A parallel circuit is one of the important electric circuits. To solve parallel circuits, we use different formulas accordingly. We can calculate the total current, total resistance, voltage, and current through specific resistors accordingly to solve parallel circuits. The total current in a parallel circuit is the sum of the current in all the branches whereas the total resistance is the reciprocal of the addition of the reciprocal of resistances.
In this article, we will discuss parallel circuits, how to solve parallel circuits, and formulas to solve parallel circuits. We will also solve some examples and discuss the applications, advantages, and disadvantages of parallel circuits. Let’s start our learning on the topic “How to solve Parallel Circuit”.
What is a Parallel Circuit?
A circuit is said to be a parallel circuit if the components connected in the circuit are parallel to each other and are connected with the same point of contact. In other words, the circuit that connects all its components in different branches and the branches are connected with the same point of contact is called a parallel circuit. In a parallel circuit, the voltage is the same for all the components, but the is distributed among the components. So, the voltage in a parallel circuit is constant and the current in the parallel circuit is variable for different components.
Construction of a Parallel Circuit
In the Parallel circuit the arrangements are done by connecting the terminals of all individual load devices so that they can share the same voltage across each component.Each branch in the circuit has same voltage,Unlike a series circuit where the current has a single path, a parallel circuit has multiple paths or branches for current flow. Even if one branch or component is disconnected, current will reach the remaining devices in the circuit. This is the major difference between the parallel.

Parallel Circuit
How to Solve Parallel Circuit?
In a parallel circuit, the voltage is the same for all the resistors connected in parallel but the current flowing through the circuit is different for all the resistors. The total current flowing through circuit is divided among the resistors connected in parallel.

Parallel Circuit
In the above diagram resistors R1, R2 and R3 are connected in parallel, and the voltage V Volts is applied on the circuit. A current ‘I’ is flowing through the parallel circuit. We know that the voltage in parallel circuit is same for all the resistors so, the same voltage is applied across the resistors R1, R2 and R3 whereas the current is divided among all the resistors R1, R2 and R3. The current flowing through R1, R2 and R3 be I1, I2 and I3 respectively. The total current flowing through the circuit is the sum of individual current flowing through each component.
The following formulas can be used accordingly to solve parallel circuit. Let V be the applied voltage on the parallel circuit with resistors R1, R2 and R3 with total current ‘I’ flow through the circuit. As we know in the parallel circuit the current is different for all the components so, the current flowing through R1, R2 and R3 is I1, I2 and I3 respectively.
Using Ohm’s Law for Parallel Circuits to Determine Current
We know that in a parallel circuit the current is divided among the resistors. So, the total current flowing through the parallel circuit is equal to the total voltage divided by total resistance. Alternatively, it can also be calculated by adding all the currents flowing in all resistors.
I = V / R
or
I = I1 + I2 + I3
How to Calculate Total Resistance in a Parallel Circuit
The total resistance in a parallel circuit is calculated by taking the reciprocal of the sum of the reciprocals of all the resistances connected in parallel. Alternatively, the total resistance in a parallel circuit is equal to the product of all the resistances connected in parallel divided by the sum of all the resistances in parallel.
1/R = [1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3]
or
R = (R1 × R2 × R3) / (R1 + R2 + R3)
Voltage in a Parallel Circuit
In a parallel circuit the voltage is same for all the resistors. The voltage across each resistor is equal to the total applied voltage in a parallel circuit.
V = V1 = V2 = V3
where,
V is applied voltage
V1, V2 and V3 are voltages across resistors R1, R2 and R3 respectively.
Current through Each Resistor
To calculate the current through each resistor we divide the voltage across the given resistor with the resistance of the desired resistor. As we know that the voltage is same for all resistors of parallel circuit. So, to get the current through a specific resistor we divide the voltage by the resistance of the resistor.
I1 = V/R1
I2 = V/R2
I3 = V/ R3
Solved Examples
Find the total resistance of the parallel circuit in which the resistances of resistors R1, R2 and R3 are 5Ω, 8Ω and 12Ω respectively.
The total resistance of parallel circuit is calculated by the formula:
R = (R1 × R2 × R3) / (R1 + R2 + R3)
R = (5 × 8 × 12) / (5 + 8 + 12)
R = 480 / 25
R = 19.2 Ω
Total resistance of given parallel circuit is 19.2 Ω.
Find the total current flowing through the parallel circuit if the voltage is 10 V and there are two resistors with resistances 10 Ω and 20 Ω connected in parallel.
The total current flowing through the parallel circuit is given by:
I = Voltage / Total resistance
Total Resistance R = (R1 × R2) / (R1 + R2)
R = (10 × 20) / (10 + 20)
R = 200 / 30
R = 6.67 Ω
I = 10 / 6.67
I = 1.5 A.
The total current flowing through the parallel circuit is 1.5 A
From the below given circuit diagram find the total current in parallel circuit
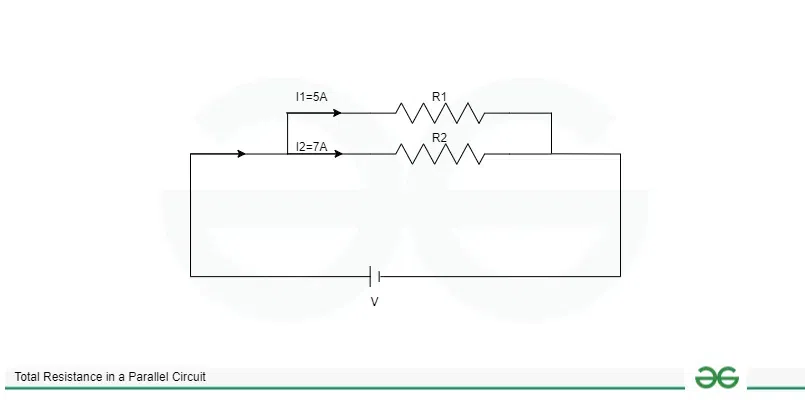
Question
The total current in parallel circuit is given by:
I = I1 + I2
I = 5 + 7
I = 12 A
The total current in given parallel circuit is 12 A.
Find the current flowing through the resistor R1 if the voltage applied is 20 V and the resistance of R1 is 10Ω.
The current flowing through the resistor R1 be I1.
I1 = V/R1
I1 = 20/10
I1 = 2 A
The current flowing through the resistor R1 is 2 A.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Parallel Circuit
There are many advantages and disadvantages of a parallel circuit. Some of these advantages and disadvantages are listed below.
Advantages
Advantages of parallel circuit are as follows:
- Each component in parallel circuit have same voltage.
- New components can be easily installed in a parallel circuit.
- In parallel circuit if one component fails, it does not affect the whole circuit.
Disadvantages
Disadvantages of parallel circuit are as follows:
- Lots of wires are required to connect components in parallel circuit.
- Parallel circuits fail when we require same current in all components.
Applications of Parallel Circuit
Applications of parallel circuits are as follows:
- Housing outlets use parallel circuit to provide same voltage.
- In factories to connect multiple equipment the parallel circuit is used so that if the one equipment fails it does not fail entire work.
- Automobile headlights use parallel circuit.
Conclusion
From the above discussion we can conclude that in a parallel circuit the current is variable, and voltage is constant for the different resistors connected in parallel. We can solve parallel circuit using the formulas of the total current, total resistance, voltage and current across specific resistor. The total current in parallel circuit is given by the ratio of the voltage to the total resistance. The total resistance in a parallel circuit is calculated by taking reciprocal of sum of the reciprocal of resistances of the resistors connected in parallel. The voltage across the resistors is same as the applied voltage in a parallel circuit.
How to Solve Parallel Circuit – FAQs
What is Parallel Circuits?
A circuit is referred to as a parallel circuit when the components are connected parallel to each other with a same point of contact.
What is the Formula for the Total Resistance in Parallel Circuit?
The formula for calculating the total resistance in parallel circuit is given by:
1/R = [1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3]
or
R = (R1 × R2 × R3) / (R1 + R2 + R3)
What can we Comment on Voltage in a Parallel Circuit?
In a parallel circuit the voltage is same as the applied voltage for all the resistors connected in parallel.
How to Find Total Current in a Parallel Circuit?
To find the total current in a parallel circuit we divide the total voltage by the total resistance.
I = V / R
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...