Introduction of Single Sign On (SSO)
Last Updated :
02 May, 2024
Single Sign On (SSO) is an authentication scheme where users can securely authenticate and gain access to multiple applications and websites by only logging in with a single username and password. For example, logging in to your Google account once will allow you to access Google applications such as Google Docs, Gmail, and Google Drive.
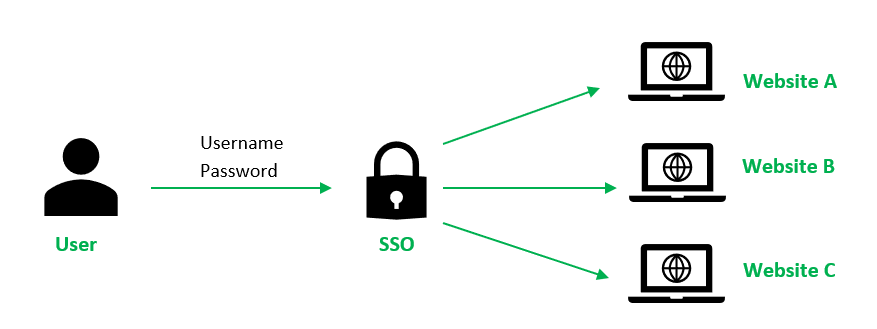
Without SSO solution, the website maintains a database of login credentials – usernames and passwords. Each time the user login to the website, it checks the user’s credentials against its database and authenticates the user.
With the SSO solution, the website does not store login credentials in its database. Instead, Single Sign On (SSO) makes use of a shared cluster of authentication servers where users are only required to enter their login credentials once for authentication. With this feature of one login and multiple access, it is crucial to protect login credentials in SSO systems. Hence it is highly recommended to integrate SSO with other strong authentication means such as smart tokens or one-time passwords to achieve multi-factor authentication.
How does SSO Login work ?
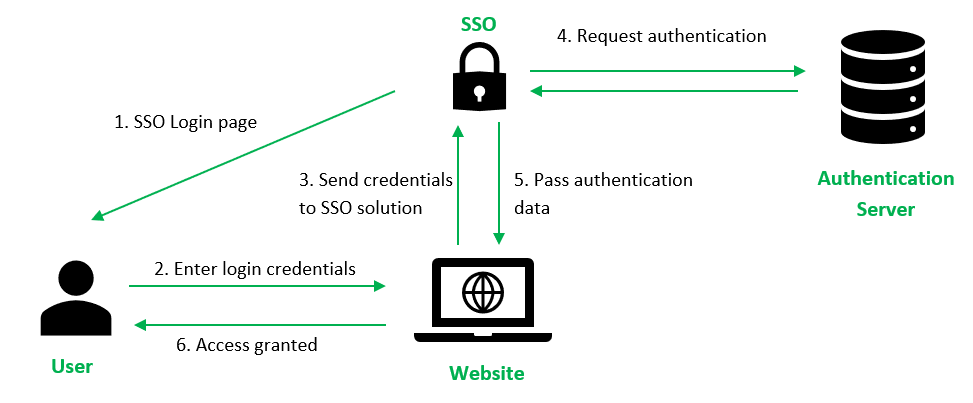
- User enters login credentials on the website and the website checks to see if the user has already been authenticated by SSO solution. If so, the SSO solution would give the user access to the website. Otherwise, it presents the user with the SSO solution for login.
- The user enters username and password on the SSO solution.
- The user’s login credentials are sent to SSO solution.
- The SSO solution seeks authentication from the identity provider, such as an Active Directory, to verify the user’s identity. Once the user’s identity is verified, the identity provider sends a verification to the SSO solution.
- The authentication information is passed from the SSO solution to the website where the user will be granted access to the website.
- Upon successful login with SSO, the website passes authentication data in the form of tokens as a form of verification that the user is authenticated as the user navigates to a different application or web page.
Advantages of SSO :
These are advantages for users, for businesses.
For Users –
- Risk of access to third party sites are mitigated as the website database do not store the user’s login credentials.
- Increased convenience for users as they only need to remember and key in login information once.
- Increased security assurance for users as website owners do not store login credentials.
For Businesses –
- Increase customer base and satisfaction as SSO provides lower barrier to entry and seamless user experience.
- Reduce IT costs for managing customer’s username and passwords.
Disadvantages of SSO :
- Increased security risk if login credentials are not securely protected and are exposed or stolen as adversaries can now access many websites and applications with a single credential.
- Authentication systems must have high availability as loss of availability can lead to denial of service for applications using a shared cluster of authentication systems.
Introduction of Single Sign On (SSO) – FAQs
What is meant by single sign-on?
Single Sign-On (SSO) allows users to access multiple applications with one set of login credentials, simplifying the login process.
What is single use sign-on?
Single Use Sign-On (SU-SO) grants access to an application or service for one session or one-time use.
What is the difference between single sign-on and same sign-on?
Single Sign-On (SSO) enables logging into multiple applications with one set of credentials. Same Sign-On refers to using the same credentials across different applications without fully integrating them.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...