HDFS Commands
Last Updated :
07 Mar, 2024
HDFS is the primary or major component of the Hadoop ecosystem which is responsible for storing large data sets of structured or unstructured data across various nodes and thereby maintaining the metadata in the form of log files. To use the HDFS commands, first you need to start the Hadoop services using the following command:
sbin/start-all.sh
To check the Hadoop services are up and running use the following command:
jps

Commands:
- ls: This command is used to list all the files. Use lsr for recursive approach. It is useful when we want a hierarchy of a folder.
Syntax:
bin/hdfs dfs -ls <path>
Example:
bin/hdfs dfs -ls /
It will print all the directories present in HDFS. bin directory contains executables so, bin/hdfs means we want the executables of hdfs particularly dfs(Distributed File System) commands.

- mkdir: To create a directory. In Hadoop dfs there is no home directory by default. So let’s first create it.
Syntax:
bin/hdfs dfs -mkdir <folder name>
creating home directory:
hdfs/bin -mkdir /user
hdfs/bin -mkdir /user/username -> write the username of your computer
Example:
bin/hdfs dfs -mkdir /geeks => '/' means absolute path
bin/hdfs dfs -mkdir geeks2 => Relative path -> the folder will be
created relative to the home directory.


-
touchz: It creates an empty file.
Syntax:
bin/hdfs dfs -touchz <file_path>
Example:
bin/hdfs dfs -touchz /geeks/myfile.txt

- copyFromLocal (or) put: To copy files/folders from local file system to hdfs store. This is the most important command. Local filesystem means the files present on the OS.
Syntax:
bin/hdfs dfs -copyFromLocal <local file path> <dest(present on hdfs)>
Example: Let’s suppose we have a file AI.txt on Desktop which we want to copy to folder geeks present on hdfs.
bin/hdfs dfs -copyFromLocal ../Desktop/AI.txt /geeks
(OR)
bin/hdfs dfs -put ../Desktop/AI.txt /geeks

- cat: To print file contents.
Syntax:
bin/hdfs dfs -cat <path>
Example:
// print the content of AI.txt present
// inside geeks folder.
bin/hdfs dfs -cat /geeks/AI.txt ->

- copyToLocal (or) get: To copy files/folders from hdfs store to local file system.
Syntax:
bin/hdfs dfs -copyToLocal <<srcfile(on hdfs)> <local file dest>
Example:
bin/hdfs dfs -copyToLocal /geeks ../Desktop/hero
(OR)
bin/hdfs dfs -get /geeks/myfile.txt ../Desktop/hero
myfile.txt from geeks folder will be copied to folder hero present on Desktop.

Note: Observe that we don’t write bin/hdfs while checking the things present on local filesystem.
- moveFromLocal: This command will move file from local to hdfs.
Syntax:
bin/hdfs dfs -moveFromLocal <local src> <dest(on hdfs)>
Example:
bin/hdfs dfs -moveFromLocal ../Desktop/cutAndPaste.txt /geeks

- cp: This command is used to copy files within hdfs. Lets copy folder geeks to geeks_copied.
Syntax:
bin/hdfs dfs -cp <src(on hdfs)> <dest(on hdfs)>
Example:
bin/hdfs dfs -cp /geeks /geeks_copied

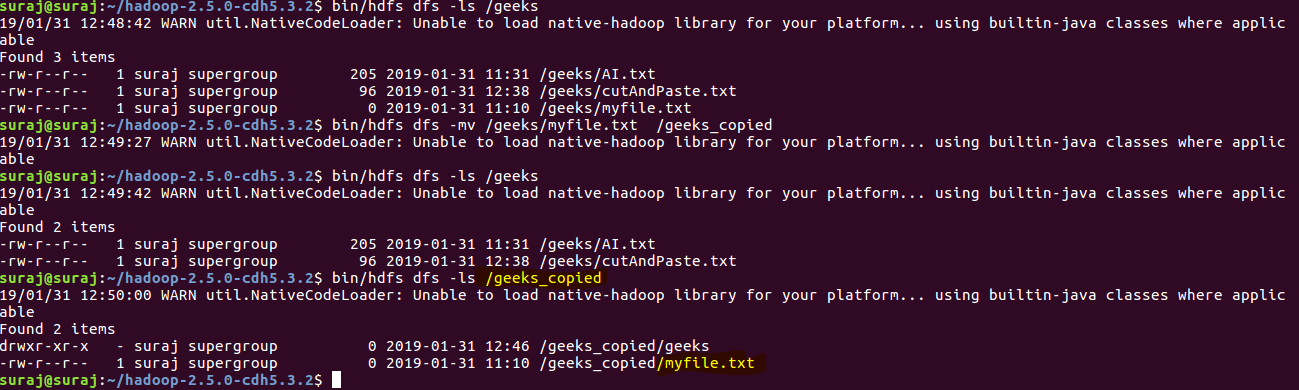
- mv: This command is used to move files within hdfs. Lets cut-paste a file myfile.txt from geeks folder to geeks_copied.
Syntax:
bin/hdfs dfs -mv <src(on hdfs)> <src(on hdfs)>
Example:
bin/hdfs dfs -mv /geeks/myfile.txt /geeks_copied
- rmr: This command deletes a file from HDFS recursively. It is very useful command when you want to delete a non-empty directory.
Syntax:
bin/hdfs dfs -rmr <filename/directoryName>
Example:
bin/hdfs dfs -rmr /geeks_copied -> It will delete all the content inside the
directory then the directory itself.

- du: It will give the size of each file in directory.
Syntax:
bin/hdfs dfs -du <dirName>
Example:
bin/hdfs dfs -du /geeks

- dus:: This command will give the total size of directory/file.
Syntax:
bin/hdfs dfs -dus <dirName>
Example:
bin/hdfs dfs -dus /geeks

- stat: It will give the last modified time of directory or path. In short it will give stats of the directory or file.
Syntax:
bin/hdfs dfs -stat <hdfs file>
Example:
bin/hdfs dfs -stat /geeks

- setrep: This command is used to change the replication factor of a file/directory in HDFS. By default it is 3 for anything which is stored in HDFS (as set in hdfs core-site.xml).
Example 1: To change the replication factor to 6 for geeks.txt stored in HDFS.
bin/hdfs dfs -setrep -R -w 6 geeks.txt
Example 2: To change the replication factor to 4 for a directory geeksInput stored in HDFS.
bin/hdfs dfs -setrep -R 4 /geeks
Note: The -w means wait till the replication is completed. And -R means recursively, we use it for directories as they may also contain many files and folders inside them.

Note: There are more commands in HDFS but we discussed the commands which are commonly used when working with Hadoop. You can check out the list of dfs commands using the following command:
bin/hdfs dfs

Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...