Maximum sum of nodes in Binary tree such that no two are adjacent | Dynamic Programming
Last Updated :
30 Nov, 2022
Given a N-ary tree with a value associated with each node, the task is to choose a subset of these nodes such that sum of chosen nodes is maximum under a constraint that no two chosen node in subset should be directly connected that is, if we have taken a node in our sum then we can’t take its any children in consideration and vice versa.
Examples:
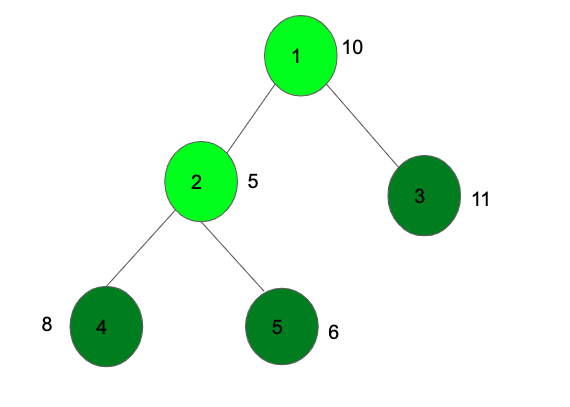
The above diagram selects the nodes with a deep green color to get the maximum value 25.
An approach to this problem has been discussed in the previous post using recursion.
In this post, we will be discussing an approach using Dynamic Programming on Trees.
While solving the problem, there arise two cases:
- For a particular node, the maximum sum can be calculated by including the node itself along with nodes from its subtree.
- Or, the maximum sum is calculated by excluding the current node and including only the nodes from its subtree.
Let us assume:
- dp1[node] to be the maximum possible sum by choosing nodes from the subtree of this node and also including the node.
- And, dp2[node] to be the maximum possible sum by choosing nodes from the subtree of the node and not including the node itself.
In the first case, if we include the current node, then its value is added and then we can not include any of its immediate children, hence the summation of dp2[] of all the children will be taken into the count to compute dp1[node]. That is,
dp1[node] = tree[node] + sum(dp2[children1], dp2[children2], …)
In the second case, if we do not include the current node, then its value is not added, but the children node can be taken or it cannot be taken, hence the summation of the maximum of both for all the children will be taken into count to compute dp2[node]. That is,
dp2[node] = tree[node] + sum(max(dp1[children1], dp2[children1]), max(dp1[children2], dp2[children2])…)
In the end, the final answer will be the maximum of dp1[root] and dp2[root].
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void dfs(int node, int parent, int dp1[], int dp2[],
list<int>* adj, int tree[])
{
int sum1 = 0, sum2 = 0;
for (auto i = adj[node].begin(); i != adj[node].end(); ++i) {
if (*i == parent)
continue;
dfs(*i, node, dp1, dp2, adj, tree);
sum1 += dp2[*i];
sum2 += max(dp1[*i], dp2[*i]);
}
dp1[node] = tree[node] + sum1;
dp2[node] = sum2;
}
int main()
{
int n = 5;
list<int>* adj = new list<int>[n + 1];
adj[1].push_back(2);
adj[2].push_back(1);
adj[1].push_back(3);
adj[3].push_back(1);
adj[2].push_back(4);
adj[4].push_back(2);
adj[2].push_back(5);
adj[5].push_back(2);
int tree[n + 1];
tree[1] = 10;
tree[2] = 5;
tree[3] = 11;
tree[4] = 6;
tree[5] = 8;
int dp1[n + 1], dp2[n + 1];
memset(dp1, 0, sizeof dp1);
memset(dp2, 0, sizeof dp2);
dfs(1, 1, dp1, dp2, adj, tree);
cout << "Maximum sum: "
<< max(dp1[1], dp2[1]) << endl;
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void
dfs(int node, int parent, int[] dp1, int[] dp2,
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> > adj, int[] tree)
{
int sum1 = 0, sum2 = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < adj.get(node).size(); j++) {
int i = adj.get(node).get(j);
if (i == parent)
continue;
dfs(i, node, dp1, dp2, adj, tree);
sum1 += dp2[i];
sum2 += Math.max(dp1[i], dp2[i]);
}
dp1[node] = tree[node] + sum1;
dp2[node] = sum2;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 5;
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> > adj
= new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> >();
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) {
adj.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
adj.get(1).add(2);
adj.get(2).add(1);
adj.get(1).add(3);
adj.get(3).add(1);
adj.get(2).add(4);
adj.get(4).add(2);
adj.get(2).add(5);
adj.get(5).add(2);
int[] tree = new int[n + 1];
tree[1] = 10;
tree[2] = 5;
tree[3] = 11;
tree[4] = 6;
tree[5] = 8;
int[] dp1 = new int[n + 1];
int[] dp2 = new int[n + 1];
dfs(1, 1, dp1, dp2, adj, tree);
System.out.println("Maximum sum: "
+ Math.max(dp1[1], dp2[1]));
}
}
|
Python3
def dfs(node, parent, dp1,
dp2, adj, tree):
sum1 = 0
sum2 = 0
for i in adj[node]:
if (i == parent):
continue;
dfs(i, node, dp1,
dp2, adj, tree);
sum1 += dp2[i];
sum2 += max(dp1[i],
dp2[i]);
dp1[node] = tree[node] + sum1;
dp2[node] = sum2;
if __name__=="__main__":
n = 5;
adj = [[] for i in range(n + 1)]
adj[1].append(2);
adj[2].append(1);
adj[1].append(3);
adj[3].append(1);
adj[2].append(4);
adj[4].append(2);
adj[2].append(5);
adj[5].append(2);
tree = [0 for i in range(n + 1)];
tree[1] = 10;
tree[2] = 5;
tree[3] = 11;
tree[4] = 6;
tree[5] = 8;
dp1 = [0 for i in range(n + 1)];
dp2 = [0 for i in range(n + 1)];
dfs(1, 1, dp1, dp2, adj, tree);
print("Maximum sum:",
max(dp1[1], dp2[1]))
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections;
class GFG
{
public static void dfs(int node, int parent, int []dp1, int []dp2,
ArrayList []adj, int []tree)
{
int sum1 = 0, sum2 = 0;
foreach(int i in adj[node])
{
if (i == parent)
continue;
dfs(i, node, dp1, dp2, adj, tree);
sum1 += dp2[i];
sum2 += Math.Max(dp1[i], dp2[i]);
}
dp1[node] = tree[node] + sum1;
dp2[node] = sum2;
}
public static void Main(string []arg)
{
int n = 5;
ArrayList []adj = new ArrayList[n + 1];
for(int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++)
{
adj[i] = new ArrayList();
}
adj[1].Add(2);
adj[2].Add(1);
adj[1].Add(3);
adj[3].Add(1);
adj[2].Add(4);
adj[4].Add(2);
adj[2].Add(5);
adj[5].Add(2);
int []tree = new int[n + 1];
tree[1] = 10;
tree[2] = 5;
tree[3] = 11;
tree[4] = 6;
tree[5] = 8;
int []dp1 = new int[n + 1];
int []dp2 = new int[n + 1];
Array.Fill(dp1, 0);
Array.Fill(dp2, 0);
dfs(1, 1, dp1, dp2, adj, tree);
Console.Write("Maximum sum: "+ Math.Max(dp1[1], dp2[1]));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function dfs(node, parent, dp1,dp2, adj, tree){
let sum1 = 0
let sum2 = 0
for(let i of adj[node]){
if (i == parent)
continue;
dfs(i, node, dp1,
dp2, adj, tree);
sum1 += dp2[i];
sum2 += Math.max(dp1[i],
dp2[i]);
}
dp1[node] = tree[node] + sum1;
dp2[node] = sum2;
}
let n = 5;
let adj = new Array(n+1);
for(let i=0;i<n+1;i++){
adj[i] = new Array();
}
adj[1].push(2);
adj[2].push(1);
adj[1].push(3);
adj[3].push(1);
adj[2].push(4);
adj[4].push(2);
adj[2].push(5);
adj[5].push(2);
let tree = new Array(n+1).fill(0);
tree[1] = 10;
tree[2] = 5;
tree[3] = 11;
tree[4] = 6;
tree[5] = 8;
let dp1 = new Array(n+1).fill(0);
let dp2 = new Array(n+1).fill(0);
dfs(1, 1, dp1, dp2, adj, tree);
document.write("Maximum sum: ", Math.max(dp1[1], dp2[1]),"</br>")
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N), as we are using recursion to traverse the tree. Where N is the number of nodes in the tree.
Auxiliary Space: O(N), as we are using extra space for the array dp.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...