How to Use Apache Kafka for Real-Time Data Streaming?
Last Updated :
18 Mar, 2024
In the present era, when data is king, many businesses are realizing that there is processing information in real-time, which is allowing Apache Kafka, the current clear leader with an excellent framework for real-time data streaming.
This article dives into the heart of Apache Kafka and its application in real-time data streaming, providing insight and practical guidance on how to use the technology.
What is Apache Kafka?
Apache Kafka is an open-source stream-processing software platform developed by the Apache Software Foundation, written in the Scala and Java languages. Kafka is designed to provide a unified, high-throughput, low-latency platform for handling real-time data feeds.
This has become a darling for most companies, especially those that have a lot of data to handle, because of its robustness, scalability, and efficiency. Kafka works with a publisher-subscriber model, and it can control data streams from multiple points and deliver them to respective consumers.
Benefits of Using Apache Kafka
- Scalability: Kafka is designed to be distributed and can scale out without downtime.
- Performance: It ensures both publish and subscribe operations are high throughput, and the disk structures give uniform performance even when many terabytes of messages are in storage.
- Durability: Kafka uses an ordered, fault-t-tolerant, and distributed commit log; this means that messages are on disk as fast as they can be written without compromising performance.
- Kafka Integration: This system easily integrates with outer systems thanks to Kafka Connect (data import/export) and offers Kafka Streams—a stream processing library.
What is Real-Time Data Streaming?
Real-time data streaming is the process of capturing, processing, and analyzing data at the point of data creation and in real-time. In batch processing, the data to be processed is usually collected, stored, and then worked upon at a different time. Real-time streaming processes the data on-the-fly, preferably within milliseconds or even seconds of its creation.
This is particularly critical in cases where the application needs to give real-time insights and take necessary real-time action, such as monitoring financial transactions for fraud detection, tracking user live interactions on websites, etc.
Benefits of Real-Time Data Streaming
- Instant Insights: Real-time analysis of data streams allows businesses to make quicker decisions.
- Enhanced User Experience: Immediate processing of data helps in providing personalized user experiences.
- Operational Efficiency: This allows for response by automated dispatchers to critical business events within the organizational setup, hence reducing human intervention and, by extension, errors.
- Risk Management: Immediate data analysis helps in identifying and mitigating risks promptly.
How to Use Apache Kafka for Real-Time Data Streaming?
Below are the steps and detailed commands to be able to run real-time data streaming through Apache Kafka effectively. This guide will assume that a person is in a Unix-like environment (Linux, MacOS, etc.) and that Kafka is downloaded and extracted.
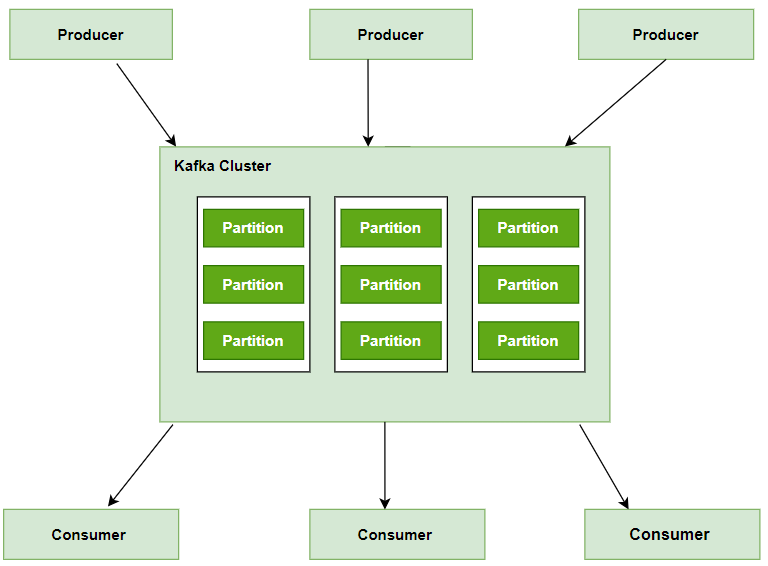
Kafka Cluster
1. Install Apache Kafka and Zookeeper
After downloading Kafka, which includes Zookeeper, from the Apache website:
# Extract Kafka
tar -xzf kafka_2.13-2.8.0.tgz
# Navigate to Kafka directory
cd kafka_2.13-2.8.0
2. Start Kafka Server
You’ll start Zookeeper first, then the Kafka server:
# Start Zookeeper
./bin/zookeeper-server-start.sh config/zookeeper.properties
# In a new terminal window or tab, start Kafka Server
./bin/kafka-server-start.sh config/server.properties
3. Create Topics
Create a topic in Kafka to which you’ll publish and from which you’ll consume messages:
# Create a Topic
./bin/kafka-topics.sh --create --topic your_topic_name --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --replication-factor 1 --partitions 1
4. Produce Data
Use Kafka’s producer to send data to your topic:
# Start Producer
./bin/kafka-console-producer.sh --topic your_topic_name --bootstrap-server localhost:9092
After running this command, you can type messages into the console to send to the topic.
5. Consume Data
Use Kafka’s consumer to read data from your topic:
# Start Consumer
./bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --topic your_topic_name --from-beginning --bootstrap-server localhost:9092
This command consumes messages from the specified topic and prints them to the console.
6. Monitor and Manage
For basic monitoring and management, you can list and describe topics:
# List all topics
./bin/kafka-topics.sh --list --bootstrap-server localhost:9092
# Describe a specific topic
./bin/kafka-topics.sh --describe --topic your_topic_name --bootstrap-server localhost:
Using Kafka for Real-time Streaming Example
For example, it would be an e-commerce company tracking users’ activities in real-time and recommending products based on their activity on the site. Here is how Kafka can be put to use:
- User Activity Tracking: For this, the company uses Kafka Producers to send data about activities of users to a topic ‘user_activity‘.
- Real-Time Processing: This means that a Kafka consumer subscribed to the topic “user_activities” should process data—all events being consumed are those from real time. Each event can have patterns or preferences processed.
- Recommendation Generation: Based on this, the system should be in a position to generate personalized product recommendations for each user.
Best Practices for Apache Kafka Deployment
- Proper Capacity Planning: Understand your workload requirements and plan Kafka cluster capacity accordingly, considering factors such as message throughput, retention policies, and storage needs.
- High Availability Configuration: Configure Kafka clusters for high availability by deploying multiple brokers across different availability zones or data centers, enabling automatic failover and replication.
- Optimized Topic Design: Design topics with consideration for partitioning, replication factors, and retention policies to ensure optimal performance and durability.
- Effective Monitoring and Alerting: Implement comprehensive monitoring and alerting solutions to track Kafka cluster health, throughput, and latency, enabling proactive management and issue resolution.
- Security Hardening: Secure Kafka clusters using encryption, authentication, and authorization mechanisms to protect data confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Conclusion
Apache Kafka offers a transformative solution for real-time data streaming, enabling scalable, fault-tolerant, and high-performance operations. Leveraging Kafka empowers businesses to construct resilient analytics pipelines, deploy event-driven microservices, and foster innovation across industries. By adhering to best practices, organizations can effectively utilize Kafka to drive actionable insights, enhance operational efficiency, and maintain competitiveness in a data-centric environment.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...