Find minimum area of rectangle with given set of coordinates
Last Updated :
17 Aug, 2022
Given an array 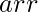 of set of points in the X-Y plane. The task is to find the minimum area of a rectangle that can be formed from these points. The sides of the rectangle should be parallel to the X and Y axes. If a rectangle cannot be formed with the given points then print
of set of points in the X-Y plane. The task is to find the minimum area of a rectangle that can be formed from these points. The sides of the rectangle should be parallel to the X and Y axes. If a rectangle cannot be formed with the given points then print 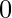 .
.
Examples:
Input: arr[][] = [[1, 1], [1, 3], [3, 1], [3, 3], [2, 2]]
Output: 4
The only rectangle possible will be formed with the points (1, 1), (1, 3), (3, 1) and (3, 3)
Input: arr[][] = [[1, 1], [1, 3], [3, 1], [3, 3], [4, 1], [4, 3]]
Output: 2
Approach: Group the points by 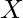 coordinates, so that points on straight vertical lines are grouped together. Then, for every pair of points in a group, for eg. coordinates (X, Y1) and (X, Y2), we check for the smallest rectangle with this pair of points as the rightmost edge of the rectangle to be formed. We can do this by keeping track of all other pairs of points we’ve visited before. Finally return the minimum possible area of the rectangle obtained.
coordinates, so that points on straight vertical lines are grouped together. Then, for every pair of points in a group, for eg. coordinates (X, Y1) and (X, Y2), we check for the smallest rectangle with this pair of points as the rightmost edge of the rectangle to be formed. We can do this by keeping track of all other pairs of points we’ve visited before. Finally return the minimum possible area of the rectangle obtained.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
CPP
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int minAreaRect(vector<vector<int>> A){
map<int,vector<int>> columns;
for(auto i:A)
columns[i[0]].push_back(i[1]);
map<pair<int,int>,int > lastx;
int ans = INT_MAX;
for (auto x:columns)
{
vector<int> column = x.second;
sort(column.begin(), column.end());
for (int j = 0; j < column.size(); j++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < j; i++)
{
int y1 = column[i];
if (lastx.find({y1, column[j]}) != lastx.end())
{
ans = min(ans, (x.first - lastx[{y1, column[j]}]) *
(column[j] - column[i]));
}
lastx[{y1, column[j]}] = x.first;
}
}
}
if (ans < INT_MAX)
return ans;
else
return 0;
}
int main()
{
vector<vector<int>> A = {{1, 1}, {1, 3}, {3, 1}, {3, 3}, {2, 2}};
cout << (minAreaRect(A));
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static int minAreaRect(int[][] points)
{
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Set<Integer> columns = new HashSet();
for (int[] point : points)
columns.add(40001 * point[0] + point[1]);
int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < points.length; ++i)
for (int j = i + 1; j < points.length; ++j) {
if (points[i][0] != points[j][0]
&& points[i][1] != points[j][1]) {
if (columns.contains(40001
* points[i][0]
+ points[j][1])
&& columns.contains(
40001 * points[j][0]
+ points[i][1])) {
ans = Math.min( ans, Math.abs(points[j][0]
- points[i][0])
* Math.abs(points[j][1]
- points[i][1]));
}
}
}
return ans < Integer.MAX_VALUE ? ans : 0;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[][] A = {{1, 1}, {1, 3}, {3, 1}, {3, 3}, {2, 2}};
System.out.println(minAreaRect(A));
}
}
|
Python
import collections
def minAreaRect(A):
columns = collections.defaultdict(list)
for x, y in A:
columns[x].append(y)
lastx = {}
ans = float('inf')
for x in sorted(columns):
column = columns[x]
column.sort()
for j, y2 in enumerate(column):
for i in range(j):
y1 = column[i]
if (y1, y2) in lastx:
ans = min(ans, (x - lastx[y1, y2]) * (y2 - y1))
lastx[y1, y2] = x
if ans < float('inf'):
return ans
else:
return 0
A = [[1, 1], [1, 3], [3, 1], [3, 3], [2, 2]]
print(minAreaRect(A))
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
public static int minAreaRect(int[, ] points)
{
HashSet<int> columns = new HashSet<int>();
for (int i = 0; i < points.GetLength(0); i++)
columns.Add(40001 * points[i, 0]
+ points[i, 1]);
int ans = Int32.MaxValue;
for (int i = 0; i < points.GetLength(0); ++i)
for (int j = i + 1; j < points.GetLength(0);
++j) {
if (points[i, 0] != points[j, 0]
&& points[i, 1] != points[j, 1]) {
if (columns.Contains(40001
* points[i, 0]
+ points[j, 1])
&& columns.Contains(
40001 * points[j, 0]
+ points[i, 1])) {
ans = Math.Min(
ans,
Math.Abs(points[j, 0]
- points[i, 0])
* Math.Abs(points[j, 1]
- points[i, 1]));
}
}
}
return ans < Int32.MaxValue ? ans : 0;
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[, ] A = {
{ 1, 1 }, { 1, 3 }, { 3, 1 }, { 3, 3 }, { 2, 2 }
};
Console.WriteLine(minAreaRect(A));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function minAreaRect(points)
{
let columns = new Set();
for (let point=0;point<points.length;point++)
columns.add(40001 * points[point][0] + points[point][1]);
let ans = Number.MAX_VALUE;
for (let i = 0; i < points.length; ++i)
for (let j = i + 1; j < points.length; ++j) {
if (points[i][0] != points[j][0]
&& points[i][1] != points[j][1]) {
if (columns.has(40001
* points[i][0]
+ points[j][1])
&& columns.has(
40001 * points[j][0]
+ points[i][1])) {
ans = Math.min( ans, Math.abs(points[j][0]
- points[i][0])
* Math.abs(points[j][1]
- points[i][1]));
}
}
}
return ans < Number.MAX_VALUE ? ans : 0;
}
let A = [[1, 1], [1, 3], [3, 1], [3, 3], [2, 2]];
document.write(minAreaRect(A));
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N*N), as we are using nested loops.
Auxiliary Space: O(N*N), as we are using extra space.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...