Given two arrays: arr1[0..m-1] and arr2[0..n-1]. Find whether arr2[] is a subset of arr1[] or not. Both arrays are not in sorted order. It may be assumed that elements in both arrays are distinct.
Examples:
Input: arr1[] = {11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7}, arr2[] = {11, 3, 7, 1}
Output: arr2[] is a subset of arr1[]
Input: arr1[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}, arr2[] = {1, 2, 4}
Output: arr2[] is a subset of arr1[]
Input: arr1[] = {10, 5, 2, 23, 19}, arr2[] = {19, 5, 3}
Output: arr2[] is not a subset of arr1[]
Naive Approach to Find whether an array is subset of another array
Use two loops: The outer loop picks all the elements of arr2[] one by one. The inner loop linearly searches for the element picked by the outer loop. If all elements are found then return 1, else return 0.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// C++ program to find whether an array
// is subset of another array
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
/* Return 1 if arr2[] is a subset of
arr1[] */
bool isSubset(int arr1[], int arr2[], int m, int n)
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (arr2[i] == arr1[j])
break;
}
/* If the above inner loop was
not broken at all then arr2[i]
is not present in arr1[] */
if (j == m)
return 0;
}
/* If we reach here then all
elements of arr2[] are present
in arr1[] */
return 1;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr1[] = { 11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7 };
int arr2[] = { 11, 3, 7, 1 };
int m = sizeof(arr1) / sizeof(arr1[0]);
int n = sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(arr2[0]);
if (isSubset(arr1, arr2, m, n))
printf("arr2[] is subset of arr1[] ");
else
printf("arr2[] is not a subset of arr1[]");
getchar();
return 0;
}
// C++ program to find whether an array
// is subset of another array
#include <stdio.h>
/* Return 1 if arr2[] is a subset of
arr1[] */
int isSubset(int arr1[], int arr2[], int m, int n)
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (arr2[i] == arr1[j])
break;
}
/* If the above inner loop was
not broken at all then arr2[i]
is not present in arr1[] */
if (j == m)
return 0;
}
/* If we reach here then all
elements of arr2[] are present
in arr1[] */
return 1;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr1[] = { 11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7 };
int arr2[] = { 11, 3, 7, 1 };
int m = sizeof(arr1) / sizeof(arr1[0]);
int n = sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(arr2[0]);
if (isSubset(arr1, arr2, m, n))
printf("arr2[] is subset of arr1[] ");
else
printf("arr2[] is not a subset of arr1[]");
getchar();
return 0;
}
// Java program to find whether an array
// is subset of another array
class GFG {
/* Return true if arr2[] is a subset
of arr1[] */
static boolean isSubset(int arr1[], int arr2[], int m,
int n)
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < m; j++)
if (arr2[i] == arr1[j])
break;
/* If the above inner loop
was not broken at all then
arr2[i] is not present in
arr1[] */
if (j == m)
return false;
}
/* If we reach here then all
elements of arr2[] are present
in arr1[] */
return true;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr1[] = { 11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7 };
int arr2[] = { 11, 3, 7, 1 };
int m = arr1.length;
int n = arr2.length;
if (isSubset(arr1, arr2, m, n))
System.out.print("arr2[] is "
+ "subset of arr1[] ");
else
System.out.print("arr2[] is "
+ "not a subset of arr1[]");
}
}
// C# program to find whether an array
// is subset of another array
using System;
class GFG {
/* Return true if arr2[] is a
subset of arr1[] */
static bool isSubset(int[] arr1, int[] arr2, int m,
int n)
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < m; j++)
if (arr2[i] == arr1[j])
break;
/* If the above inner loop
was not broken at all then
arr2[i] is not present in
arr1[] */
if (j == m)
return false;
}
/* If we reach here then all
elements of arr2[] are present
in arr1[] */
return true;
}
// Driver function
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr1 = { 11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7 };
int[] arr2 = { 11, 3, 7, 1 };
int m = arr1.Length;
int n = arr2.Length;
if (isSubset(arr1, arr2, m, n))
Console.WriteLine("arr2[] is subset"
+ " of arr1[] ");
else
Console.WriteLine("arr2[] is not a "
+ "subset of arr1[]");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sam007
<script>
// JavaScript program to find whether an array
// is subset of another array
/* Return true if arr2[] is a subset
of arr1[] */
function isSubset(arr1, arr2, m, n)
{
let i = 0;
let j = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < m; j++)
if (arr2[i] == arr1[j])
break;
/* If the above inner loop
was not broken at all then
arr2[i] is not present in
arr1[] */
if (j == m)
return false;
}
/* If we reach here then all
elements of arr2[] are present
in arr1[] */
return true;
}
// Driver Code
let arr1 = [ 11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7 ];
let arr2 = [ 11, 3, 7, 1 ];
let m = arr1.length;
let n = arr2.length;
if (isSubset(arr1, arr2, m, n))
document.write("arr2[] is "
+ "subset of arr1[] ");
else
document.write("arr2[] is "
+ "not a subset of arr1[]");
</script>
<?php
// PHP program to find whether an array
// is subset of another array
/* Return 1 if arr2[] is a subset of
arr1[] */
function isSubset($arr1, $arr2, $m, $n)
{
$i = 0;
$j = 0;
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++)
{
for ($j = 0; $j < $m; $j++)
{
if($arr2[$i] == $arr1[$j])
break;
}
/* If the above inner loop was
not broken at all then arr2[i]
is not present in arr1[] */
if ($j == $m)
return 0;
}
/* If we reach here then all
elements of arr2[] are present
in arr1[] */
return 1;
}
// Driver code
$arr1 = array(11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7);
$arr2 = array(11, 3, 7, 1);
$m = count($arr1);
$n = count($arr2);
if(isSubset($arr1, $arr2, $m, $n))
echo "arr2[] is subset of arr1[] ";
else
echo "arr2[] is not a subset of arr1[]";
// This code is contributed by anuj_67.
?>
# Python 3 program to find whether an array
# is subset of another array
# Return 1 if arr2[] is a subset of
# arr1[]
def isSubset(arr1, arr2, m, n):
i = 0
j = 0
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if(arr2[i] == arr1[j]):
break
# If the above inner loop was
# not broken at all then arr2[i]
# is not present in arr1[]
if (j == m):
return 0
# If we reach here then all
# elements of arr2[] are present
# in arr1[]
return 1
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
arr1 = [11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7]
arr2 = [11, 3, 7, 1]
m = len(arr1)
n = len(arr2)
if(isSubset(arr1, arr2, m, n)):
print("arr2[] is subset of arr1[] ")
else:
print("arr2[] is not a subset of arr1[]")
# This code is contributed by ita_c
Outputarr2[] is subset of arr1[]
Time Complexity: O(m*n)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Find whether an array is subset of another array using Sorting and Binary Search
The idea is to sort the given array arr1[], and then for each element in arr2[] do a binary search for it in sorted arr1[]. If the element is not found then return 0. If all elements are present then return 1.
Illustration:
Given array arr1[] = { 11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7 } and arr2[] = { 11, 3, 7, 1 }.
Step 1: We will sort the array arr1[], and have arr1[] = { 1, 3, 7, 11, 13, 21}.
Step 2: We will look for each element in arr2[] in arr1[] using binary search.
- arr2[] = { 11, 3, 7, 1 }, 11 is present in arr1[] = { 1, 3, 7, 11, 13, 21}
- arr2[] = { 11, 3, 7, 1 }, 3 is present in arr1[] = { 1, 3, 7, 11, 13, 21}
- arr2[] = { 11, 3, 7, 1 }, 7 is present in arr1[] = { 1, 3, 7, 11, 13, 21}
- arr2[] = { 11, 3, 7, 1 }, 1 is present in arr1[] = { 1, 3, 7, 11, 13, 21}
As all the elements are found we can conclude arr2[] is the subset of arr1[].
Algorithm:
The algorithm is pretty straightforward.
- Sort the first array arr1[].
- Look for the elements of arr2[] in sorted arr1[].
- If we encounter a particular value that is present in arr2[] but not in arr1[], the code will terminate, arr2[] can never be the subset of arr1[].
- Else arr2[] is the subset of arr1[].
Below is the code implementation of the above approach :
C++
// C++ program to find whether an array
// is subset of another array
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/* Function prototypes */
void quickSort(int* arr, int si, int ei);
int binarySearch(int arr[], int low, int high, int x);
/* Return 1 if arr2[] is a subset of arr1[] */
bool isSubset(int arr1[], int arr2[], int m, int n)
{
int i = 0;
quickSort(arr1, 0, m - 1);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (binarySearch(arr1, 0, m - 1, arr2[i]) == -1)
return 0;
}
/* If we reach here then all elements
of arr2[] are present in arr1[] */
return 1;
}
/* FOLLOWING FUNCTIONS ARE ONLY FOR
SEARCHING AND SORTING PURPOSE */
/* Standard Binary Search function*/
int binarySearch(int arr[], int low, int high, int x)
{
if (high >= low) {
/*low + (high - low)/2;*/
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
/* Check if arr[mid] is the first
occurrence of x. arr[mid] is first
occurrence if x is one of the following
is true:
(i) mid == 0 and arr[mid] == x
(ii) arr[mid-1] < x and arr[mid] == x */
if ((mid == 0 || x > arr[mid - 1])
&& (arr[mid] == x))
return mid;
else if (x > arr[mid])
return binarySearch(arr, (mid + 1), high, x);
else
return binarySearch(arr, low, (mid - 1), x);
}
return -1;
}
void exchange(int* a, int* b)
{
int temp;
temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
int partition(int A[], int si, int ei)
{
int x = A[ei];
int i = (si - 1);
int j;
for (j = si; j <= ei - 1; j++) {
if (A[j] <= x) {
i++;
exchange(&A[i], &A[j]);
}
}
exchange(&A[i + 1], &A[ei]);
return (i + 1);
}
/* Implementation of Quick Sort
A[] --> Array to be sorted
si --> Starting index
ei --> Ending index
*/
void quickSort(int A[], int si, int ei)
{
int pi; /* Partitioning index */
if (si < ei) {
pi = partition(A, si, ei);
quickSort(A, si, pi - 1);
quickSort(A, pi + 1, ei);
}
}
/*Driver code */
int main()
{
int arr1[] = { 11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7 };
int arr2[] = { 11, 3, 7, 1 };
int m = sizeof(arr1) / sizeof(arr1[0]);
int n = sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(arr2[0]);
if (isSubset(arr1, arr2, m, n))
cout << "arr2[] is subset of arr1[] ";
else
cout << "arr2[] is not a subset of arr1[] ";
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Shivi_Aggarwal
// C program to find whether an array
// is subset of another array
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdio.h>
/* Function prototypes */
void quickSort(int* arr, int si, int ei);
int binarySearch(int arr[], int low, int high, int x);
/* Return 1 if arr2[] is a subset of arr1[] */
bool isSubset(int arr1[], int arr2[], int m, int n)
{
int i = 0;
quickSort(arr1, 0, m - 1);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (binarySearch(arr1, 0, m - 1, arr2[i]) == -1)
return 0;
}
/* If we reach here then all elements of arr2[]
are present in arr1[] */
return 1;
}
/* FOLLOWING FUNCTIONS ARE ONLY FOR SEARCHING
AND SORTING PURPOSE */
/* Standard Binary Search function*/
int binarySearch(int arr[], int low, int high, int x)
{
if (high >= low) {
/*low + (high - low)/2;*/
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
/* Check if arr[mid] is the first
occurrence of x.
arr[mid] is first occurrence if x is
one of the following
is true:
(i) mid == 0 and arr[mid] == x
(ii) arr[mid-1] < x and arr[mid] == x
*/
if ((mid == 0 || x > arr[mid - 1])
&& (arr[mid] == x))
return mid;
else if (x > arr[mid])
return binarySearch(arr, (mid + 1), high, x);
else
return binarySearch(arr, low, (mid - 1), x);
}
return -1;
}
void exchange(int* a, int* b)
{
int temp;
temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
int partition(int A[], int si, int ei)
{
int x = A[ei];
int i = (si - 1);
int j;
for (j = si; j <= ei - 1; j++) {
if (A[j] <= x) {
i++;
exchange(&A[i], &A[j]);
}
}
exchange(&A[i + 1], &A[ei]);
return (i + 1);
}
/* Implementation of Quick Sort
A[] --> Array to be sorted
si --> Starting index
ei --> Ending index
*/
void quickSort(int A[], int si, int ei)
{
int pi; /* Partitioning index */
if (si < ei) {
pi = partition(A, si, ei);
quickSort(A, si, pi - 1);
quickSort(A, pi + 1, ei);
}
}
/*Driver code */
int main()
{
int arr1[] = { 11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7 };
int arr2[] = { 11, 3, 7, 1 };
int m = sizeof(arr1) / sizeof(arr1[0]);
int n = sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(arr2[0]);
if (isSubset(arr1, arr2, m, n))
printf("arr2[] is subset of arr1[] ");
else
printf("arr2[] is not a subset of arr1[] ");
return 0;
}
// Java program to find whether an array
// is subset of another array
class Main {
/* Return true if arr2[] is a subset of arr1[] */
static boolean isSubset(int arr1[], int arr2[], int m,
int n)
{
int i = 0;
sort(arr1, 0, m - 1);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (binarySearch(arr1, 0, m - 1, arr2[i]) == -1)
return false;
}
/* If we reach here then all elements of arr2[]
are present in arr1[] */
return true;
}
/* FOLLOWING FUNCTIONS ARE ONLY
FOR SEARCHING AND
* SORTING PURPOSE */
/* Standard Binary Search function*/
static int binarySearch(int arr[], int low, int high,
int x)
{
if (high >= low) {
/*low + (high - low)/2;*/
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
/* Check if arr[mid] is the first occurrence of
x. arr[mid] is first occurrence if x is one of
the following is true: (i) mid == 0 and
arr[mid] == x (ii) arr[mid-1] < x and arr[mid]
== x
*/
if ((mid == 0 || x > arr[mid - 1])
&& (arr[mid] == x))
return mid;
else if (x > arr[mid])
return binarySearch(arr, (mid + 1), high,
x);
else
return binarySearch(arr, low, (mid - 1), x);
}
return -1;
}
/* This function takes last element as pivot,
places the pivot element at its correct
position in sorted array, and places all
smaller (smaller than pivot) to left of
pivot and all greater elements to right
of pivot */
static int partition(int arr[], int low, int high)
{
int pivot = arr[high];
int i = (low - 1);
for (int j = low; j < high; j++) {
// If current element is smaller than or
// equal to pivot
if (arr[j] <= pivot) {
i++;
// swap arr[i] and arr[j]
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
// swap arr[i+1] and arr[high] (or pivot)
int temp = arr[i + 1];
arr[i + 1] = arr[high];
arr[high] = temp;
return i + 1;
}
/* The main function that implements QuickSort()
arr[] --> Array to be sorted,
low --> Starting index,
high --> Ending index */
static void sort(int arr[], int low, int high)
{
if (low < high) {
/* pi is partitioning index, arr[pi] is
now at right place */
int pi = partition(arr, low, high);
// Recursively sort elements before
// partition and after partition
sort(arr, low, pi - 1);
sort(arr, pi + 1, high);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr1[] = { 11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7 };
int arr2[] = { 11, 3, 7, 1 };
int m = arr1.length;
int n = arr2.length;
if (isSubset(arr1, arr2, m, n))
System.out.print("arr2[] is subset of arr1[] ");
else
System.out.print(
"arr2[] is not a subset of arr1[]");
}
}
// C# program to find whether an array
// is subset of another array
using System;
public class GFG {
/* Return true if arr2[] is a subset of arr1[] */
static bool isSubset(int[] arr1, int[] arr2, int m,
int n)
{
int i = 0;
sort(arr1, 0, m - 1);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (binarySearch(arr1, 0, m - 1, arr2[i]) == -1)
return false;
}
/* If we reach here then all elements of arr2[]
are present in arr1[] */
return true;
}
/* FOLLOWING FUNCTIONS ARE ONLY FOR SEARCHING AND
* SORTING PURPOSE */
/* Standard Binary Search function*/
static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int low, int high,
int x)
{
if (high >= low) {
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
/* Check if arr[mid] is the first
occurrence of x.
arr[mid] is first occurrence if x
is one of the following
is true:
(i) mid == 0 and arr[mid] == x
(ii) arr[mid-1] < x and arr[mid] == x
*/
if ((mid == 0 || x > arr[mid - 1])
&& (arr[mid] == x))
return mid;
else if (x > arr[mid])
return binarySearch(arr, (mid + 1), high,
x);
else
return binarySearch(arr, low, (mid - 1), x);
}
return -1;
}
/* This function takes last element as pivot,
places the pivot element at its correct
position in sorted array, and places all
smaller (smaller than pivot) to left of
pivot and all greater elements to right
of pivot */
static int partition(int[] arr, int low, int high)
{
int pivot = arr[high];
int i = (low - 1);
int temp = 0;
for (int j = low; j < high; j++) {
// If current element is smaller than or
// equal to pivot
if (arr[j] <= pivot) {
i++;
// swap arr[i] and arr[j]
temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
// swap arr[i+1] and arr[high] (or pivot)
temp = arr[i + 1];
arr[i + 1] = arr[high];
arr[high] = temp;
return i + 1;
}
/* The main function that implements QuickSort()
arr[] --> Array to be sorted,
low --> Starting index,
high --> Ending index */
static void sort(int[] arr, int low, int high)
{
if (low < high) {
/* pi is partitioning index, arr[pi] is
now at right place */
int pi = partition(arr, low, high);
// Recursively sort elements before
// partition and after partition
sort(arr, low, pi - 1);
sort(arr, pi + 1, high);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr1 = { 11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7 };
int[] arr2 = { 11, 3, 7, 1 };
int m = arr1.Length;
int n = arr2.Length;
if (isSubset(arr1, arr2, m, n))
Console.Write("arr2[] is subset of arr1[] ");
else
Console.Write(
"arr2[] is not a subset of arr1[]");
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
<script>
// Javascript program to find whether an array
// is subset of another array
// Return true if arr2[] is a subset of arr1[]
function isSubset(arr1, arr2, m, n)
{
let i = 0;
sort(arr1, 0, m - 1);
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (binarySearch(arr1, 0, m - 1,
arr2[i]) == -1)
return false;
}
// If we reach here then all elements
// of arr2[] are present in arr1[]
return true;
}
/* FOLLOWING FUNCTIONS ARE ONLY
FOR SEARCHING AND
* SORTING PURPOSE */
/* Standard Binary Search function*/
function binarySearch(arr, low, high, x)
{
if (high >= low)
{
// low + (high - low)/2;
let mid = Math.floor((low + high) / 2);
// Check if arr[mid] is the first occurrence of
// x. arr[mid] is first occurrence if x is one of
// the following is true: (i) mid == 0 and
// arr[mid] == x (ii) arr[mid-1] < x and arr[mid] == x
if ((mid == 0 || x > arr[mid - 1]) &&
(arr[mid] == x))
return mid;
else if (x > arr[mid])
return binarySearch(arr, (mid + 1),
high, x);
else
return binarySearch(arr, low,
(mid - 1), x);
}
return -1;
}
/* This function takes last element as pivot,
places the pivot element at its correct
position in sorted array, and places all
smaller (smaller than pivot) to left of
pivot and all greater elements to right
of pivot */
function partition(arr, low, high)
{
let pivot = arr[high];
let i = (low - 1);
for(let j = low; j < high; j++)
{
// If current element is smaller than or
// equal to pivot
if (arr[j] <= pivot)
{
i++;
// Swap arr[i] and arr[j]
let temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
// Swap arr[i+1] and arr[high] (or pivot)
let temp = arr[i + 1];
arr[i + 1] = arr[high];
arr[high] = temp;
return i + 1;
}
/* The main function that implements QuickSort()
arr[] --> Array to be sorted,
low --> Starting index,
high --> Ending index */
function sort(arr,low,high)
{
if (low < high)
{
// pi is partitioning index, arr[pi]
// is now at right place
let pi = partition(arr, low, high);
// Recursively sort elements before
// partition and after partition
sort(arr, low, pi - 1);
sort(arr, pi + 1, high);
}
}
// Driver Code
let arr1 = [ 11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7 ];
let arr2 = [ 11, 3, 7, 1 ];
let m = arr1.length;
let n = arr2.length;
if (isSubset(arr1, arr2, m, n))
document.write("arr2[] is subset of arr1[] ");
else
document.write("arr2[] is not a subset of arr1[]");
// This code is contributed by patel2127
</script>
<?php
// PHP program to find whether an array
// is subset of another array
/* Return 1 if arr2[] is a subset of arr1[] */
function isSubset($arr1, $arr2,
$m, $n)
{
$i = 0;
quickSort($arr1, 0, $m-1);
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++)
{
if (binarySearch($arr1, 0, $m - 1,
$arr2[$i]) == -1)
return 0;
}
/* If we reach here then all elements
of arr2[] are present in arr1[] */
return 1;
}
/* FOLLOWING FUNCTIONS ARE ONLY FOR
SEARCHING AND SORTING PURPOSE */
/* Standard Binary Search function*/
function binarySearch($arr, $low, $high, $x)
{
if($high >= $low)
{
$mid = (int)(($low + $high)/2);
/* Check if arr[mid] is the first
occurrence of x.
arr[mid] is first occurrence if
x is one of the following
is true:
(i) mid == 0 and arr[mid] == x
(ii) arr[mid-1] < x and arr[mid] == x */
if(( $mid == 0 || $x > $arr[$mid-1])
&& ($arr[$mid] == $x))
return $mid;
else if($x > $arr[$mid])
return binarySearch($arr,
($mid + 1), $high, $x);
else
return binarySearch($arr,
$low, ($mid -1), $x);
}
return -1;
}
function exchange(&$a, &$b)
{
$temp = $a;
$a = $b;
$b = $temp;
}
function partition(&$A, $si, $ei)
{
$x = $A[$ei];
$i = ($si - 1);
for ($j = $si; $j <= $ei - 1; $j++)
{
if($A[$j] <= $x)
{
$i++;
exchange($A[$i], $A[$j]);
}
}
exchange ($A[$i + 1], $A[$ei]);
return ($i + 1);
}
/* Implementation of Quick Sort
A[] --> Array to be sorted
si --> Starting index
ei --> Ending index
*/
function quickSort(&$A, $si, $ei)
{
/* Partitioning index */
if($si < $ei)
{
$pi = partition($A, $si, $ei);
quickSort($A, $si, $pi - 1);
quickSort($A, $pi + 1, $ei);
}
}
/*Driver code */
$arr1 = array(11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7);
$arr2 = array(11, 3, 7, 1);
$m = count($arr1);
$n = count($arr2);
if(isSubset($arr1, $arr2, $m, $n))
echo "arr2[] is subset of arr1[] ";
else
echo "arr2[] is not a subset of arr1[] ";
// This code is contributed by chandan_jnu
?>
# Python3 program to find whether an array
# is subset of another array
# Return 1 if arr2[] is a subset of arr1[]
def isSubset(arr1, arr2, m, n):
i = 0
quickSort(arr1, 0, m-1)
for i in range(n):
if (binarySearch(arr1, 0, m - 1, arr2[i]) == -1):
return 0
# If we reach here then all elements
# of arr2[] are present in arr1[]
return 1
# FOLLOWING FUNCTIONS ARE ONLY FOR
# SEARCHING AND SORTING PURPOSE
# Standard Binary Search function
def binarySearch(arr, low, high, x):
if(high >= low):
mid = (low + high)//2
# Check if arr[mid] is the first
# occurrence of x.
# arr[mid] is first occurrence if x is
# one of the following
# is true:
# (i) mid == 0 and arr[mid] == x
# (ii) arr[mid-1] < x and arr[mid] == x
if((mid == 0 or x > arr[mid-1]) and (arr[mid] == x)):
return mid
elif(x > arr[mid]):
return binarySearch(arr, (mid + 1), high, x)
else:
return binarySearch(arr, low, (mid - 1), x)
return -1
def partition(A, si, ei):
x = A[ei]
i = (si - 1)
for j in range(si, ei):
if(A[j] <= x):
i += 1
A[i], A[j] = A[j], A[i]
A[i + 1], A[ei] = A[ei], A[i + 1]
return (i + 1)
# Implementation of Quick Sort
# A[] --> Array to be sorted
# si --> Starting index
# ei --> Ending index
def quickSort(A, si, ei):
# Partitioning index
if(si < ei):
pi = partition(A, si, ei)
quickSort(A, si, pi - 1)
quickSort(A, pi + 1, ei)
# Driver code
arr1 = [11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7]
arr2 = [11, 3, 7, 1]
m = len(arr1)
n = len(arr2)
if(isSubset(arr1, arr2, m, n)):
print("arr2[] is subset of arr1[] ")
else:
print("arr2[] is not a subset of arr1[] ")
# This code is contributed by chandan_jnu
Outputarr2[] is subset of arr1[]
Time Complexity: O(mLog(m) + nlog(m)). O(mLog(m)) for sorting and O(nlog(m)) for binary searching each element of one array in another. In the above code, Quick Sort is used and the worst-case time complexity of Quick Sort is O(m2).
Auxiliary Space: O(n)
Find whether an array is subset of another array using Sorting and Merging
The idea is to sort the two arrays and then iterate on the second array looking for the same values on the first array using two pointers. Whenever we encounter the same values we will increment both the pointer and if we encounter any values less than that of the second array, we will increment the value of the pointer pointing to the first array. If the value is greater than that of the second array, we know the second array is not the subset of the first array.
Illustration:

Algorithm:
The initial step will be to sort the two arrays.
- Set two pointers j and i for arr1[] and arr2[] respectively.
- If arr1[j] < arr2[i], we will increase j by 1.
- If arr1[j] = arr2[i], we will increase j and i by 1.
- If arr1[j] > arr2[i], we will terminate as arr2[] is not the subset of arr1[].
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// C++ program to find whether an array
// is subset of another array
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/* Return 1 if arr2[] is a subset of arr1[] */
bool isSubset(int arr1[], int arr2[], int m, int n)
{
int i = 0, j = 0;
if (m < n)
return 0;
// Sort both the arrays
sort(arr1, arr1 + m);
sort(arr2, arr2 + n);
// Iterate till they do not exceed their sizes
while (i < n && j < m) {
// If the element is smaller then
// Move ahead in the first array
if (arr1[j] < arr2[i])
j++;
// If both are equal, then move
// both of them forward
else if (arr1[j] == arr2[i]) {
j++;
i++;
}
// If we do not have an element smaller
// or equal to the second array then break
else if (arr1[j] > arr2[i])
return 0;
}
return (i < n) ? false : true;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr1[] = { 11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7 };
int arr2[] = { 11, 3, 7, 1 };
int m = sizeof(arr1) / sizeof(arr1[0]);
int n = sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(arr2[0]);
if (isSubset(arr1, arr2, m, n))
printf("arr2[] is subset of arr1[] ");
else
printf("arr2[] is not a subset of arr1[] ");
return 0;
}
// C program to find whether an array
// is subset of another array
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Merges two subarrays of arr[].
// First subarray is arr[l..m]
// Second subarray is arr[m+1..r]
void merge(int arr[], int l, int m, int r)
{
int i, j, k;
int n1 = m - l + 1;
int n2 = r - m;
/* create temp arrays */
int L[n1], R[n2];
/* Copy data to temp arrays L[] and R[] */
for (i = 0; i < n1; i++)
L[i] = arr[l + i];
for (j = 0; j < n2; j++)
R[j] = arr[m + 1 + j];
/* Merge the temp arrays back into arr[l..r]*/
i = 0; // Initial index of first subarray
j = 0; // Initial index of second subarray
k = l; // Initial index of merged subarray
while (i < n1 && j < n2) {
if (L[i] <= R[j]) {
arr[k] = L[i];
i++;
}
else {
arr[k] = R[j];
j++;
}
k++;
}
/* Copy the remaining elements of L[], if there
are any */
while (i < n1) {
arr[k] = L[i];
i++;
k++;
}
/* Copy the remaining elements of R[], if there
are any */
while (j < n2) {
arr[k] = R[j];
j++;
k++;
}
}
/* l is for left index and r is right index of the
sub-array of arr to be sorted */
void mergeSort(int arr[], int l, int r)
{
if (l < r) {
// Same as (l+r)/2, but avoids overflow for
// large l and h
int m = l + (r - l) / 2;
// Sort first and second halves
mergeSort(arr, l, m);
mergeSort(arr, m + 1, r);
merge(arr, l, m, r);
}
}
/* Return 1 if arr2[] is a subset of arr1[] */
int isSubset(int arr1[], int arr2[], int m, int n)
{
int i = 0, j = 0;
if (m < n)
return 0;
// Sort both the arrays
mergeSort(arr1, 0, m - 1);
mergeSort(arr2, 0, n - 1);
// Iterate till they do not exceed their sizes
while (i < n && j < m) {
// If the element is smaller then
// Move ahead in the first array
if (arr1[j] < arr2[i])
j++;
// If both are equal, then move
// both of them forward
else if (arr1[j] == arr2[i]) {
j++;
i++;
}
// If we do not have an element smaller
// or equal to the second array then break
else if (arr1[j] > arr2[i])
return 0;
}
return (i < n) ? 0 : 1;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr1[] = { 11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7 };
int arr2[] = { 11, 3, 7, 1 };
int m = sizeof(arr1) / sizeof(arr1[0]);
int n = sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(arr2[0]);
if (isSubset(arr1, arr2, m, n))
printf("arr2[] is subset of arr1[] ");
else
printf("arr2[] is not a subset of arr1[] ");
return 0;
}
// Java code to find whether an array is subset of
// another array
import java.util.Arrays;
class GFG {
/* Return true if arr2[] is a subset of arr1[] */
static boolean isSubset(int arr1[], int arr2[], int m,
int n)
{
int i = 0, j = 0;
if (m < n)
return false;
Arrays.sort(arr1); // sorts arr1
Arrays.sort(arr2); // sorts arr2
while (i < n && j < m) {
if (arr1[j] < arr2[i])
j++;
else if (arr1[j] == arr2[i]) {
j++;
i++;
}
else if (arr1[j] > arr2[i])
return false;
}
if (i < n)
return false;
else
return true;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr1[] = { 11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7 };
int arr2[] = { 11, 3, 7, 1 };
int m = arr1.length;
int n = arr2.length;
if (isSubset(arr1, arr2, m, n))
System.out.println("arr2[] is subset of arr1[] ");
else
System.out.println(
"arr2[] is not a subset of arr1[] ");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Kamal Rawal
// C# code to find whether an array
// is subset of another array
using System;
class GFG {
// Return true if arr2[] is
// a subset of arr1[] */
static bool isSubset(int[] arr1, int[] arr2, int m,
int n)
{
int i = 0, j = 0;
if (m < n)
return false;
// sorts arr1
Array.Sort(arr1);
// sorts arr2
Array.Sort(arr2);
while (i < n && j < m) {
if (arr1[j] < arr2[i])
j++;
else if (arr1[j] == arr2[i]) {
j++;
i++;
}
else if (arr1[j] > arr2[i])
return false;
}
if (i < n)
return false;
else
return true;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr1 = { 11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7 };
int[] arr2 = { 11, 3, 7, 1 };
int m = arr1.Length;
int n = arr2.Length;
if (isSubset(arr1, arr2, m, n))
Console.Write("arr2[] is subset of arr1[] ");
else
Console.Write("arr2[] is not a subset of arr1[] ");
}
}
// This code is contributed by nitin mittal.
<script>
// JavaScript program to find whether an array
// is subset of another array
// Return 1 if arr2[] is a subset of arr1[]
function isSubset(arr1, arr2, m, n)
{
let i = 0, j = 0;
if (m < n)
return 0;
// Sort both the arrays
arr1.sort((a, b) => a - b);
arr2.sort((a, b) => a - b);
// Iterate till they do not exceed their sizes
while (i < n && j < m)
{
// If the element is smaller then
// Move ahead in the first array
if (arr1[j] < arr2[i])
j++;
// If both are equal, then move
// both of them forward
else if (arr1[j] == arr2[i])
{
j++;
i++;
}
// If we do not have an element smaller
// or equal to the second array then break
else if (arr1[j] > arr2[i])
return 0;
}
return (i < n) ? false : true;
}
// Driver Code
let arr1 = [ 11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7 ];
let arr2 = [ 11, 3, 7, 1 ];
let m = arr1.length;
let n = arr2.length;
if (isSubset(arr1, arr2, m, n))
document.write("arr2[] is subset of arr1[] ");
else
document.write("arr2[] is not a subset of arr1[] ");
// This code is contributed by Manoj.
</script>
<?php
// PHP program to find whether an array
// is subset of another array
/* Return 1 if arr2[] is a subset of arr1[] */
function isSubset( $arr1, $arr2, $m, $n)
{
$i = 0; $j = 0;
if ($m < $n)
return 0;
sort($arr1);
sort($arr2);
while ($i < $n and $j < $m )
{
if( $arr1[$j] <$arr2[$i] )
$j++;
else if( $arr1[$j] == $arr2[$i] )
{
$j++;
$i++;
}
else if( $arr1[$j] > $arr2[$i] )
return 0;
}
return ($i < $n) ? false : true;
}
/*Driver code */
$arr1 = array(11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7);
$arr2 = array(11, 3, 7, 1);
$m = count($arr1);
$n = count($arr2);
if(isSubset($arr1, $arr2, $m, $n))
echo "arr2[] is subset of arr1[] ";
else
echo "arr2[] is not a subset of arr1[] ";
// This code is contributed by anuj_67.
?>
# Python3 program to find whether an array
# is subset of another array
# Return 1 if arr2[] is a subset of arr1[] */
def isSubset(arr1, arr2, m, n):
i = 0
j = 0
if m < n:
return 0
arr1.sort()
arr2.sort()
while i < n and j < m:
if arr1[j] < arr2[i]:
j += 1
elif arr1[j] == arr2[i]:
j += 1
i += 1
elif arr1[j] > arr2[i]:
return 0
return False if i < n else True
# Driver code
arr1 = [11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7]
arr2 = [11, 3, 7, 1]
m = len(arr1)
n = len(arr2)
if isSubset(arr1, arr2, m, n) == True:
print("arr2[] is subset of arr1[] ")
else:
printf("arr2[] is not a subset of arr1[] ")
# This code is contributed by Shrikant13
Outputarr2[] is subset of arr1[]
Time Complexity: O(mLog(m) + nLog(n)) which is better than approach 2.
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Thanks to Parthsarthi for suggesting this method.
Find whether an array is a subset of another array using Hashing
The idea is to insert all the elements of the first array in a HashSet, and then iterate on the second array and find if the element exists in the HashSet, if the HashSet doesn’t contain any particular value then the second array is not the subset of the first array.
Note: This approach works perfectly if there are no duplicate elements.
Illustration:
Given array arr1[] = { 11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7 } and arr2[] = { 11, 3, 7, 1 }.
Step 1: We will store the array arr1[] elements in HashSet
Step 2: We will look for each element in arr2[] in arr1[] using binary search.
- arr2[] = { 11, 3, 7, 1 }, 11 is present in the HashSet = { 1, 3, 7, 11, 13, 21}
- arr2[] = { 11, 3, 7, 1 }, 3 is present in the HashSet = { 1, 3, 7, 11, 13, 21}
- arr2[] = { 11, 3, 7, 1 }, 7 is present in the HashSet = { 1, 3, 7, 11, 13, 21}
- arr2[] = { 11, 3, 7, 1 }, 1 is present in the HashSet = { 1, 3, 7, 11, 13, 21}
As all the elements are found we can conclude arr2[] is the subset of arr1[].
Algorithm:
The algorithm is pretty straightforward.
- Store the first array arr1[] in a HashSet.
- Look for the elements of arr2[] in the HashSet.
- If we encounter a particular value that is present in arr2[] but not in the HashSet, the code will terminate, arr2[] can never be the subset of arr1[].
- Else arr2[] is the subset of arr1[].
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// C++ code to find whether an array is subset of
// another array
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/* Return true if arr2[] is a subset of arr1[] */
bool isSubset(int arr1[], int m, int arr2[], int n)
{
// Using STL set for hashing
set<int> hashset;
// hashset stores all the values of arr1
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
hashset.insert(arr1[i]);
}
// loop to check if all elements of arr2 also
// lies in arr1
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (hashset.find(arr2[i]) == hashset.end())
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr1[] = { 11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7 };
int arr2[] = { 11, 3, 7, 1 };
int m = sizeof(arr1) / sizeof(arr1[0]);
int n = sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(arr2[0]);
if (isSubset(arr1, m, arr2, n))
cout << "arr2[] is subset of arr1[] "
<< "\n";
else
cout << "arr2[] is not a subset of arr1[] "
<< "\n";
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Satvik Shrivas
// Java code to find whether an array is subset of
// another array
import java.util.HashSet;
class GFG {
/* Return true if arr2[] is a subset of arr1[] */
static boolean isSubset(int arr1[], int arr2[], int m,
int n)
{
HashSet<Integer> hset = new HashSet<>();
// hset stores all the values of arr1
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (!hset.contains(arr1[i]))
hset.add(arr1[i]);
}
// loop to check if all elements
// of arr2 also lies in arr1
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!hset.contains(arr2[i]))
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr1[] = { 11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7 };
int arr2[] = { 11, 3, 7, 1 };
int m = arr1.length;
int n = arr2.length;
if (isSubset(arr1, arr2, m, n))
System.out.println("arr2[] is subset of arr1[] ");
else
System.out.println(
"arr2[] is not a subset of arr1[] ");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Kamal Rawal
# Python3 program to find whether an array
# is subset of another array
# Return true if arr2[] is a subset
# of arr1[]
def isSubset(arr1, m, arr2, n):
# Using STL set for hashing
hashset = set()
# hset stores all the values of arr1
for i in range(0, m):
hashset.add(arr1[i])
# Loop to check if all elements
# of arr2 also lies in arr1
for i in range(0, n):
if arr2[i] in hashset:
continue
else:
return False
return True
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr1 = [11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7]
arr2 = [11, 3, 7, 1]
m = len(arr1)
n = len(arr2)
if (isSubset(arr1, m, arr2, n)):
print("arr2[] is subset of arr1[] ")
else:
print("arr2[] is not a subset of arr1[] ")
# This code is contributed by akhilsaini
<script>
// Javascript code to find whether an
// array is subset of another array
// Return true if arr2[] is a
// subset of arr1[]
function isSubset(arr1, arr2, m, n)
{
let hset = new Set();
// hset stores all the values of arr1
for(let i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
if (!hset.has(arr1[i]))
hset.add(arr1[i]);
}
// Loop to check if all elements
// of arr2 also lies in arr1
for(let i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (!hset.has(arr2[i]))
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Driver Code
let arr1 = [ 11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7 ];
let arr2 = [ 11, 3, 7, 1 ];
let m = arr1.length;
let n = arr2.length;
if (isSubset(arr1, arr2, m, n))
document.write("arr2 is a subset of arr1");
else
document.write("arr2 is not a subset of arr1");
// This code is contributed by unknown2108
</script>
<?php
// function to check if arr2[] is a subset of arr1[]
function isSubset($arr1, $arr2) {
// use array_flip to speed up the search
$hashset = array_flip($arr1);
// loop through arr2 and check if all elements
// also lies in arr1
foreach ($arr2 as $elem) {
if (!isset($hashset[$elem])) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// test the function
$arr1 = array(11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7);
$arr2 = array(11, 3, 7, 1);
if (isSubset($arr1, $arr2)) {
echo "arr2[] is a subset of arr1[]\n";
} else {
echo "arr2[] is not a subset of arr1[]\n";
}
# Python3 program to find whether an array
# is subset of another array
# Return true if arr2[] is a subset
# of arr1[]
def isSubset(arr1, m, arr2, n):
# Using STL set for hashing
hashset = set()
# hset stores all the values of arr1
for i in range(0, m):
hashset.add(arr1[i])
# Loop to check if all elements
# of arr2 also lies in arr1
for i in range(0, n):
if arr2[i] in hashset:
continue
else:
return False
return True
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr1 = [11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7]
arr2 = [11, 3, 7, 1]
m = len(arr1)
n = len(arr2)
if (isSubset(arr1, m, arr2, n)):
print("arr2[] is subset of arr1[] ")
else:
print("arr2[] is not a subset of arr1[] ")
# This code is contributed by akhilsaini
Outputarr2[] is subset of arr1[]
Time Complexity: O(m+n)
Auxiliary Space: O(m)
Find whether an array is a subset of another array using Set
The idea is to insert all the elements of the first array and second array in the set, if the size of the set is equal to the size of arr1[] then the arr2[] is the subset of arr1[]. As no new elements are found in arr2[] hence is the subset.
Note: This approach works perfectly if there are no duplicate elements.
Illustration:
Given array arr1[] = { 11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7 } and arr2[] = { 11, 3, 7, 1 }.
Step 1: We will store the array arr1[] and arr2[] elements in Set
- The final Set = { 1, 3, 7, 11, 13, 21}
Step 2: Size of arr1[] = 6 and size of the Set = 6
- Hence no new elements are found in arr2[]
As all the elements are found we can conclude arr2[] is the subset of arr1[].
Algorithm:
The algorithm is pretty straightforward.
- Store the first array arr1[] in a Set.
- Store the first array arr1[] in the same Set.
- If the size of arr1[] = size of the Set, arr2[] is the subset of arr1[].
- Else arr2[] is not the subset of arr1[].
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// code
int arr1[] = { 11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7 };
int arr2[] = { 11, 3, 7, 1 };
int m = sizeof(arr1) / sizeof(arr1[0]);
int n = sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(arr2[0]);
unordered_set<int> s;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
s.insert(arr1[i]);
}
int p = s.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
s.insert(arr2[i]);
}
if (s.size() == p) {
cout << "arr2[] is subset of arr1[] "
<< "\n";
}
else {
cout << "arr2[] is not subset of arr1[] "
<< "\n";
}
return 0;
}
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr1[] = { 11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7 };
int arr2[] = { 11, 3, 7, 1 };
int m = arr1.length;
int n = arr2.length;
Set<Integer> s = new HashSet<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
s.add(arr1[i]);
}
int p = s.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
s.add(arr2[i]);
}
if (s.size() == p) {
System.out.println("arr2[] is subset of arr1[] "
+ "\n");
}
else {
System.out.println(
"arr2[] is not subset of arr1[] "
+ "\n");
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG {
static public void Main()
{
int[] arr1 = { 11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7 };
int[] arr2 = { 11, 3, 7, 1 };
int m = arr1.Length;
int n = arr2.Length;
HashSet<int> s = new HashSet<int>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
s.Add(arr1[i]);
}
int p = s.Count;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
s.Add(arr2[i]);
}
if (s.Count == p) {
Console.WriteLine("arr2[] is subset of arr1[] "
+ "\n");
}
else {
Console.WriteLine(
"arr2[] is not subset of arr1[] "
+ "\n");
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by rag2127
<script>
let arr1=[11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7];
let arr2=[11, 3, 7, 1 ];
let m=arr1.length;
let n=arr2.length;
let s = new Set();
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
s.add(arr1[i]);
}
let p = s.size;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
s.add(arr2[i]);
}
if (s.size == p)
{
document.write("arr2[] is subset of arr1[] " + "<br>");
}
else
{
document.write("arr2[] is not subset of arr1[] " + "<br>" );
}
// This code is contributed by ab2127
</script>
# Python3 code
arr1 = [11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7]
arr2 = [11, 3, 7, 1]
m = len(arr1)
n = len(arr2)
s = set()
for i in range(m):
s.add(arr1[i])
p = len(s)
for i in range(n):
s.add(arr2[i])
if (len(s) == p):
print("arr2[] is subset of arr1[] ")
else:
print("arr2[] is not subset of arr1[] ")
# This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07.
Outputarr2[] is subset of arr1[]
Time Complexity: O(m+n) because we are using unordered_set and inserting in it, If we would be using an ordered set inserting would have taken log n increasing the TC to O(mlogm+nlogn), but order does not matter in this approach.
Auxiliary Space: O(n+m)
Find whether an array is a subset of another array using the Frequency Table
The idea is to store the frequency of the elements present in the first array, then look for the elements present in arr2[] in the frequency array. As no new elements are found in arr2[] hence is the subset.
Illustration:
Given array arr1[] = { 11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7 } and arr2[] = { 11, 3, 7, 1 }.
Step 1: We will store the array arr1[] elements frequency in the frequency array
- The frequency array will look like this
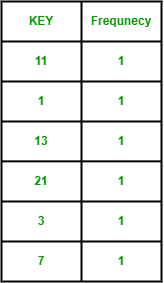
frequency array
Step 2: We will look for arr2[] elements in the frequency array.
- arr2[] = { 11, 3, 7, 1 }, 11 is present in the frequency array
- arr2[] = { 11, 3, 7, 1 }, 3 is present in the frequency array
- arr2[] = { 11, 3, 7, 1 }, 7 is present in the frequency array
- arr2[] = { 11, 3, 7, 1 }, 1 is present in the frequency array
As all the elements are found we can conclude arr2[] is the subset of arr1[].
Algorithm:
The algorithm is pretty straightforward.
- Store the frequency of the first array elements of arr1[] in the frequency array.
- Iterate on the arr2[] and look for its elements in the frequency array.
- If the value is found in the frequency array reduce the frequency value by one.
- If for any elements in arr2[] frequency is less than 1, we will conclude arr2[] is not the subset of arr1[],
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
Java
// Java program to find whether an array
// is subset of another array
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Return true if arr2[] is a subset of arr1[]
static boolean isSubset(int[] arr1, int m, int[] arr2,
int n)
{
// Create a Frequency Table using STL
HashMap<Integer, Integer> frequency
= new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
// Increase the frequency of each element
// in the frequency table.
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
frequency.put(arr1[i],
frequency.getOrDefault(arr1[i], 0)
+ 1);
}
// Decrease the frequency if the
// element was found in the frequency
// table with the frequency more than 0.
// else return 0 and if loop is
// completed return 1.
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (frequency.getOrDefault(arr2[i], 0) > 0)
frequency.put(arr2[i],
frequency.get(arr1[i]) - 1);
else {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] arr1 = { 11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7 };
int[] arr2 = { 11, 3, 7, 1 };
int m = arr1.length;
int n = arr2.length;
if (isSubset(arr1, m, arr2, n))
System.out.println(
"arr2[] is subset of arr1[] ");
else
System.out.println(
"arr2[] is not a subset of arr1[] ");
}
}
// This code is contributed by akhilsaini
// C# program to find whether an array
// is subset of another array
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
// Return true if arr2[] is a subset of arr1[]
static bool isSubset(int[] arr1, int m, int[] arr2,
int n)
{
// Create a Frequency Table using STL
Dictionary<int, int> frequency
= new Dictionary<int, int>();
// Increase the frequency of each element
// in the frequency table.
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (frequency.ContainsKey(arr1[i]))
frequency[arr1[i]] += 1;
else
frequency[arr1[i]] = 1;
}
// Decrease the frequency if the
// element was found in the frequency
// table with the frequency more than 0.
// else return 0 and if loop is
// completed return 1.
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (frequency[arr2[i]] > 0)
frequency[arr2[i]] -= 1;
else {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr1 = { 11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7 };
int[] arr2 = { 11, 3, 7, 1 };
int m = arr1.Length;
int n = arr2.Length;
if (isSubset(arr1, m, arr2, n))
Console.WriteLine(
"arr2[] is subset of arr1[] ");
else
Console.WriteLine(
"arr2[] is not a subset of arr1[] ");
}
}
// This code is contributed by akhilsaini
<script>
// javascript program to find whether an array
// is subset of another array
/* Return true if arr2[] is a subset of arr1[] */
function isSubset(arr1,m,arr2,n)
{
// Create a Frequency Table using STL
let frequency = new Array(arr1);
// Increase the frequency of each element
// in the frequency table.
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
frequency[arr1[i]]++;
}
// Decrease the frequency if the
// element was found in the frequency
// table with the frequency more than 0.
// else return 0 and if loop is
// completed return 1.
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (frequency[arr2[i]] > 0)
frequency[arr2[i]]--;
else
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// Driver Code
let arr1 = [11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7 ];
let arr2 = [ 11, 3, 7, 1 ];
let m = arr1.length;
let n = arr2.length;
if (isSubset(arr1, m, arr2, n))
document.write("arr2[] is subset of arr1[] "
+ "\n");
else
document.write("arr2[] is not a subset of arr1[] "
+ "\n");
// This code is contributed by vaibhavrabadiya117.
</script>
// C++ program to find whether an array
// is subset of another array
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/* Return true if arr2[] is a subset of arr1[] */
bool isSubset(int arr1[], int m, int arr2[], int n)
{
// Create a Frequency Table using STL
map<int, int> frequency;
// Increase the frequency of each element
// in the frequency table.
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
frequency[arr1[i]]++;
}
// Decrease the frequency if the
// element was found in the frequency
// table with the frequency more than 0.
// else return 0 and if loop is
// completed return 1.
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (frequency[arr2[i]] > 0)
frequency[arr2[i]]--;
else {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr1[] = { 11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7 };
int arr2[] = { 11, 3, 7, 1 };
int m = sizeof(arr1) / sizeof(arr1[0]);
int n = sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(arr2[0]);
if (isSubset(arr1, m, arr2, n))
cout << "arr2[] is subset of arr1[] "
<< "\n";
else
cout << "arr2[] is not a subset of arr1[] "
<< "\n";
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Dhawal Sarin.
# Python3 program to find whether an array
# is subset of another array
# Return true if arr2[] is a subset of arr1[]
def isSubset(arr1, m, arr2, n):
# Create a Frequency Table using STL
frequency = {}
# Increase the frequency of each element
# in the frequency table.
for i in range(0, m):
if arr1[i] in frequency:
frequency[arr1[i]] = frequency[arr1[i]] + 1
else:
frequency[arr1[i]] = 1
# Decrease the frequency if the
# element was found in the frequency
# table with the frequency more than 0.
# else return 0 and if loop is
# completed return 1.
for i in range(0, n):
if (frequency[arr2[i]] > 0):
frequency[arr2[i]] -= 1
else:
return False
return True
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr1 = [11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7]
arr2 = [11, 3, 7, 1]
m = len(arr1)
n = len(arr2)
if (isSubset(arr1, m, arr2, n)):
print("arr2[] is subset of arr1[] ")
else:
print("arr2[] is not a subset of arr1[] ")
# This code is contributed by akhilsaini
Outputarr2[] is subset of arr1[]
Time Complexity: O(m log (m+n)) which is better than methods 1,2,3
Auxiliary Space: O(m)
Note that method 1, method 2, method 4, and method 5 don’t handle the cases when we have duplicates in arr2[]. For example, {1, 4, 4, 2} is not a subset of {1, 4, 2}, but these methods will print it as a subset.
Please write comments if you find the above codes/algorithms incorrect, or find other ways to solve the same problem.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...