How to read multiple Excel files in R
Last Updated :
18 Jul, 2021
In this article, we will discuss how to merge multiple Excel files in the R programming language.
Modules Used:
- dplyr: The dplyr package in R is a structure of data manipulation that provides a uniform set of verbs, helping to resolve the most frequent data manipulation hurdles.
- plyr: The “plyr” package in R is used to work with data, including its enhancements and manipulations.
- readxl: This package is used to work with excel files in R
- readr: This package is used to read files in R
Functions Used:
- list.files() function produces a character vector of the names of files or directories in the named directory.
Syntax: list.files(path = “.”, pattern = NULL, all.files = FALSE,full.names = FALSE, recursive = FALSE, ignore.case = FALSE, include.dirs = FALSE, no.. = FALSE)
- lapply() function returns a list of the same length as X, each element of which is the result of applying FUN to the corresponding element of X.
Syntax: lapply(X, FUN, …)
- bind_rows() function is an efficient implementation of the common pattern of do.call(rbind, dfs) or do.call(cbind, dfs) for binding many data frames into one.
Syntax: bind_rows(…, .id = NULL)
Files in use:

gfg_data1.xlsx

gfg_data2.xlsx

gfg_data3.xlsx
Example: Merging Excel using R
R
library("dplyr")
library("plyr")
library("readr")
library("readxl")
gfg_data <- list.files(path = "Location/to/folder",
pattern = "*.xlsx",
full.names = TRUE) %>%
lapply(read_excel) %>%
bind_rows
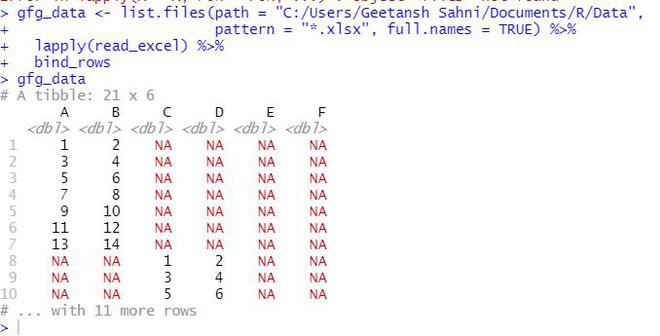
gfg_data
|
Output:
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...