LinkedHashSet in Java with Examples
Last Updated :
11 Sep, 2023
The LinkedHashSet is an ordered version of HashSet that maintains a doubly-linked List across all elements. When the iteration order is needed to be maintained this class is used. When iterating through a HashSet the order is unpredictable, while a LinkedHashSet lets us iterate through the elements in the order in which they were inserted. When cycling through LinkedHashSet using an iterator, the elements will be returned in the order in which they were inserted.
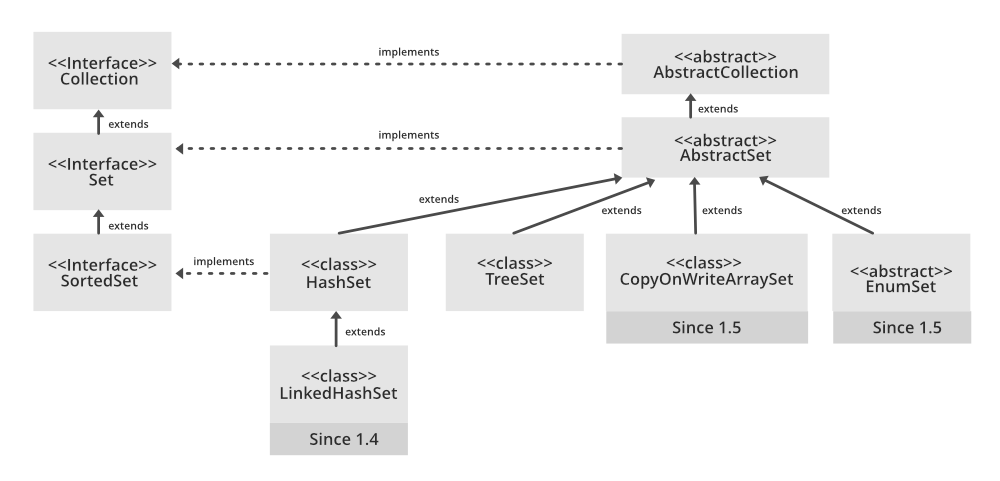
The Hierarchy of LinkedHashSet is as follows:
Parameters: The type of elements maintained by this set
All Implemented Interfaces are as listed below:
Serializable
Cloneable,
Iterable<E>
Collection<E>
Set<E>
Syntax: Declaration
public class LinkedHashSet<E> extends HashSet<E> implements Set<E>, Cloneable, Serializable
- Contains unique elements only like HashSet. It extends the HashSet class and implements the Set interface.
- Maintains insertion order.
Constructors of LinkedHashSet Class
1. LinkedHashSet(): This constructor is used to create a default HashSet
LinkedHashSet<E> hs = new LinkedHashSet<E>();
2. LinkedHashSet(Collection C): Used in initializing the HashSet with the elements of the collection C.
LinkedHashSet<E> hs = new LinkedHashSet<E>(Collection c);
3. LinkedHashSet(int size): Used to initialize the size of the LinkedHashSet with the integer mentioned in the parameter.
LinkedHashSet<E> hs = new LinkedHashSet<E>(int size);
4. LinkedHashSet(int capacity, float fillRatio): Can be used to initialize both the capacity and the fill ratio, also called the load capacity of the LinkedHashSet with the arguments mentioned in the parameter. When the number of elements exceeds the capacity of the hash set is multiplied with the fill ratio thus expanding the capacity of the LinkedHashSet.
LinkedHashSet<E> hs = new LinkedHashSet<E>(int capacity, int fillRatio);
Example:
Java
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedHashSet<String> linkedset
= new LinkedHashSet<String>();
linkedset.add("A");
linkedset.add("B");
linkedset.add("C");
linkedset.add("D");
linkedset.add("A");
linkedset.add("E");
System.out.println("Size of LinkedHashSet = "
+ linkedset.size());
System.out.println("Original LinkedHashSet:"
+ linkedset);
System.out.println("Removing D from LinkedHashSet: "
+ linkedset.remove("D"));
System.out.println(
"Trying to Remove Z which is not "
+ "present: " + linkedset.remove("Z"));
System.out.println("Checking if A is present="
+ linkedset.contains("A"));
System.out.println("Updated LinkedHashSet: "
+ linkedset);
}
}
|
Output
Size of LinkedHashSet = 5
Original LinkedHashSet:[A, B, C, D, E]
Removing D from LinkedHashSet: true
Trying to Remove Z which is not present: false
Checking if A is present=true
Updated LinkedHashSet: [A, B, C, E]
Performing Various Operations on the LinkedHashSet Class
Let’s see how to perform a few frequently used operations on the LinkedHashSet.
Operation 1: Adding Elements
In order to add an element to the LinkedHashSet, we can use the add() method. This is different from HashSet because in HashSet, the insertion order is not retained but is retained in the LinkedHashSet.
Example:
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedHashSet<String> hs = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
hs.add("Geek");
hs.add("For");
hs.add("Geeks");
System.out.println("LinkedHashSet : " + hs);
}
}
|
Output:
LinkedHashSet : [Geek, For, Geeks]
Operation 2: Removing Elements
The values can be removed from the LinkedHashSet using the remove() method.
Example:
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedHashSet<String> hs
= new LinkedHashSet<String>();
hs.add("Geek");
hs.add("For");
hs.add("Geeks");
hs.add("A");
hs.add("B");
hs.add("Z");
System.out.println("Initial HashSet " + hs);
hs.remove("B");
System.out.println("After removing element " + hs);
System.out.println(hs.remove("AC"));
}
}
|
Output:
Initial HashSet [Geek, For, Geeks, A, B, Z]
After removing element [Geek, For, Geeks, A, Z]
false
Operation 3: Iterating through LinkedHashSet
Iterate through the elements of LinkedHashSet using the iterator() method. The most famous one is to use the enhanced for loop.
Example:
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Set<String> hs = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
hs.add("Geek");
hs.add("For");
hs.add("Geeks");
hs.add("A");
hs.add("B");
hs.add("Z");
Iterator itr = hs.iterator();
while (itr.hasNext())
System.out.print(itr.next() + ", ");
System.out.println();
for (String s : hs)
System.out.print(s + ", ");
System.out.println();
}
}
|
Output:
Geek, For, Geeks, A, B, Z,
Geek, For, Geeks, A, B, Z,
Methods of LinkedHashSet
Here, E is the type of element stored.
|
METHOD
|
DESCRIPTION
|
| spliterator() |
Creates a late-binding and fail-fast Spliterator over the elements in this set. |
Methods Declared in class java.util.AbstractSet
|
METHOD
|
DESCRIPTION
|
| equals(Object o) |
Compares the specified object with this set for equality. |
| hashCode() |
Returns the hash code value for this set. |
| removeAll(Collection c) |
Removes from this set all of its elements that are contained in the specified collection (optional operation). |
Methods declared in class java.util.AbstractCollection
|
METHOD
|
DESCRIPTION
|
| addAll?(Collection<? extends E> c) |
Adds all of the elements in the specified collection to this collection (optional operation). |
| containsAll?(Collection<?> c) |
Returns true if this collection contains all of the elements in the specified collection. |
| retainAll?(Collection<?> c) |
Retains only the elements in this collection that are contained in the specified collection (optional operation). |
| toArray() |
Returns an array containing all of the elements in this collection. |
| toArray?(T[] a) |
Returns an array containing all of the elements in this collection; the runtime type of the returned array is that of the specified array. |
| toString() |
Returns a string representation of this collection. |
Methods declared in interface java.util.Collection
|
METHOD
|
DESCRIPTION
|
| parallelStream() |
Returns a possibly parallel Stream with this collection as its source. |
|
removeIf(Predicate<? super
E> filter)
|
Removes all of the elements of this collection that satisfy the given predicate. |
| stream() |
Returns a sequential Stream with this collection as its source. |
Methods declared in class java.util.HashSet
|
METHOD
|
DESCRIPTION
|
| add(E e) |
Adds the specified element to this set if it is not already present. |
| clear() |
Removes all of the elements from this set. |
| clone() |
Returns a shallow copy of this HashSet instance: the elements themselves are not cloned. |
| contains(Object o) |
Returns true if this set contains the specified element. |
| isEmpty() |
Returns true if this set contains no elements. |
| iterator() |
Returns an iterator over the elements in this set. |
| remove(Object o) |
Removes the specified element from this set if it is present. |
| size() |
Returns the number of elements in this set (its cardinality). |
Methods declared in interface java.lang.Iterable
|
METHOD
|
DESCRIPTION
|
|
forEach(Consumer<? super
T> action)
|
Performs the given action for each element of the Iterable until all elements have been processed or the action throws an exception. |
Methods declared in interface java.util.Set
| METHOD |
DESCRIPTION |
| add(element) |
This method is used to add a specific element to the set. The function adds the element only if the specified element is not already present in the set else the function returns False if the element is already present in the Set. |
| addAll(Collection c) |
This method is used to append all of the elements from the mentioned collection to the existing set. The elements are added randomly without following any specific order. |
| clear() |
This method is used to remove all the elements from the set but not delete the set. The reference for the set still exists. |
| contains(element) |
This method is used to check whether a specific element is present in the Set or not. |
| containsAll(Collection c) |
This method is used to check whether the set contains all the elements present in the given collection or not. This method returns true if the set contains all the elements and returns false if any of the elements are missing. |
| hashCode() |
This method is used to get the hashCode value for this instance of the Set. It returns an integer value which is the hashCode value for this instance of the Set. |
| isEmpty() |
This method is used to check whether the set is empty or not. |
| iterator() |
This method is used to return the iterator of the set. The elements from the set are returned in random order. |
| remove(element) |
This method is used to remove the given element from the set. This method returns True if the specified element is present in the Set otherwise it returns False. |
| removeAll(collection) |
This method is used to remove all the elements from the collection which are present in the set. This method returns true if this set changed as a result of the call. |
| retainAll(collection) |
This method is used to retain all the elements from the set which are mentioned in the given collection. This method returns true if this set changed as a result of the call. |
| size() |
This method is used to get the size of the set. This returns an integer value which signifies the number of elements. |
| toArray() |
This method is used to form an array of the same elements as that of the Set. |
| toArray?(T[] a) |
Returns an array containing all of the elements in this set; the runtime type of the returned array is that of the specified array. |
Following is the difference between LinkedHashMap and LinkedHashSet:
| Categories |
LinkedHashMap |
LinkedHashSet |
| Operation |
Usd to store key-value pairs. |
Used to store collection of things |
| Duplicates |
Take unique an no duplicate keys but can takeduplicate values |
Stores no duplicate element |
| Implements |
HashMap |
HashSet |
| Example |
Map<String, Integer> lhm = new LinkedHashMap<String, Integer>(); |
Set<String> lhs = new LinkedhashSet<String>(); |
Note: Keeping the insertion order in both LinkedHashmap and LinkedHashset have additional associated costs, both in terms of spending additional CPU cycles and needing more memory. If you do not need the insertion order maintained, it is recommended to use the lighter-weight HashSet and HashMap instead.
See your article appearing on the GeeksforGeeks’s main page and help other Geeks.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...