Introduction of Lexical Analysis
Last Updated :
07 Mar, 2024
Lexical Analysis is the first phase of the compiler also known as a scanner. It converts the High level input program into a sequence of Tokens.
- Lexical Analysis can be implemented with the Deterministic finite Automata.
- The output is a sequence of tokens that is sent to the parser for syntax analysis
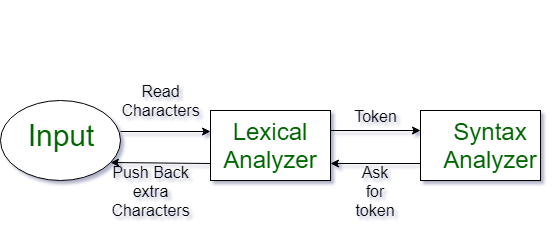 What is a Token?
What is a Token?
A lexical token is a sequence of characters that can be treated as a unit in the grammar of the programming languages. Example of tokens:
- Type token (id, number, real, . . . )
- Punctuation tokens (IF, void, return, . . . )
- Alphabetic tokens (keywords)
Keywords; Examples-for, while, if etc.
Identifier; Examples-Variable name, function name, etc.
Operators; Examples '+', '++', '-' etc.
Separators; Examples ',' ';' etc
Example of Non-Tokens:
- Comments, preprocessor directive, macros, blanks, tabs, newline, etc.
Lexeme: The sequence of characters matched by a pattern to form the corresponding token or a sequence of input characters that comprises a single token is called a lexeme. eg- “float”, “abs_zero_Kelvin”, “=”, “-”, “273”, “;” .
How Lexical Analyzer Works?
- Input preprocessing: This stage involves cleaning up the input text and preparing it for lexical analysis. This may include removing comments, whitespace, and other non-essential characters from the input text.
- Tokenization: This is the process of breaking the input text into a sequence of tokens. This is usually done by matching the characters in the input text against a set of patterns or regular expressions that define the different types of tokens.
- Token classification: In this stage, the lexer determines the type of each token. For example, in a programming language, the lexer might classify keywords, identifiers, operators, and punctuation symbols as separate token types.
- Token validation: In this stage, the lexer checks that each token is valid according to the rules of the programming language. For example, it might check that a variable name is a valid identifier, or that an operator has the correct syntax.
- Output generation: In this final stage, the lexer generates the output of the lexical analysis process, which is typically a list of tokens. This list of tokens can then be passed to the next stage of compilation or interpretation.

- The lexical analyzer identifies the error with the help of the automation machine and the grammar of the given language on which it is based like C, C++, and gives row number and column number of the error.
Suppose we pass a statement through lexical analyzer – a = b + c; It will generate token sequence like this: id=id+id; Where each id refers to it’s variable in the symbol table referencing all details For example, consider the program
int main()
{
// 2 variables
int a, b;
a = 10;
return 0;
}
All the valid tokens are:
'int' 'main' '(' ')' '{' 'int' 'a' ',' 'b' ';'
'a' '=' '10' ';' 'return' '0' ';' '}'
Above are the valid tokens. You can observe that we have omitted comments. As another example, consider below printf statement.  There are 5 valid token in this printf statement. Exercise 1: Count number of tokens:
There are 5 valid token in this printf statement. Exercise 1: Count number of tokens:
int main()
{
int a = 10, b = 20;
printf("sum is:%d",a+b);
return 0;
}
Answer: Total number of token: 27.
Exercise 2: Count number of tokens: int max(int i);
- Lexical analyzer first read int and finds it to be valid and accepts as token.
- max is read by it and found to be a valid function name after reading (
- int is also a token , then again I as another token and finally ;
Answer: Total number of tokens 7:
int, max, ( ,int, i, ), ;
- We can represent in the form of lexemes and tokens as under
| Lexemes |
Tokens |
Lexemes |
Tokens |
|
| while |
WHILE |
a |
IDENTIEFIER |
|
| ( |
LAPREN |
= |
ASSIGNMENT |
|
| a |
IDENTIFIER |
a |
IDENTIFIER |
|
| >= |
COMPARISON |
– |
ARITHMETIC |
|
| b |
IDENTIFIER |
2 |
INTEGER |
|
| ) |
RPAREN |
; |
SEMICOLON |
|
Advantages
- Simplifies Parsing:Breaking down the source code into tokens makes it easier for computers to understand and work with the code. This helps programs like compilers or interpreters to figure out what the code is supposed to do. It’s like breaking down a big puzzle into smaller pieces, which makes it easier to put together and solve.
- Error Detection: Lexical analysis will detect lexical errors such as misspelled keywords or undefined symbols early in the compilation process. This helps in improving the overall efficiency of the compiler or interpreter by identifying errors sooner rather than later.
- Efficiency: Once the source code is converted into tokens, subsequent phases of compilation or interpretation can operate more efficiently. Parsing and semantic analysis become faster and more streamlined when working with tokenized input.
Disadvantages
- Limited Context: Lexical analysis operates based on individual tokens and does not consider the overall context of the code. This can sometimes lead to ambiguity or misinterpretation of the code’s intended meaning especially in languages with complex syntax or semantics.
- Overhead: Although lexical analysis is necessary for the compilation or interpretation process, it adds an extra layer of overhead. Tokenizing the source code requires additional computational resources which can impact the overall performance of the compiler or interpreter.
- Debugging Challenges: Lexical errors detected during the analysis phase may not always provide clear indications of their origins in the original source code. Debugging such errors can be challenging especially if they result from subtle mistakes in the lexical analysis process.
Below is previous year GATE question on Lexical analysis. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/lexical-analysis-gq/
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...