Insulation resistance is a basic boundary in the domain of electrical engineering, filling in as a vital defense for the respectability and unwavering quality of electrical systems. This article dives into the central parts of Insulation resistance, investigating its definition, factors impacting it, techniques for estimation, systems for support, applications, and finishing-up experiences.
The ability of a material to prevent the flow of electric current is measured by its insulation resistance. It assumes an urgent part in forestalling spillage flows and guaranteeing the security and usefulness of electrical frameworks. An effective barrier against unintended current paths with a high insulation resistance safeguards equipment and prevents electrical accidents.
What is Insulation Resistance?
An insulating resistance refers to the resistance offered by an insulating material to the flow of electric current. It is a measure of how well the insulation stops current leakage. To reduce the likelihood of short circuits or electrical faults, insulation materials like varnish, rubber, or plastic are frequently used to coat conductors and separate them from one another.
Factors Affecting Insulation Resistance
A few variables can essentially influence the protection obstruction of electrical frameworks. For electrical components’ reliability and safety, as well as the prevention of leakage currents, insulation resistance is essential. Here are key factors that impact protection opposition:
- Material for Insulation: A crucial factor is the kind of insulation material used in electrical components. Various materials, like elastic, plastic, stain, or paper, show differing levels of protection from electric flow.
- Temperature Impact: Protection opposition is profoundly temperature-subordinate. The resistance tends to decrease with temperature. Consequently, temperature variations must be taken into account and, if necessary, corrected during insulation resistance measurements.
- Dampness Entrance: Insulation resistance can be significantly reduced by moisture by opening up unintended electric current pathways. The dielectric properties of insulation materials are compromised by water and humidity, resulting in decreased resistance.
- Chemicals and the Dust: The presence of impurities, like residue, soil, or synthetic substances, on the outer layer of protecting materials can prompt a decrease in protection obstruction. Current leakage is made possible by conductive paths created by contaminants.
- Changes over time: With delayed use, protection materials can debase because of elements like warm pressure, mechanical pressure, or openness to ecological circumstances. The maturing system can bring about a slow decrease in protection obstruction.
- High Voltage Activity: Presenting protection to higher voltages than it is intended for can prompt pressure and breakdown. The insulation’s effectiveness over time may be compromised by microscopic damage caused by high-voltage stress.
- Regular checks: The overall resistance can be affected by the frequency of insulation resistance testing. Ordinary testing recognizes potential issues right off the bat, forestalling further crumbling.
- Length of cable Runs: In lengthy link runs, the protection obstruction might differ along the length. Due to factors like increased surface area and the possibility of damage, longer cables may experience higher resistance.
- Non-Uniform Voltage Appropriation: Non-uniform conveyance of voltage across protection can influence opposition. The insulation’s ability to resist current flow may be affected by higher electric field intensity in some areas.
Measurement of Insulation Resistance
Insulation Resistance is a basic boundary in the assessment of the insulation state of electrical systems and equipment. It is measured to ensure the respectability of the insulation that isolates conductive parts from one another and starting from the earliest stage. The Insulation Resistance test is commonly performed utilizing a megohmmeter (otherwise called a megger).
Insulation-Resistance
Insulation resistance is a basic boundary in the electrical and electronic businesses, as it guarantees the wellbeing and dependability of electrical frameworks. It is the measurement of a material’s resistance to the flow of current through it. Because it prevents leakage currents and ensures the proper operation of electrical equipment, it is especially important in insulating materials. The estimation of Insulation resistance is regularly done utilizing a high-voltage direct current (DC) source.
In below we have a detailed explanation of the measurement process:
- The Measurement’s Purpose: The primary objective of measuring insulation resistance is to evaluate the integrity of electrical system insulation. It recognizes potential blames like protection breakdown, dampness entrance, or tainting that can think twice about wellbeing and execution of electrical equipment.
- Equipment Required: Insulation resistance Analyzer (Megohmmeter): This specific instrument produces a high DC voltage and measures the protection obstruction in megaohms.
- Lead Testers: Cables or probes that are insulated and connect the insulation resistance tester to the apparatus that is being tested.
- Preparation: De-energize and isolate the equipment that will be tested from the power source. Remove any components or parallel paths that could have an impact on the measurement.
- Choice of Test Voltage: The test voltage is chosen in view of industry guidelines, hardware details, and the kind of insulation being tried. Common test voltages include 2,500 V, 500 V, and 1,000 V.
- Test Connections: The insulation resistance tester’s positive lead should be connected to the conductor that is being tested, and the negative lead should be connected to the ground or the equipment’s metallic frame. For three-phase systems, perform Insulation resistance measurements phase-to-phase and phase to-ground.
- Execution of Test: Apply the chose test voltage for a particular length (typically 1 moment) and measure the subsequent current moving through the insulation. The Insulation resistance (IR) is determined utilizing Ohm’s Law:
IR = Current / Voltage
- Measurements Recorded: Record the Insulation resistance values for each test, and think about them against adequate least qualities indicated by norms or hardware producers.
- Interpretation of Results: Better insulation integrity is indicated by insulation resistance values that are higher. A decline in Insulation resistance might demonstrate protection weakening, defilement, or dampness entrance.
- Temperature Amendment: Insulation resistance is temperature-subordinate. Depending on the temperature outside, some measurements may need to be adjusted.
- Maintenance and Follow-up: Routinely booked Insulation resistance tests are important for preventive upkeep programs. If a low insulation resistance is found, additional research and corrective measures like cleaning, drying, or replacing the insulation may be required.
- Considerations for Safety: Always use appropriate personal protective equipment and adhere to safety procedures. Before conducting insulation resistance tests, check to see that the equipment has been turned off.
To ensure safe and accurate testing, specific instruments are needed to measure insulation resistance. The most important tools used in the insulation resistance testing procedure are as follows:
Insulation Resistance Tester (Megohmmeter)
The primary instrument used to measure insulation resistance is this one. Megohmmeters come in a variety of designs and voltage ranges. Normal test voltages incorporate 500 V, 1,000 V, and 2,500 V. Megohmmeters normally have elements, for example, voltage show, obstruction estimation, and some of the time the capacity to perform polarization list (PI) and dielectric assimilation proportion (DAR) tests.
Test Leads
Protected test leads are fundamental for interfacing the protection obstruction analyzer to the gear being tried. They forestall accidental short-circuits and ensure the security of the administrator. Test leads ought to be in good shape, and their insulation ought to be regularly examined for signs of damage or wear.
Accessories and Adapters
In order to properly connect the insulation resistance tester and the equipment, additional adapters or accessories may be required, depending on its configuration. Specialized adapters are required for certain pieces of equipment that have particular terminals or connection points.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
During insulation resistance testing, safety is the most important consideration. Individual defensive hardware, for example, security gloves, wellbeing glasses, and, now and again, protecting mats or covers ought to be utilized to safeguard the administrator from electric shock perils.
Temperature Estimation Apparatuses
Temperature can have a significant impact on insulation resistance measurements in some instances. Temperature rectification might be required, and instruments, for example, thermometers or infrared thermographic cameras might be utilized to quantify surrounding temperature.
Documentation Instruments
The results of the insulation resistance test should be recorded for future analysis and reference. It is necessary to use paper, a pencil, or electronic devices to record measurements. The date, time, test voltage, and any corrective actions taken should all be recorded with the test results.
Inspection Tools
Prior to performing insulation resistance testing, outwardly assess the gear for any noticeable indications of harm, disintegration, or tainting. Review instruments, for example, electric lamps might be required for this reason.
Lockout/Tagout Equipment
Before performing insulation resistance testing, check to see that the appropriate lockout and tagout equipment is available to disconnect the equipment from the power source. During testing, this prevents accidental energization and ensures the operator’s safety.
Warnings and labels for the equipment
To let people know that insulation resistance testing is taking place, clearly label the equipment that is being tested with appropriate warnings. During testing, this assists in preventing accidental equipment re-energization.
Importance of Insulation Resistance in Power Generation
The importance of Insulation Resistance in power generation is discussed below in all aspects :
Equipment Reliability
- In power age offices, different sorts of electrical hardware, like generators, transformers, and links, are utilized. insulation Resistance testing guarantees the unwavering quality of the protection frameworks in these parts.
- A high insulation Resistance esteem shows that the insulation is looking great, decreasing the gamble of electrical deficiencies and hardware disappointments.
Electrical Failure Prevention
- Insulation breakdown can occur in generators, particularly those operating at high voltages, as a result of moisture ingress, contamination, or aging. Insulation resistance testing on a regular basis assists in identifying potential problems before they result in electrical failures.
- Early location of falling apart insulation takes into account ideal upkeep or substitution, forestalling exorbitant free time and hardware harm.
Consistence with Norms
- In power generation, it is essential to adhere to industry standards and regulations. Protection obstruction testing is in many cases a compulsory prerequisite determined by norms to ensure the unwavering quality and security of electrical systems.
Safety
- Guaranteeing the insulation honesty is fundamental for the security of faculty working in power age offices. Flawed insulation can prompt short-circuits, electrical flames, or electrical shocks.
- insulation Resistance testing distinguishes and moderate dangers related with weakening protection, adding to a more secure work space.
Maintenance Preventative
- In order to reduce the number of unplanned breakdowns and extend the equipment’s lifespan, power generation facilities implement preventive maintenance programs. These programs include insulation resistance testing on a regular basis, which helps facilitate prompt maintenance actions and lowers the likelihood of unanticipated failures.
Importance of Insulation Resistance in Power Distribution
The importance of Insulation Resistance in Power Distribution is discussed below in all aspects :
Maintaining Network Integrity
- Power dispersion systems include a perplexing organization of transformers, switchgear, links, and different parts. By identifying potential issues that could compromise the insulation of these components, insulation resistance testing aids in maintaining the integrity of the distribution network.
Stopping Outages
- Outages can result from insulation failure in power distribution components, affecting the electrical supply’s dependability. Insulation resistance testing recognizes flimsy parts in the protection, considering proactive measures to forestall blackouts and guarantee constant power dissemination.
Safety
- Power distribution systems eventually supply power to homes, organizations, and opposite end-users. ensuring the honesty of insulation is crucial for the security of people utilizing electrical apparatuses and gear associated with the distribution network.
Fault Detection
- Insulation resistance testing can support the discovery and area of issues in power appropriation frameworks. Maintenance personnel can focus their efforts on specific components by locating areas of compromised insulation, thereby increasing the efficiency of fault identification and resolution.
Nature of Force Supply
- Insulation resistance is a critical boundary in ensure the nature of force provided to end-clients. The distribution system’s efficiency can be harmed by leakage currents and power losses caused by low insulation resistance.
- By identifying and addressing insulation issues that could affect the performance of distribution equipment, regular testing aids in maintaining the quality of the power.
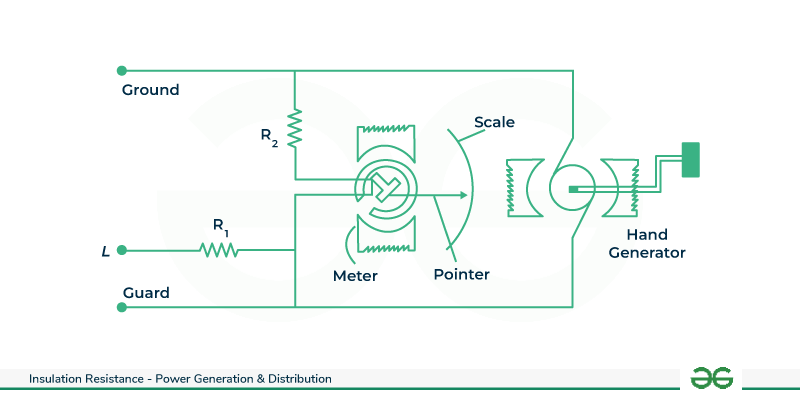
Method for Measuring Insulation Resistance
An electrical device’s insulation resistance can be measured using a variety of instruments.
- Direct-demonstrating ohmmeter with hand driven dc generator. This is privately known as hand driven megger . Since Megger is one of the most outstanding known producer of this instrument.
- Ohmmeter with direct indication and a dc generator driven by a motor. The local term for this is motorized megger.
- Direct-showing ohmmeter with independent battery.
- Direct-showing ohmmeter with independent rectifier. An external AC supply provides power to this instrument.
- With a self-contained galvanometer and battery, a resistance bridge circuit
Using an external dc supply, we can measure the resistance of the insulation. All things considered, we take voltage and current perusing with the assistance of a dc voltmeter and a miniature ran dc ammeter, separately.
R = V / I
In this scenario, we can use ohm’s law to determine the insulation resistance, where V is the reading from the voltmeter and I is the reading from the ammeter.
The ammeter is miniature run on the grounds that, an exceptionally small current finishes through the protection during assessment and he current is in that range as it were. However, the micrometer must measure both the absorption current and the initial capacitive charging current when the voltage is applied. Therefore, the ammeter ought to be able to withstand both of these currents at least initially. In the event of insulation failure while measuring, the voltmeter, ammeter, and source ought to be able to withstand a short circuit current.
At the point when we utilize direct showing ohmmeter of just megger, the leads of the instrument are associated across the protector to be tried. The insulation resistance value can be directly seen on the analog or digital dial of the instrument after it has been driven. In order to obtain a reading that is both more accurate and free of errors, the reading is taken after a standard time delay in both of the aforementioned methods of measuring insulation resistance.
Maintaining Good Insulation Resistance
To ensure the security, constancy, and ideal execution of electrical systems, it require good insulation resistance should be kept up with. Insulation that is of great goes about as an protection against leakage currents and prevents unexpected electrical ways that could bring about glitches or threats to somewhere safe and secure. Significant methods for safeguarding insulation resistance are as per the following:
- Regular Inspections: Direct normal visual assessments of electrical parts to distinguish indications of wear, harm, or tainting on protection surfaces.
- Moisture Control: By sealing entry points and ensuring that the right environmental conditions are maintained, moisture infiltration can be minimized. Dampness altogether lessens protection opposition.
- Cleanliness: To avoid the buildup of dust and dirt that can compromise the integrity of the insulation, keep the equipment and the surrounding areas clean.
- Fix all loose connections: Guarantee all electrical associations are appropriately fixed to forestall overheating and corruption of protection.
- Temperature Checking: Keep an eye on operating temperatures to stop the insulation from deteriorating more quickly. Execute warm checking frameworks if necessary.
- Protection from Surge: Introduce flood assurance gadgets to defend against transient voltage spikes that can pressure protection.
- Testing for Insulation Resistance: Utilize a megohmmeter for routine insulation resistance tests. This recognizes likely issues before they lead to disappointments.
Applications of Insulation Resistance
The safety, dependability, and proper operation of electrical systems are guaranteed by the insulation resistance, which plays a crucial role in numerous applications across various industries. Common uses for insulation resistance include the following:
- Aerospace Industry: In the aviation sector, Insulation Resistance testing is fundamental for ensuring the dependability of electrical systems in airplane, satellites, and space investigation equipment.
- High-Voltage Testing: In high-voltage applications, for example, power transmission and circulation, protection obstruction testing is significant to keeping up with the protection respectability of links, transformers, and other high-voltage hardware.
- Audits of Electrical Safety: A crucial component of electrical safety audits is routine insulation resistance testing, which ensures compliance with safety standards and regulations to prevent hazards.
- Maintaining electrical equipment: Customary insulation testing is essential for preventive upkeep programs for electrical gear like motors, generators, transformers, switchgear, and cables. It aids in the identification of potential issues prior to equipment failure.
- Telecommunications: It used to check the integrity of the insulation in the telecommunication infrastructure, which includes cables, connectors, and equipment, to keep the quality of the signal transmission high
Conclusion
In conclusion, Insulation resistance remains as a key part in the domain of electrical engineering, shielding the respectability, dependability, and safety of electrical systems. The capacity of protecting materials to oppose the progression of electric flow is principal in forestalling spillage flows and keeping up with the protection hindrances that safeguard against electrical faults. Customary protection opposition testing, led with tirelessness and adherence to industry principles, arises as a proactive methodology to distinguish possible issues before they heighten, adding to the life span of electrical parts.
The meaning of insulation resistance traverses across assorted applications, from engines and generators to links, transformers, and basic framework like power circulation frameworks. It fills in as a symptomatic device, giving experiences into the strength of protection materials and considering opportune mediations to address corruption. As innovation progresses and electrical systems become more mind boggling, the job of insulation resistance stays crucial in guaranteeing the heartiness of our interconnected and zapped world. In essence, the thoroughness of insulation resistance testing upholds the fundamental principles of electrical safety and dependability in addition to preventing breakdowns.
FAQs on Insulation Resistance
1. How often should insulation resistance testing be conducted?
The equipment’s criticality, industry standards, and environmental conditions all play a role in frequency. For the most part, yearly testing is suggested for basic systems.
2. Will insulation resistance testing be performed during hardware activity?
While some testing should be possible with gear stimulated, it’s ordinarily prescribed to perform insulation resistance tests during booked closures to guarantee security and exactness.
3. Why is insulation resistance significant in power transformers?
Insulation resistance testing in power transformers surveys the soundness of the insulation system, forestalling disappointments and guaranteeing the transformer’s unwavering quality in electrical power appropriation.
4. What are typical indications that electrical system insulation has degraded?
Normal signs remember a downfall for insulation resistance values, strange intensity age, whimsical hardware conduct, and noticeable harm to protection materials.
5. What is the effect of temperature on insulation resistance?
Temperature altogether affects protection opposition. Insulation resistance tends to decrease with temperature. Amendments for temperature varieties are many times applied during testing.
6. How is insulation resistance estimated?
A megohmmeter or megger is used to measure insulation resistance. The test includes applying a high voltage across the protection and estimating the subsequent current.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...