Height of binary tree considering even level leaves only
Last Updated :
29 Jul, 2022
Find the height of the binary tree given that only the nodes on the even levels are considered valid leaf nodes.
The height of a binary tree is the number of edges between the tree’s root and its furthest leaf. But what if we bring a twist and change the definition of a leaf node? Let us define a valid leaf node as the node that has no children and is at an even level (considering the root node as an odd level node).
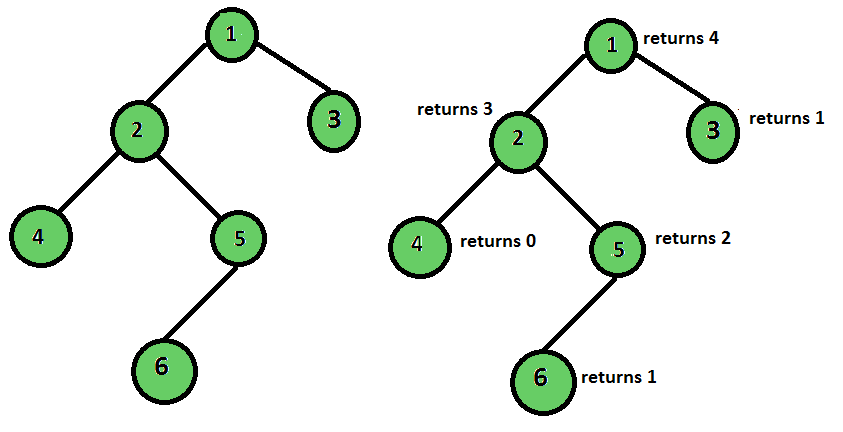
Output: Height of the tree is 4
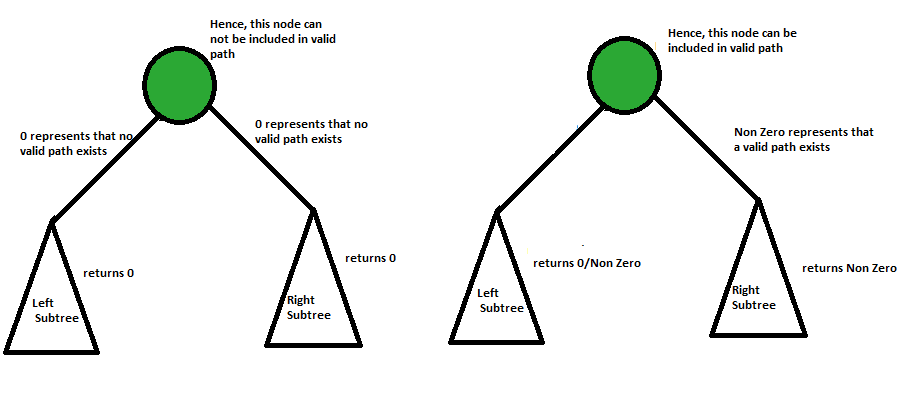
Approach: The approach to this problem is slightly different from the normal height finding approach. In the return step, we check if the node is a valid root node or not. If it is valid, return 1, else we return 0. Now in the recursive step- if the left and the right sub-tree both yield 0, the current node yields 0 too because in that case there is no path from the current node to a valid leaf node. But in the case at least one of the values returned by the children is non-zero, it means the leaf node on that path is a valid leaf node, and hence that path can contribute to the final result, so we return the max of the values returned + 1 for the current node.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* left;
struct Node* right;
};
int heightOfTreeUtil(Node* root, bool isEven)
{
if (!root)
return 0;
if (!root->left && !root->right) {
if (isEven)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
int left = heightOfTreeUtil(root->left, !isEven);
int right = heightOfTreeUtil(root->right, !isEven);
if (left == 0 && right == 0)
return 0;
return (1 + max(left, right));
}
struct Node* newNode(int data)
{
struct Node* node =
(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
int heightOfTree(Node* root)
{
return heightOfTreeUtil(root, false);
}
int main()
{
struct Node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
root->left->right->left = newNode(6);
cout << "Height of tree is " << heightOfTree(root);
return 0;
}
|
Java
class GfG {
static class Node {
int data;
Node left;
Node right;
}
static int heightOfTreeUtil(Node root, boolean isEven)
{
if (root == null)
return 0;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
if (isEven == true)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
int left = heightOfTreeUtil(root.left, !isEven);
int right = heightOfTreeUtil(root.right, !isEven);
if (left == 0 && right == 0)
return 0;
return (1 + Math.max(left, right));
}
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node node = new Node();
node.data = data;
node.left = null;
node.right = null;
return (node);
}
static int heightOfTree(Node root)
{
return heightOfTreeUtil(root, false);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
root.left.right.left = newNode(6);
System.out.println("Height of tree is " + heightOfTree(root));
}
}
|
Python3
class newNode:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
def heightOfTreeUtil(root, isEven):
if (not root):
return 0
if (not root.left and not root.right):
if (isEven):
return 1
else:
return 0
left = heightOfTreeUtil(root.left, not isEven)
right = heightOfTreeUtil(root.right, not isEven)
if (left == 0 and right == 0):
return 0
return (1 + max(left, right))
def heightOfTree(root):
return heightOfTreeUtil(root, False)
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = newNode(1)
root.left = newNode(2)
root.right = newNode(3)
root.left.left = newNode(4)
root.left.right = newNode(5)
root.left.right.left = newNode(6)
print("Height of tree is",
heightOfTree(root))
|
C#
using System;
class GfG
{
class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left;
public Node right;
}
static int heightOfTreeUtil(Node root,
bool isEven)
{
if (root == null)
return 0;
if (root.left == null &&
root.right == null)
{
if (isEven == true)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
int left = heightOfTreeUtil(root.left, !isEven);
int right = heightOfTreeUtil(root.right, !isEven);
if (left == 0 && right == 0)
return 0;
return (1 + Math.Max(left, right));
}
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node node = new Node();
node.data = data;
node.left = null;
node.right = null;
return (node);
}
static int heightOfTree(Node root)
{
return heightOfTreeUtil(root, false);
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
root.left.right.left = newNode(6);
Console.WriteLine("Height of tree is " +
heightOfTree(root));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
function heightOfTreeUtil(root, isEven) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
if (isEven == true)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
var left = heightOfTreeUtil(root.left, !isEven);
var right = heightOfTreeUtil(root.right, !isEven);
if (left == 0 && right == 0)
return 0;
return (1 + Math.max(left, right));
}
function newNode(data) {
var node = new Node();
node.data = data;
node.left = null;
node.right = null;
return (node);
}
function heightOfTree(root) {
return heightOfTreeUtil(root, false);
}
var root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
root.left.right.left = newNode(6);
document.write("Height of tree is " + heightOfTree(root));
</script>
|
Output
Height of tree is 4
Time Complexity: O(n), Where n is the number of nodes in a given binary tree.
Auxiliary Space: O(n), If we don’t consider the size of the recursive call stack for function calls then O(1), otherwise O(n).
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...