First Array: 1 2 3 5 8 9
Second Array: 10 13 15 20
Time Complexity: O(M * N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Merge two sorted arrays with O(1) extra space using Euclidean Division Lemma:
To solve the problem follow the below idea:
We can merge the two arrays as in merge sort and simultaneously use Euclidean Division Lemma i.e. (((Operation on array) % x) * x).
Follow the below steps to solve the problem:
- Merge the two arrays as we do in merge sort, while simultaneously using Euclidean Division Lemma, i.e. (((Operation on the array) % x) * x)
- After merging divide both arrays with x
- Where x needs to be a number greater than all elements of the array
- Here in this case x, (according to the constraints) can be 10e7 + 1
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// C++ program to merge two sorted arrays without using
// extra space
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void merge(int arr1[], int arr2[], int n, int m)
{
// three pointers to iterate
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
// for euclid's division lemma
int x = 10e7 + 1;
// in this loop we are rearranging the elements of arr1
while (i < n && (j < n && k < m)) {
// if both arr1 and arr2 elements are modified
if (arr1[j] >= x && arr2[k] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k] % x) {
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
// if only arr1 elements are modified
else if (arr1[j] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k]) {
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
// if only arr2 elements are modified
else if (arr2[k] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k] % x) {
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
// if none elements are modified
else {
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k]) {
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
i++;
}
// we can copy the elements directly as the other array
// is exhausted
while (j < n && i < n) {
arr1[i++] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
while (k < m && i < n) {
arr1[i++] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
// we need to reset i
i = 0;
// in this loop we are rearranging the elements of arr2
while (i < m && (j < n && k < m)) {
// if both arr1 and arr2 elements are modified
if (arr1[j] >= x && arr2[k] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k] % x) {
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
// if only arr1 elements are modified
else if (arr1[j] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k]) {
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
// if only arr2 elements are modified
else if (arr2[k] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k] % x) {
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
else {
// if none elements are modified
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k]) {
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
i++;
}
// we can copy the elements directly as the other array
// is exhausted
while (j < n && i < m) {
arr2[i++] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
while (k < m && i < m) {
arr2[i++] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
// we need to reset i
i = 0;
// we need to divide the whole arr1 by x
while (i < n) {
arr1[i++] /= x;
}
// we need to reset i
i = 0;
// we need to divide the whole arr2 by x
while (i < m) {
arr2[i++] /= x;
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int ar1[] = { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
int ar2[] = { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
int m = sizeof(ar1) / sizeof(ar1[0]);
int n = sizeof(ar2) / sizeof(ar2[0]);
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
cout << "After Merging \nFirst Array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
cout << ar1[i] << " ";
cout << "\nSecond Array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << ar2[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by @ancientmoon8 (Mayank
// Kashyap)
// Java program to merge two sorted arrays without using
// extra space
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static void merge(int arr1[], int arr2[], int n, int m)
{
// three pointers to iterate
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
// for euclid's division lemma
int x = 10000000 + 7;
// in this loop we are rearranging the elements of
// arr1
while (i < n && (j < n && k < m)) {
// if both arr1 and arr2 elements are modified
if (arr1[j] >= x && arr2[k] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k] % x) {
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
// if only arr1 elements are modified
else if (arr1[j] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k]) {
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
// if only arr2 elements are modified
else if (arr2[k] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k] % x) {
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
// if none elements are modified
else {
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k]) {
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
i++;
}
// we can copy the elements directly as the other
// array is exchausted
while (j < n && i < n) {
arr1[i++] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
while (k < m && i < n) {
arr1[i++] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
// we need to reset i
i = 0;
// in this loop we are rearranging the elements of
// arr2
while (i < m && (j < n && k < m)) {
// if both arr1 and arr2 elements are modified
if (arr1[j] >= x && arr2[k] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k] % x) {
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
// if only arr1 elements are modified
else if (arr1[j] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k]) {
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
// if only arr2 elements are modified
else if (arr2[k] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k] % x) {
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
else {
// if none elements are modified
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k]) {
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
i++;
}
// we can copy the elements directly as the other
// array is exhausted
while (j < n && i < m) {
arr2[i++] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
while (k < m && i < m) {
arr2[i++] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
// we need to reset i
i = 0;
// we need to divide the whole arr1 by x
while (i < n) {
arr1[i++] /= x;
}
// we need to reset i
i = 0;
// we need to divide the whole arr2 by x
while (i < m) {
arr2[i++] /= x;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int ar1[] = { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
int ar2[] = { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
int m = ar1.length;
int n = ar2.length;
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
System.out.print("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
System.out.print(ar1[i] + " ");
System.out.print("\nSecond Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(ar2[i] + " ");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Aarti_Rathi
# Python3 program to merge two sorted arrays without using extra space
def merge(arr1, arr2, n, m):
# three pointers to iterate
i = 0
j = 0
k = 0
# for euclid's division lemma
x = 10e7 + 1
# in this loop we are rearranging the elements of arr1
while i < n and (j < n and k < m):
# if both arr1 and arr2 elements are modified
if arr1[j] >= x and arr2[k] >= x:
if arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k] % x:
arr1[i] += (arr1[j] % x) * x
j += 1
else:
arr1[i] += (arr2[k] % x) * x
k += 1
# if only arr1 elements are modified
elif arr1[j] >= x:
if arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k]:
arr1[i] += (arr1[j] % x) * x
j += 1
else:
arr1[i] += (arr2[k] % x) * x
k += 1
# if only arr2 elements are modified
elif arr2[k] >= x:
if arr1[j] <= arr2[k] % x:
arr1[i] += (arr1[j] % x) * x
j += 1
else:
arr1[i] += (arr2[k] % x) * x
k += 1
# if none elements are modified
else:
if arr1[j] <= arr2[k]:
arr1[i] += (arr1[j] % x) * x
j += 1
else:
arr1[i] += (arr2[k] % x) * x
k += 1
i += 1
# we can copy the elements directly as the other array
# is exchausted
while j < n and i < n:
arr1[i] += (arr1[j] % x) * x
i += 1
j += 1
while k < m and i < n:
arr1[i] += (arr2[k] % x) * x
i += 1
k += 1
# we need to reset i
i = 0
# in this loop we are rearranging the elements of arr2
while i < m and (j < n and k < m):
# if both arr1 and arr2 elements are modified
if arr1[j] >= x and arr2[k] >= x:
if arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k] % x:
arr2[i] += (arr1[j] % x) * x
j += 1
else:
arr2[i] += (arr2[k] % x) * x
k += 1
# if only arr1 elements are modified
elif arr1[j] >= x:
if arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k]:
arr2[i] += (arr1[j] % x) * x
j += 1
else:
arr2[i] += (arr2[k] % x) * x
k += 1
# if only arr2 elements are modified
elif arr2[k] >= x:
if arr1[j] <= arr2[k] % x:
arr2[i] += (arr1[j] % x) * x
j += 1
else:
arr2[i] += (arr2[k] % x) * x
k += 1
else:
# if none elements are modified
if arr1[j] <= arr2[k]:
arr2[i] += (arr1[j] % x) * x
j += 1
else:
arr2[i] += (arr2[k] % x) * x
k += 1
i += 1
# we can copy the elements directly as the other array
# is exhausted
while j < n and i < m:
arr2[i] += (arr1[j] % x) * x
i += 1
j += 1
while k < m and i < m:
arr2[i] += (arr2[k] % x) * x
i += 1
k += 1
# we need to reset i
i = 0
# we need to divide the whole arr1 by x
while i < n:
arr1[i] /= x
i += 1
# we need to reset i
i = 0
# we need to divide the whole arr2 by x
while i < m:
arr2[i] /= x
i += 1
# Driver program
ar1 = [1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20]
ar2 = [2, 3, 8, 13]
m = len(ar1)
n = len(ar2)
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n)
print("After Merging \nFirst Array:", end=" ")
for i in range(m):
print(int(ar1[i]), end=" ")
print("\nSecond Array:", end=" ")
for i in range(n):
print(int(ar2[i]), end=" ")
# This code is contributed by Tapesh(tapeshdua420)
// C# program to merge two sorted arrays without using
// extra space
using System;
public class GFG {
static void merge(int[] arr1, int[] arr2, int n, int m)
{
// three pointers to iterate
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
// for euclid's division lemma
int x = 10000000 + 1;
// in this loop we are rearranging the elements of
// arr1
while (i < n && (j < n && k < m)) {
// if both arr1 and arr2 elements are modified
if (arr1[j] >= x && arr2[k] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k] % x) {
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
// if only arr1 elements are modified
else if (arr1[j] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k]) {
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
// if only arr2 elements are modified
else if (arr2[k] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k] % x) {
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
// if none elements are modified
else {
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k]) {
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
i++;
}
// we can copy the elements directly as the other
// array is exchausted
while (j < n && i < n) {
arr1[i++] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
while (k < m && i < n) {
arr1[i++] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
// we need to reset i
i = 0;
// in this loop we are rearranging the elements of
// arr2
while (i < m && (j < n && k < m)) {
// if both arr1 and arr2 elements are modified
if (arr1[j] >= x && arr2[k] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k] % x) {
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
// if only arr1 elements are modified
else if (arr1[j] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k]) {
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
// if only arr2 elements are modified
else if (arr2[k] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k] % x) {
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
else {
// if none elements are modified
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k]) {
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
i++;
}
// we can copy the elements directly as the other
// array is exhausted
while (j < n && i < m) {
arr2[i++] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
while (k < m && i < m) {
arr2[i++] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
// we need to reset i
i = 0;
// we need to divide the whole arr1 by x
while (i < n) {
arr1[i++] /= x;
}
// we need to reset i
i = 0;
// we need to divide the whole arr2 by x
while (i < m) {
arr2[i++] /= x;
}
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int[] ar1 = { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
int[] ar2 = { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
int m = ar1.Length;
int n = ar2.Length;
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
Console.Write("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
Console.Write(ar1[i] + " ");
Console.Write("\nSecond Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
Console.Write(ar2[i] + " ");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Aarti_Rathi
// JavaScript program to merge two sorted arrays without using extra space
static merge(arr1, arr2, n, m)
{
// three pointers to iterate
var i = 0;
var j = 0;
var k = 0;
// for euclid's division lemma
var x = 10000000 + 7;
// in this loop we are rearranging the elements of arr1
while (i < n && (j < n && k < m))
{
// if both arr1 and arr2 elements are modified
if (arr1[j] >= x && arr2[k] >= x)
{
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k] % x)
{
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else
{
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
else if (arr1[j] >= x)
{
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k])
{
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else
{
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
else if (arr2[k] >= x)
{
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k] % x)
{
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else
{
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
else
{
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k])
{
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else
{
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
i++;
}
// we can copy the elements directly as the other array
// is exchausted
while (j < n && i < n)
{
arr1[i++] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
while (k < m && i < n)
{
arr1[i++] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
// we need to reset i
i = 0;
// in this loop we are rearranging the elements of arr2
while (i < m && (j < n && k < m))
{
// if both arr1 and arr2 elements are modified
if (arr1[j] >= x && arr2[k] >= x)
{
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k] % x)
{
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else
{
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
else if (arr1[j] >= x)
{
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k])
{
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else
{
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
else if (arr2[k] >= x)
{
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k] % x)
{
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else
{
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
else
{
// if none elements are modified
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k])
{
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else
{
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
i++;
}
// we can copy the elements directly as the other array
// is exhausted
while (j < n && i < m)
{
arr2[i++] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
while (k < m && i < m)
{
arr2[i++] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
// we need to reset i
i = 0;
// we need to divide the whole arr1 by x
while (i < n)
{
arr1[i++] /= x;
}
// we need to reset i
i = 0;
// we need to divide the whole arr2 by x
while (i < m)
{
arr2[i++] /= x;
}
}
var ar1 = [1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20];
var ar2 = [2, 3, 8, 13];
var m = ar1.length;
var n = ar2.length;
GFG.merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
console.log("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
for (var i=0; i < m; i++)
{
console.log(parseInt(ar1[i]) + " ");
}
console.log("\nSecond Array: ");
for (var i=0; i < n; i++)
{
console.log(parseInt(ar2[i]) + " ");
}
// This code is contributed by Aarti_Rathi
OutputAfter Merging
First Array: 1 2 3 5 8 9
Second Array: 10 13 15 20
Time Complexity: O(M + N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1), since no extra space has been taken
Another Approach: Using shell sorting or gap method
Algorithm:
- Assume the two arrays as a single continuous array and find the gap value, gap = ceil(size of ar1 + size of ar2)/2 )
- Until the gap doesn’t become zero, perform the following operations:
- Take two pointers left and right and place them at index 0 and left + gap index respectively.
- Run a while loop until right is less than len i.e. m+n.
- Their are 3 different cases inside this while loop.
- When both the left and right pointers are in the ar1[]. Then compare the ar1[left] and ar1[right]. If ar1[left] > ar1[right], then swap the ar1[left] and ar1[right].
- When the left pointer is in ar1[] and right pointer is in ar2[] and if ar1[left] > ar2[right-m], then swap the ar1[left] and ar2[right-m].
- When both the left and right pointers are in the ar2[] and if ar1[left] > ar2[right-m], then swap the ar1[left] and ar2[right-m].
- If the right pointer reaches the end i.e. m+n, decrement the gap value by ceil(gap/2).
C++
//C++ program to merge two sorted array using constant space
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// swap function
void swapIfGrtr(int ar1[], int ar2[], int i, int j){
if(ar1[i] > ar2[j]){
swap(ar1[i], ar2[j]);
}
}
void merge(int ar1[], int ar2[], int m, int n){
int len = m+n;
int gap = len/2 + (len%2);
while(gap>0){
int left=0, right = left + gap;
while(right<len){
//if left pointer is in ar1[] and right in ar2[]
if(left<m && right>=m){
swapIfGrtr(ar1, ar2, left, right-m);
}
//if both left and right pointers are in ar2[]
else if(left>=m && right>=m){
swapIfGrtr(ar2, ar2, left-m, right-m);
}
//if both left and right pointers are in ar1[]
else{
swapIfGrtr(ar1, ar1, left, right);
}
left++;
right++;
}
if(gap==1){
break;
}
//decrement the gap value if right reaches the end i.e len
gap = (gap/2) + (gap%2);
}
}
int main() {
int ar1[] = { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
int ar2[] = { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
int m = sizeof(ar1) / sizeof(ar1[0]);
int n = sizeof(ar2) / sizeof(ar2[0]);
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
cout << "After Merging \nFirst Array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
cout << ar1[i] << " ";
cout << "\nSecond Array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << ar2[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
//This code is contributed by 525tamannacse1
public class MergeSortedArrays {
// Function to swap elements if the first array element
// is greater
static void swapIfGreater(int[] ar1, int[] ar2, int i,
int j)
{
if (ar1[i] > ar2[j]) {
int temp = ar1[i];
ar1[i] = ar2[j];
ar2[j] = temp;
}
}
// Function to merge two sorted arrays
static void merge(int[] ar1, int[] ar2, int m, int n)
{
int len = m + n;
int gap = (len / 2) + (len % 2);
while (gap > 0) {
int left = 0;
int right = left + gap;
while (right < len) {
// If the left pointer is in ar1[] and the
// right in ar2[]
if (left < m && right >= m) {
swapIfGreater(ar1, ar2, left,
right - m);
}
// If both left and right pointers are in
// ar2[]
else if (left >= m && right >= m) {
swapIfGreater(ar2, ar2, left - m,
right - m);
}
// If both left and right pointers are in
// ar1[]
else {
swapIfGreater(ar1, ar1, left, right);
}
left++;
right++;
}
if (gap == 1) {
break;
}
// Decrement the gap value if right reaches the
// end (i.e., len)
gap = (gap / 2) + (gap % 2);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] ar1 = { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
int[] ar2 = { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
int m = ar1.length;
int n = ar2.length;
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
System.out.print("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
System.out.print(ar1[i] + " ");
}
System.out.print("\nSecond Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.print(ar2[i] + " ");
}
}
}
# Python code
#swap function
def swapIfGreater(ar1, ar2, i, j):
if ar1[i] > ar2[j]:
ar1[i], ar2[j] = ar2[j], ar1[i]
def merge(ar1, ar2, m, n):
len_arr = m + n
gap = len_arr // 2 + (len_arr % 2)
while gap > 0:
left, right = 0, gap
while right < len_arr:
# If left pointer is in ar1[] and right in ar2[]
if left < m and right < m:
swapIfGreater(ar1, ar1, left, right)
# If left pointer is in ar1[] and right in ar2[]
elif left < m and right >= m:
swapIfGreater(ar1, ar2, left, right - m)
# If both left and right pointers are in ar2[]
else:
swapIfGreater(ar2, ar2, left - m, right - m)
left += 1
right += 1
if gap == 1:
break
# Decrement the gap value if right reaches the end i.e len_arr
gap = (gap // 2) + (gap % 2)
if __name__ == "__main__":
ar1 = [1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20]
ar2 = [2, 3, 8, 13]
m = len(ar1)
n = len(ar2)
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n)
print("After Merging")
print("First Array:", *ar1)
print("Second Array:", *ar2)
# This code is contributed by guptapratik
using System;
namespace MergeSortedArrays
{
class Program
{
// swap function
static void SwapIfGrtr(int[] ar1, int[] ar2, int i, int j)
{
if (ar1[i] > ar2[j])
{
int temp = ar1[i];
ar1[i] = ar2[j];
ar2[j] = temp;
}
}
static void Merge(int[] ar1, int[] ar2, int m, int n)
{
int len = m + n;
int gap = len / 2 + (len % 2);
while (gap > 0)
{
int left = 0, right = left + gap;
while (right < len)
{
// if left pointer is in ar1[] and right in ar2[]
if (left < m && right >= m)
{
SwapIfGrtr(ar1, ar2, left, right - m);
}
// if both left and right pointers are in ar2[]
else if (left >= m && right >= m)
{
SwapIfGrtr(ar2, ar2, left - m, right - m);
}
// if both left and right pointers are in ar1[]
else
{
SwapIfGrtr(ar1, ar1, left, right);
}
left++;
right++;
}
if (gap == 1)
{
break;
}
// decrement the gap value if right reaches the end i.e len
gap = (gap / 2) + (gap % 2);
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] ar1 = { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
int[] ar2 = { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
int m = ar1.Length;
int n = ar2.Length;
Merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
Console.WriteLine("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
Console.Write(ar1[i] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine("\nSecond Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
Console.Write(ar2[i] + " ");
}
}
}
}
// Function to swap elements in two arrays if the element in the
// first array is greater than the element in the second array
function swapIfGrtr(ar1, ar2, i, j) {
if (ar1[i] > ar2[j]) {
[ar1[i], ar2[j]] = [ar2[j], ar1[i]];
}
}
// Function to merge two sorted arrays in-place
function merge(ar1, ar2, m, n) {
const len = m + n;
let gap = Math.ceil(len / 2);
while (gap > 0) {
let left = 0;
let right = left + gap;
while (right < len) {
// Check different cases for merging elements from ar1 and ar2
if (left < m && right >= m) {
swapIfGrtr(ar1, ar2, left, right - m);
} else if (left >= m && right >= m) {
swapIfGrtr(ar2, ar2, left - m, right - m);
} else {
swapIfGrtr(ar1, ar1, left, right);
}
left++;
right++;
}
if (gap === 1) {
break;
}
gap = Math.ceil(gap / 2);
}
}
// Arrays to be merged
const ar1 = [1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20];
const ar2 = [2, 3, 8, 13];
const m = ar1.length;
const n = ar2.length;
// Call the merge function to merge the arrays in-place
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
// Output the merged arrays
console.log("After Merging \nFirst Array: " + ar1.join(" "));
console.log("Second Array: " + ar2.join(" "));
OutputAfter Merging
First Array: 1 2 3 5 8 9
Second Array: 10 13 15 20
Time Complexity: O(m+n)*O(log (m+n)), the outer loop runs from m+n to 1 and its everytime divided by 1. So, outer loop complexity is O(log(m+n)). The inner loop time complexity is O(m+n).
Space Complexity: O(1), as no extra space is used.
Related Articles:
Merge two sorted arrays
Merge k sorted arrays | Set 1
Efficiently merging two sorted arrays with O(1) extra space
Thanks to Shubham Chauhan for suggesting 1st solution and Himanshu Kaushik for the 2nd solution.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...